©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 16, 2022; 10(11): 3511-3517
Published online Apr 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i11.3511
Published online Apr 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i11.3511
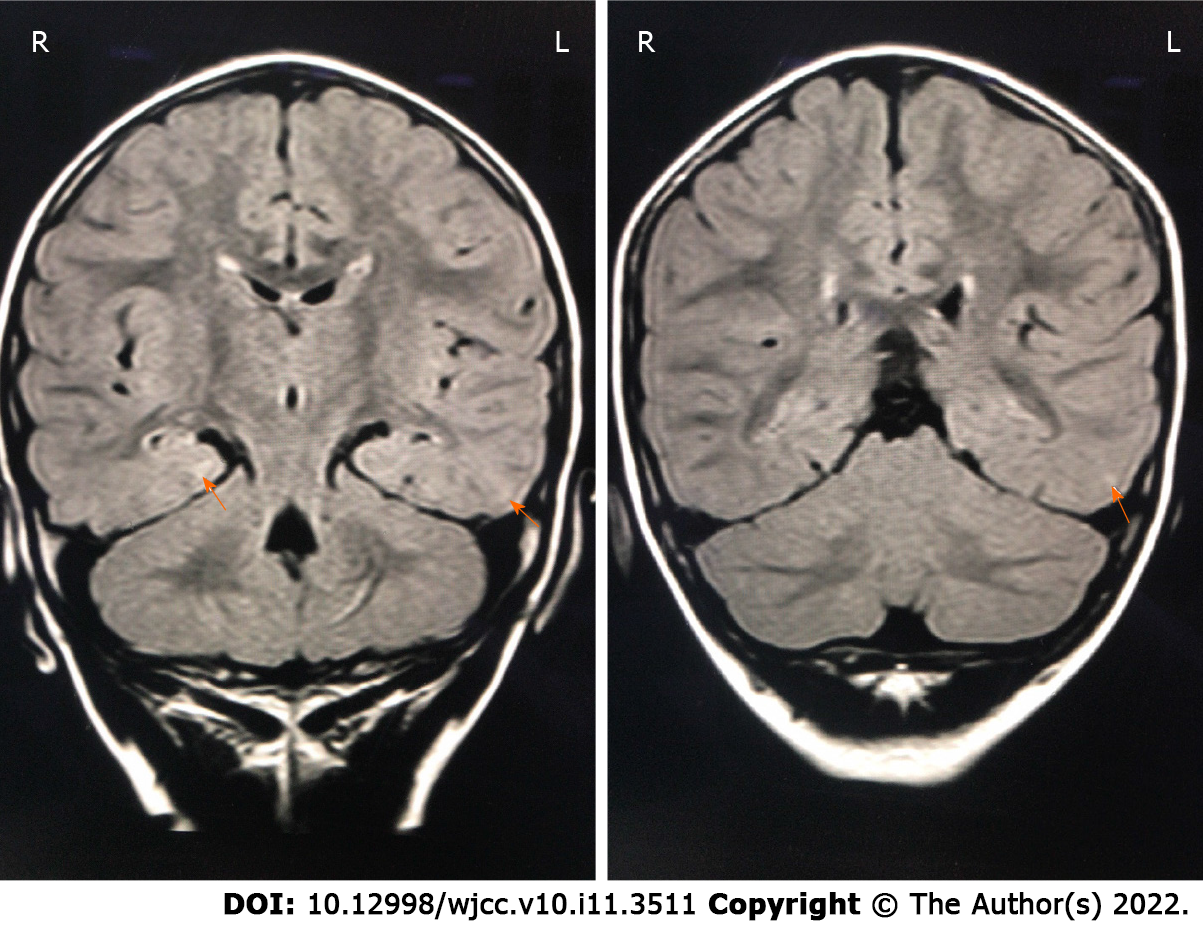
Figure 1 The patient’s cranial magnetic resonance images.
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery showed patchy high-signal areas in the posterior part of bilateral lateral ventricle, and in the subcortical white matter of left occipital and temporal lobes (orange arrows).
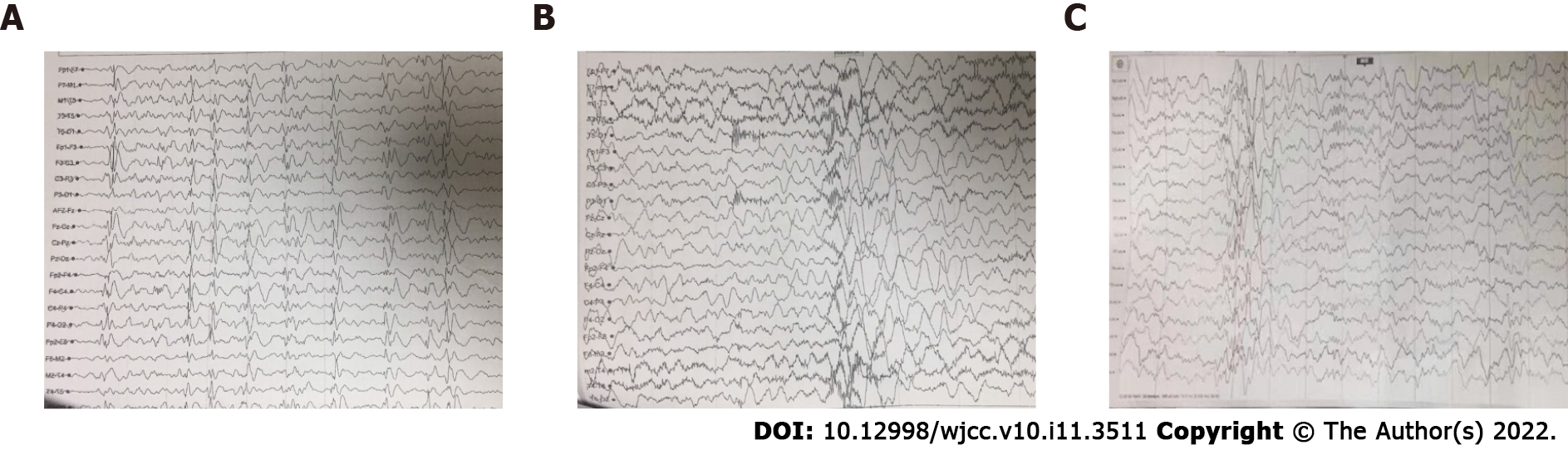
Figure 2 Video-electroencephalography recordings of this patient before and after perampanel treatment.
A: Before treatment with perampanel (PER). The basic waves were irregular and slow, and multifocal generalized sharp and (multi-) spike wave discharges were frequent over the whole brain; B: Before treatment with PER. Seizures were observed during the monitoring, with 8-10 tics in each seizure, and the high-amplitude slow waves with high-frequency discharges were recorded in video-electroencephalography; C: During treatment with PER. The frequency of abnormal multifocal discharges was decreased, and no seizure was observed during the monitoring.
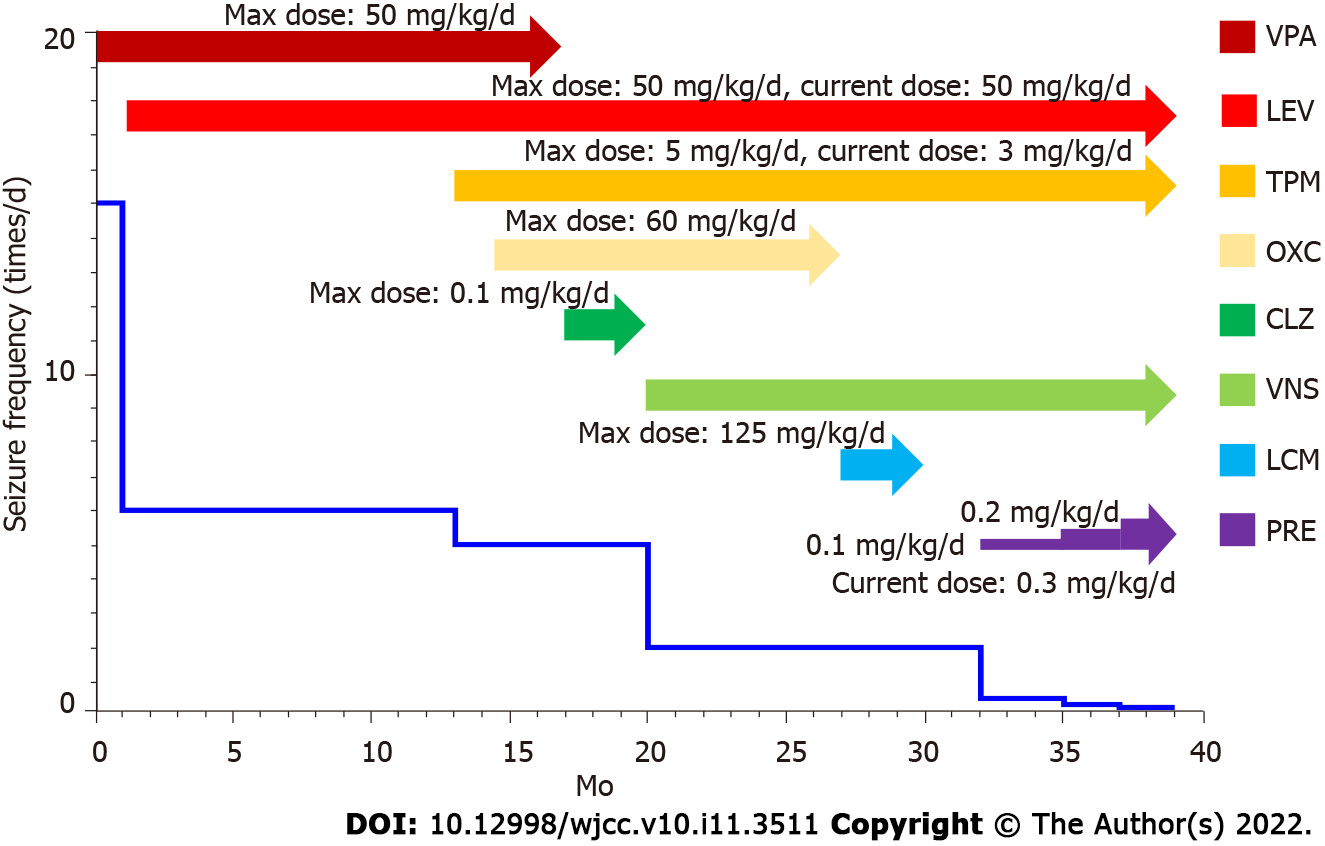
Figure 3 Clinical course of antiseizure drugs and seizure frequency since diagnosis (19 mo old).
VPA: Valproate sodium; LEV: Levetiracetam; TPM: Topiramate; OXC: Oxcarbazepine; CLZ: Clonazepam; VNS: Vagus nerve stimulation; LCM: Lacosamide; PRE: Perampanel.
- Citation: Yang H, Yu D. Young children with multidrug-resistant epilepsy and vagus nerve stimulation responding to perampanel: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(11): 3511-3517
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i11/3511.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i11.3511