Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2022; 10(23): 8360-8366
Published online Aug 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8360
Published online Aug 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8360
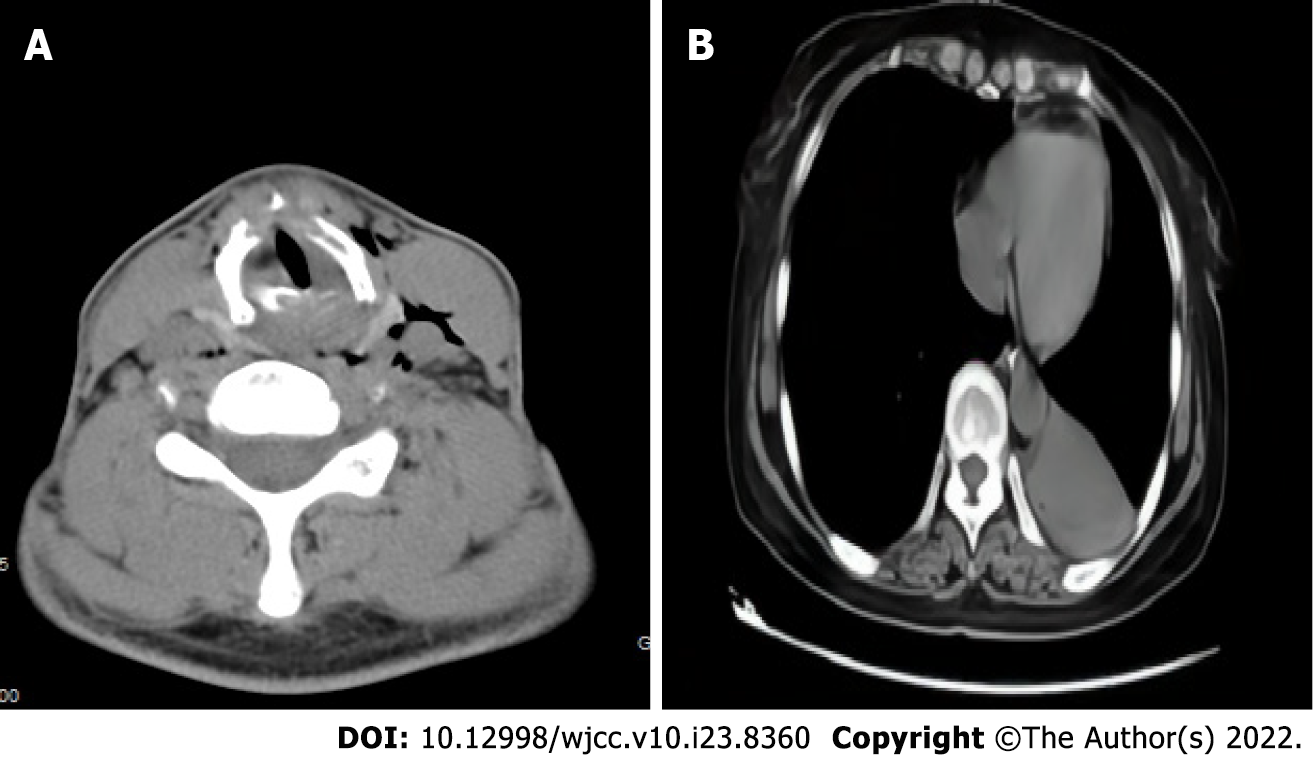
Figure 1 Computed tomography.
A: The neck computed tomography of case 1 showed throat stenosis and thickened ventricular and vocal bands; B: The chest computed tomography of case 2 showed new atelectasis of the lower left lung.
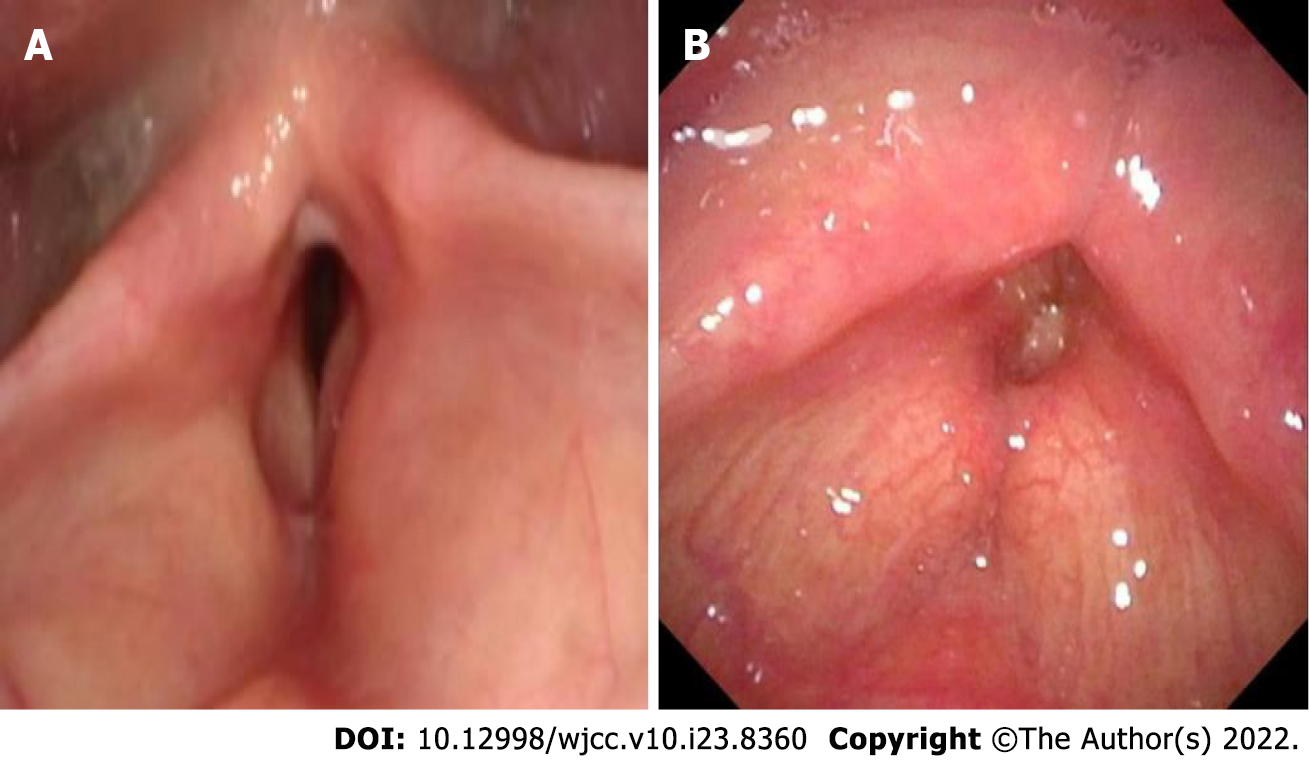
Figure 2 The electronic fiber nasolaryngoscopy.
A: The electronic fiber nasolaryngoscopy of case 1 showed bilateral vocal cord mucosal edema and the appearance of the vocal cords shows as the change of fish abdomen. Narrow glottis, submucosal edema and stenosis were also seen; B: The electronic fiber nasolaryngoscopy of case 2. Two weeks after tracheal extubation, electronic fiber nasolaryngoscopy showed no bilateral ventricular edema, narrow throat cavity, and rima glottidis.
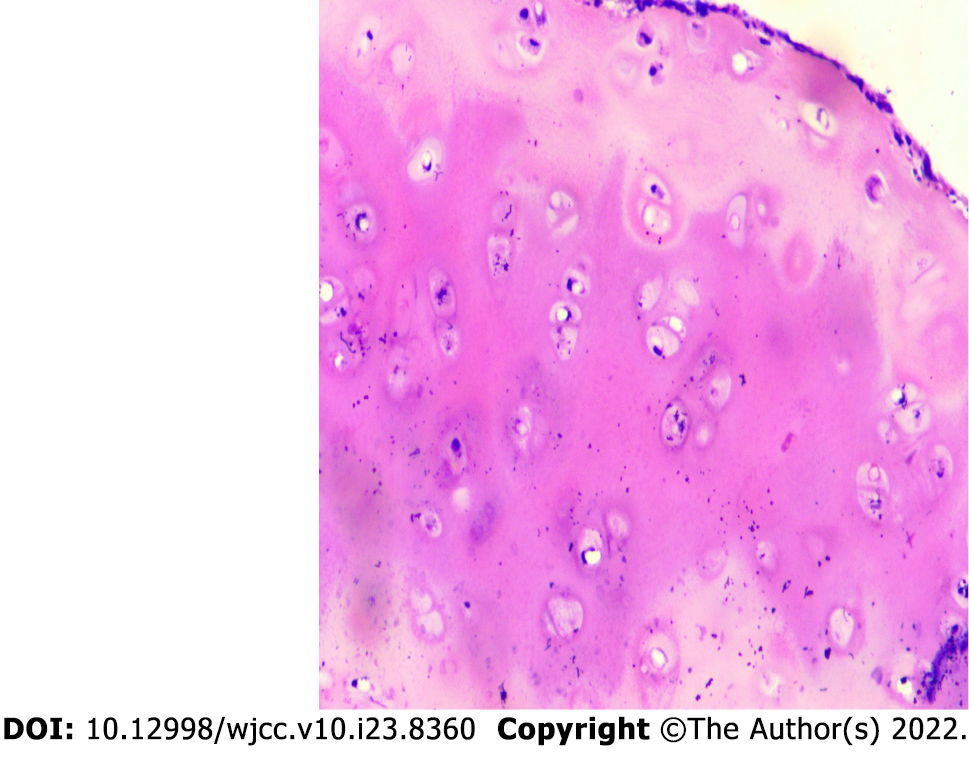
Figure 3 The pathological examination of case 1 of HE 100× showed fibrotic tissue around chondrocytes, chronic inflammatory cell infiltration among the chondrocytes.
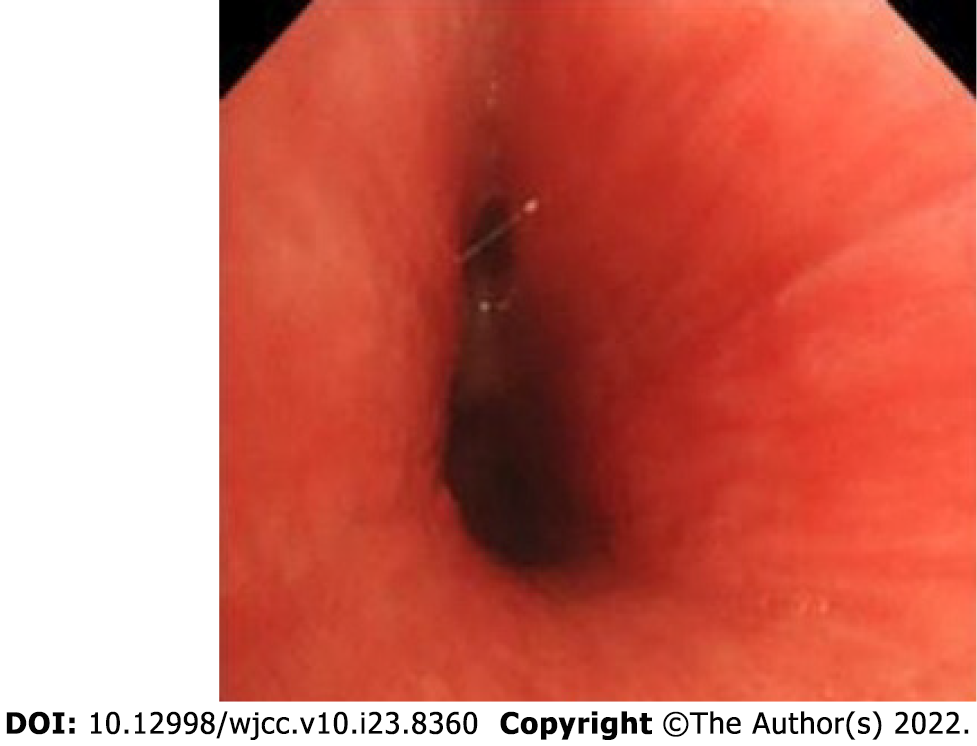
Figure 4 The fiber bronchoscopy of case 2 demonstrated obvious tracheal mucosal congestion and edema, unclear tracheal cartilage ring, and diffuse stenosis of the lumen.
- Citation: Zhai SY, Zhang YH, Guo RY, Hao JW, Wen SX. Relapsing polychondritis causing breathlessness: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(23): 8360-8366
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i23/8360.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8360