©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2022; 10(17): 5833-5840
Published online Jun 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i17.5833
Published online Jun 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i17.5833
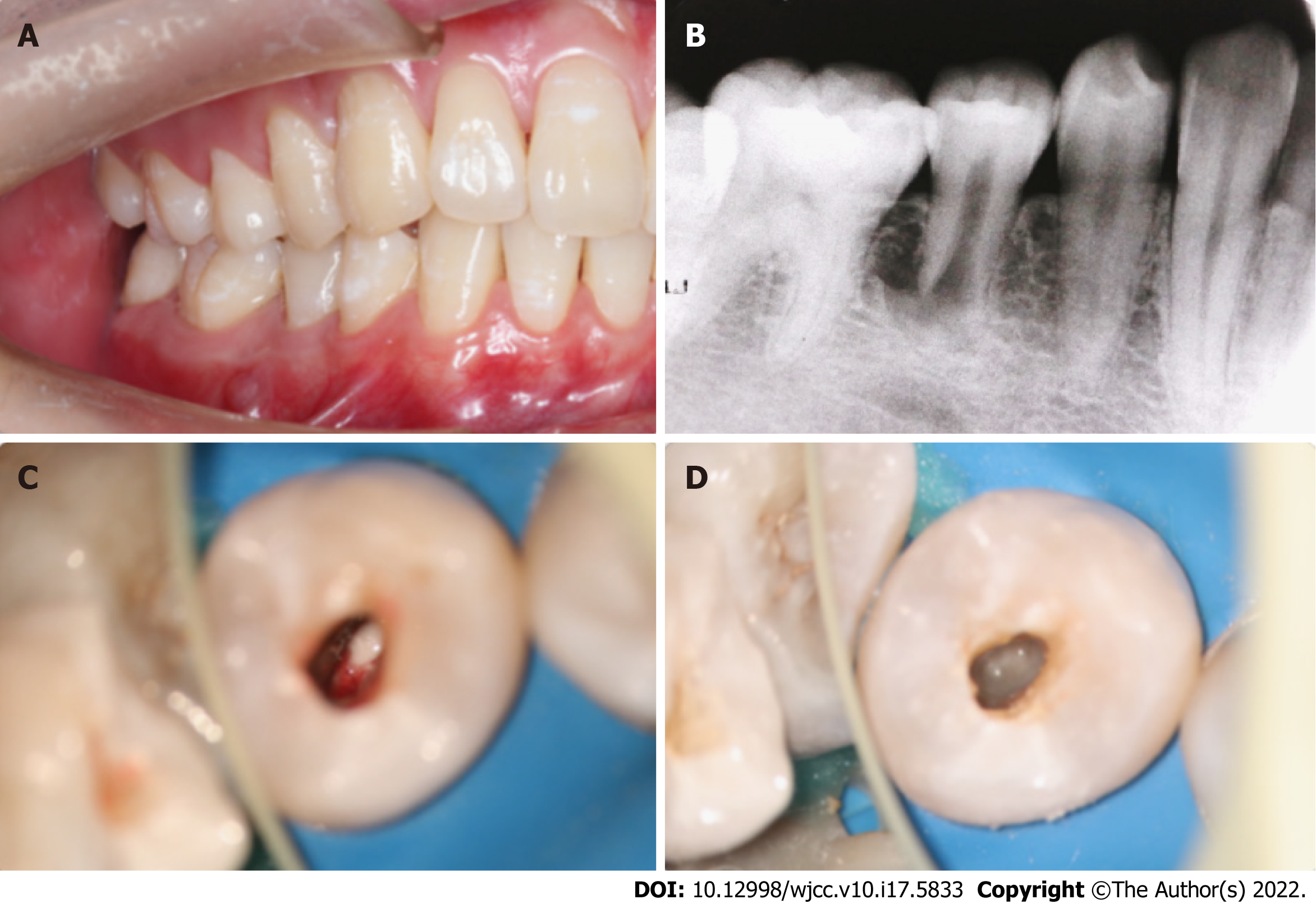
Figure 1 First treatment visit.
A: Preoperative view; B: A preoperative periapical radiograph; C: Pus could be seen in the root canal; D: Triple antibiotic paste was used to seal the root canal.
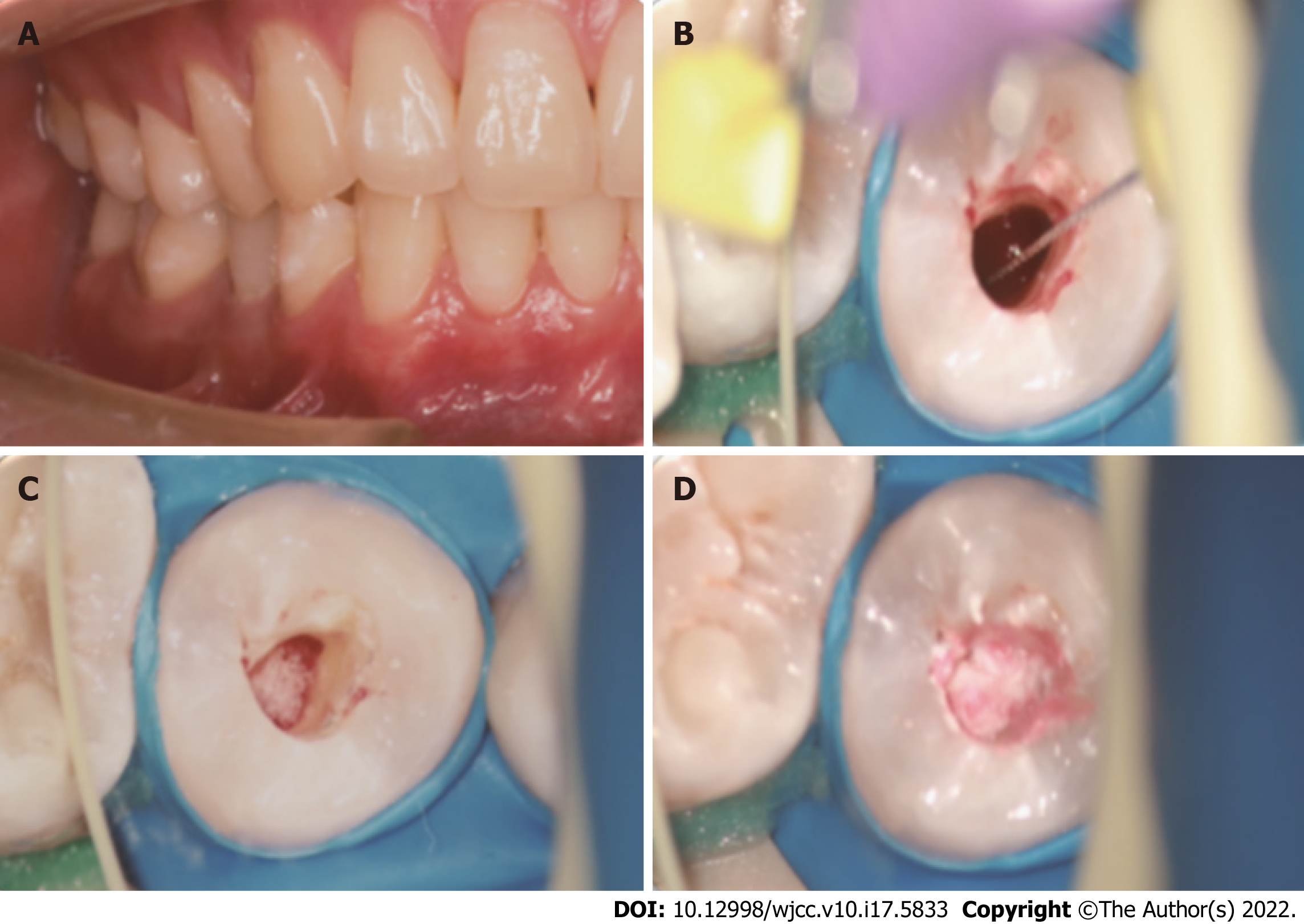
Figure 2 Second treatment visit.
A: Second treatment visit view; B: A #10 K-file was used to provoke periapical bleeding into the canal; C: Placed an absorbable gelatine sponge; D: Placed an iRoot BP.
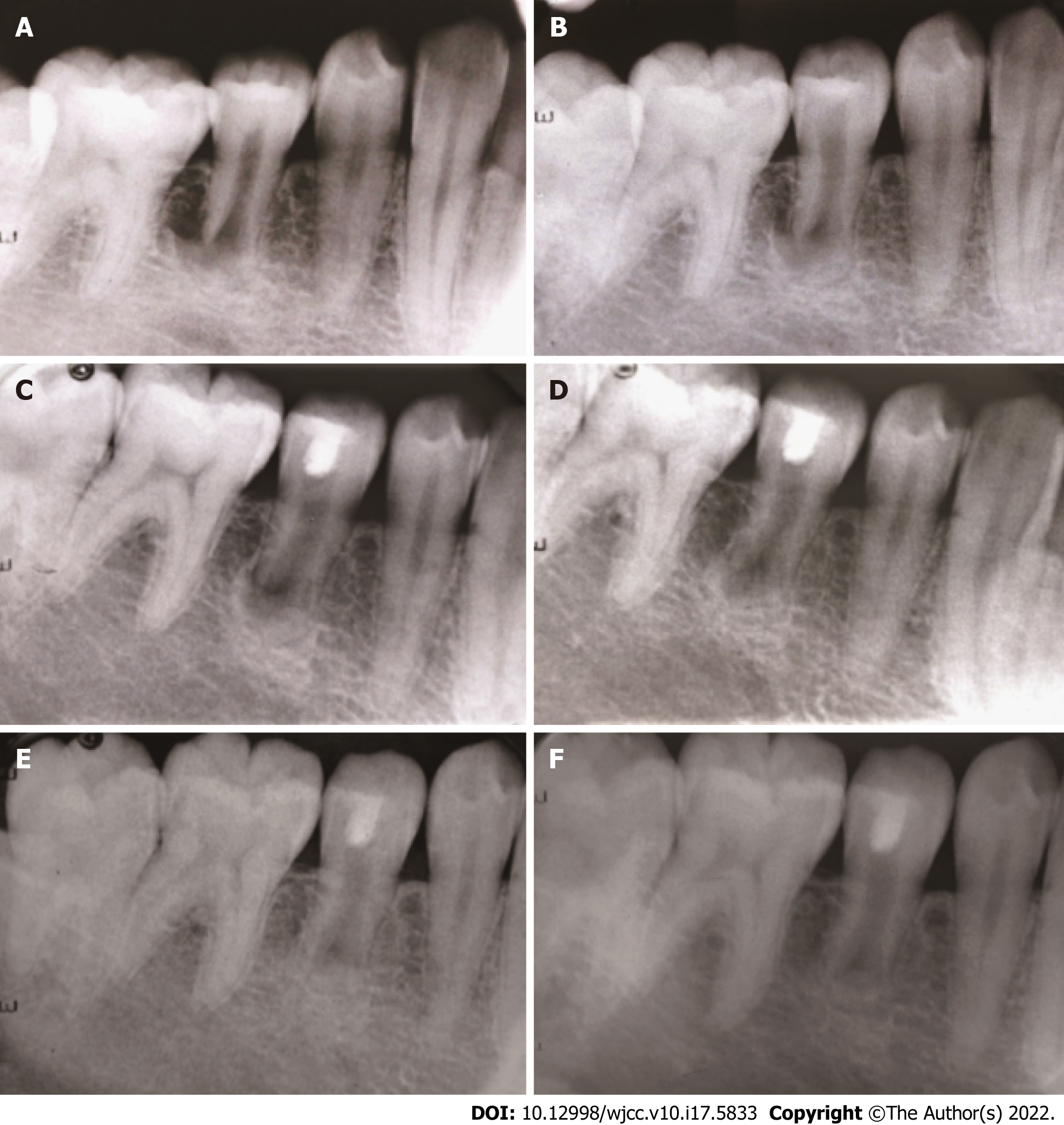
Figure 3 Periapical radiographs.
A: A preoperative periapical radiograph; B: An intraoperative periapical radiograph; C: At the 6-mo follow-up, a periapical radiograph; D: At the 12-mo follow-up, a periapical radiograph; E: At the 24-mo follow-up, a periapical radiograph; F: At the 36-mo follow-up, a periapical radiograph.
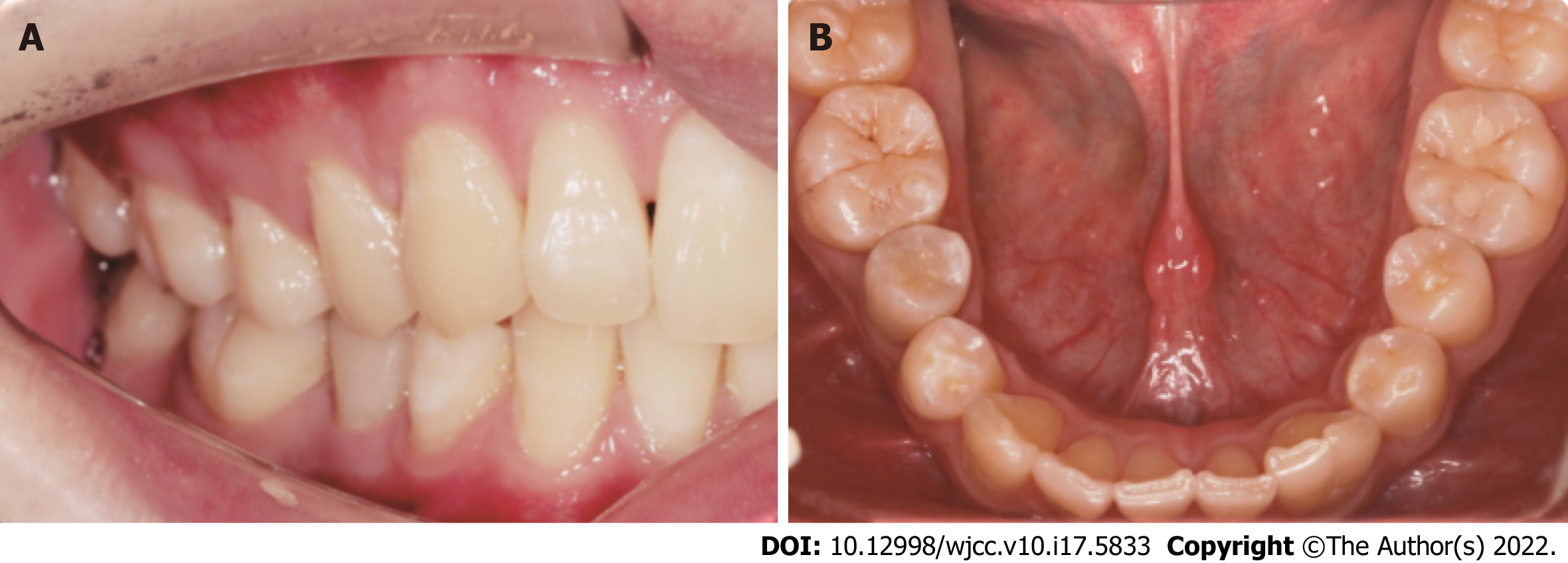
Figure 4 Postoperative view.
A and B: At the 36-mo follow-up, a postoperative view.
- Citation: Yang YQ, Wu BL, Zeng JK, Jiang C, Chen M. Pulp revascularization on an adult mandibular right second premolar: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(17): 5833-5840
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i17/5833.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i17.5833