©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 16, 2023; 11(8): 1753-1760
Published online Mar 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i8.1753
Published online Mar 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i8.1753
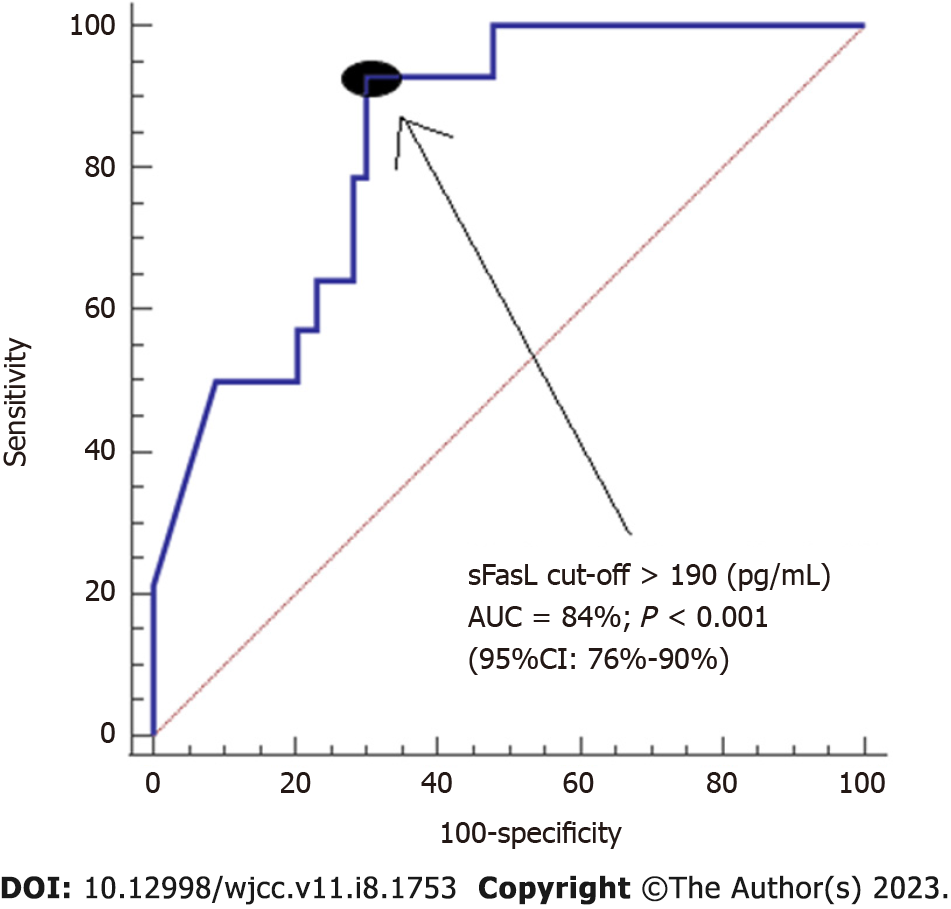
Figure 1 Receiver operation characteristic of serum soluble FasL levels previously to liver transplantation due to hepatocellular carcinoma for the prediction of one-year liver transplantation mortality.
Area under curve of serum soluble FasL (sFasL) levels and sensitivity/specificity of serum sFasL levels > 190 pg/mL are reported. AUC: Area under curve; sFasL: Soluble FasL.
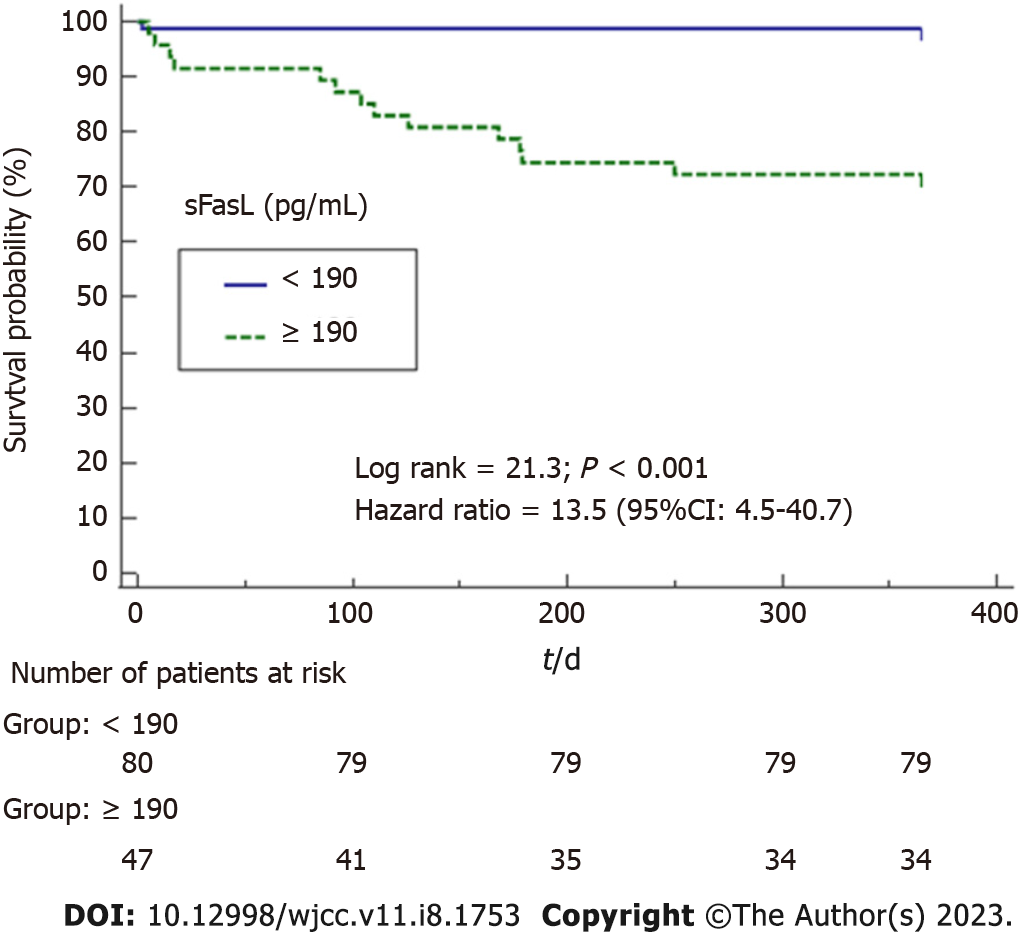
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier survival analysis using mortality (as dependent variable) during first year of liver transplantation due to hepatocellular carcinoma and serum soluble FasL levels previously to liver transplantation lower/higher than 190 pg/mL (as independent variable).
Both survival curves were compared by log rank and hazard ratio. sFasL: Soluble FasL.
- Citation: Lorente L, Rodriguez ST, Sanz P, González-Rivero AF, Pérez-Cejas A, Padilla J, Díaz D, González A, Martín MM, Jiménez A, Cerro P, Portero J, Barrera MA. Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma that die during the first year of liver transplantation have high blood sFasL concentrations . World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(8): 1753-1760
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i8/1753.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i8.1753