©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Virology. Aug 12, 2015; 4(3): 295-302
Published online Aug 12, 2015. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v4.i3.295
Published online Aug 12, 2015. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v4.i3.295
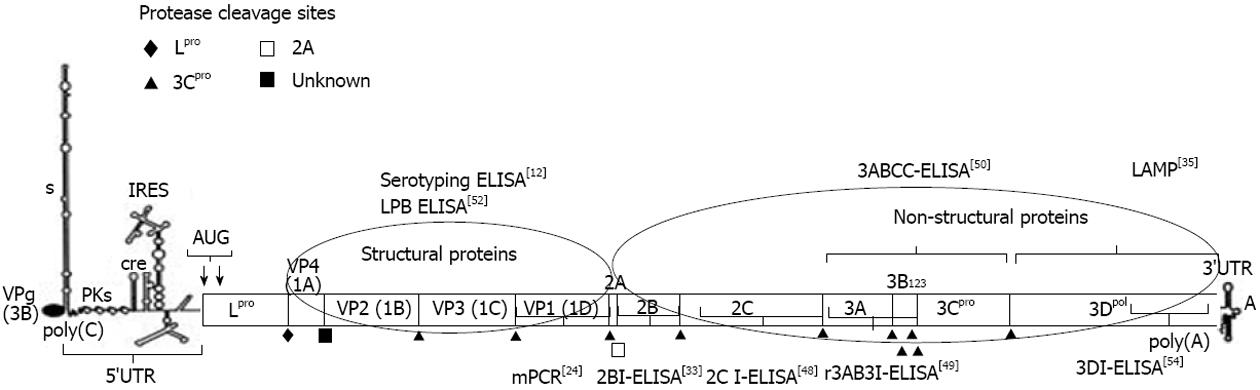
Figure 1 Genome structure of the foot-and-mouth disease virus.
Describes in details the different regions of foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) which codes four structural and 8 non-structural proteins. The regions of genome encoding structural proteins are targeted for FMDV serotype determination by various assays, whereas the genome regions coding for non-structural proteins are targeted for serotype independent diagnosis. The SP of FMDV is targeted for serotyping by antigen trapping enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or for measurement of antibody response by liquid phase blocking ELISA. Antibodies against various non-structural proteins are targeted for differentiation of FMD infected from vaccinated animals.
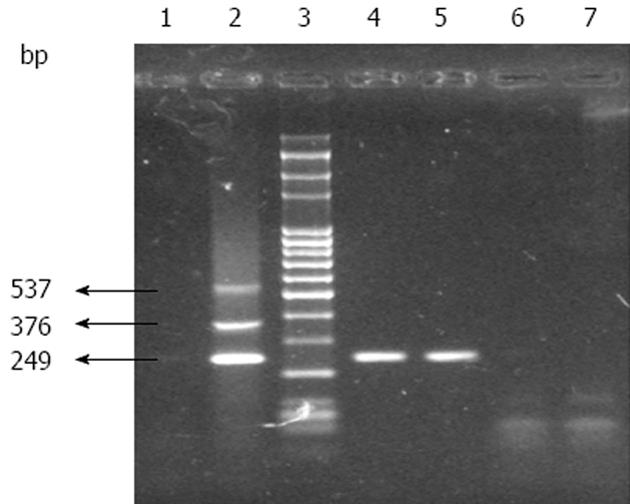
Figure 2 Depicting the foot-and-mouth disease virus serotyping by gel based multiplex polymerase chain reaction assay.
Foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype determined by gel based ready-to-use lyophilized one-step realtime-polymerase chain reaction. Lane 1; negative control; Lane 2: Positive control of serotypes O (249 bp), A (376 bp) and serotype Asia1 (537 bp); Lane 3: 100 bp DNA ladder; Lane 4 and 5: Positive sample of serotype O; Lane 6 and 7: Negative samples for FMD.
- Citation: Sharma GK, Mahajan S, Matura R, Subramaniam S, Ranjan R, Biswal J, Rout M, Mohapatra JK, Dash BB, Sanyal A, Pattnaik B. Diagnostic assays developed for the control of foot-and-mouth disease in India. World J Virology 2015; 4(3): 295-302
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v4/i3/295.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v4.i3.295