Published online Aug 12, 2015. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v4.i3.303
Peer-review started: March 2, 2015
First decision: May 14, 2015
Revised: May 25, 2015
Accepted: July 29, 2015
Article in press: August 3, 2015
Published online: August 12, 2015
Processing time: 165 Days and 16.9 Hours
AIM: To investigate the potential associations among major depression, quality of life, and suicidal behavior in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) patients.
METHODS: A detailed MEDLINE search was carried out to identify all articles and book chapters in English published from January 1995 to January 2015.
RESULTS: Based on the main findings, the prevalence of major depressive disorder (MDD) ranged from 14.0% to 27.2%. Furthermore, the prevalence of suicidal ideation varied from 13.6% to 31.0% whereas, attempted suicides were reported to range from 3.9% to 32.7%. Interestingly, various associated risk factors for both depression and suicide were identified in HIV patients. Finally, consistent associations were reported among MDD, suicidal ideation, and poor quality of life in individuals living with HIV.
CONCLUSION: Although additional studies are needed to elucidate this complex association, our results suggest the importance of early detection of both MDD and suicidality in patients living with HIV.
Core tip: Among patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) the prevalence of major depressive disorder (MDD), suicidal ideation, and attempted suicides ranged from 14.0% to 27.2%, from 13.6% to 31.0%, and from 3.9% to 32.7%, respectively. Multiple risk factors for both depression and suicide were identified in HIV patients. Importantly, a consistent association has been reported between MDD, suicidal ideation, and poor quality of life in individuals living with HIV. The early detection and adequate treatment of depressive symptoms and suicidality should be considered fundamental tasks when managing HIV infected patients, particularly in those individuals who are severely medically ill.
- Citation: Serafini G, Montebovi F, Lamis DA, Erbuto D, Girardi P, Amore M, Pompili M. Associations among depression, suicidal behavior, and quality of life in patients with human immunodeficiency virus. World J Virology 2015; 4(3): 303-312
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v4/i3/303.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v4.i3.303
Chronic medical conditions such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection have been found to be associated with elevated stigma and discrimination, psychological distress, and poor social support[1]. Almost half of individuals diagnosed with HIV suffer from one or more comorbid psychiatric disorders[2] and experience a poorer health-related quality of life compared to individuals without comorbidities[3].
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a highly comorbid psychiatric condition in patients with HIV, and the presence of MDD is associated with poor adherence to treatment, disease progression, and lower quality of life[4]. It has been well established that depressive symptoms may contribute to both HIV progression and mortality[5]. For example, in a 7-year longitudinal study, Ickovics et al[6] found that women with HIV and chronic depressive symptoms had twice the risk of dying by suicide compared to those with few or no depressive symptoms. Specifically, the mortality rates were 54% among patients with chronic depressive symptoms and 48% among those with intermittent depressive symptoms as compared to 21% for women having few or no depressive symptoms and low CD4 cell counts[6]. MDD is also associated with premature drop-out and poorer outcomes after treatment[7,8], as well as persistent drug use in heroin users[9].
In addition to depression, suicidality, which includes both suicide ideation and attempts, is considered to be another major psychiatric problem associated with HIV/acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)[10]. Similar to MDD, an association between suicidality, poor quality of life, poor adherence to antiretroviral therapy, and non-disclosure of HIV status to significant others has been also reported[10,11]. Overall, socio-demographic variables (e.g., female gender, younger age); psychiatric conditions such as substance abuse, MDD, and a history of prior suicide attempts; neuropsychiatric side-effects of antiretroviral therapy and psychotropic medication; psychosocial factors including heterosexual orientation, poor social support, loss of employment, maltreatment, and sexual abuse; and clinical factors (e.g., stress reactions, the perception of pain, physical impairment, psychological/physical symptoms, and AIDS diagnosis) have been found to contribute to suicidality among HIV patients[12-19].
Thus, individuals with HIV infection may have a higher risk of suicide than those individuals without HIV[20-22]. In addition, many individuals living with HIV are reluctant to disclose their HIV serostatus to friends and/or family due to the fear of stigmatization[23,24]. Moreover, individuals who experience this type of fear may have disadvantages with regards to seeking HIV testing, education, or treatment[25].
Interestingly, the introduction of antiretroviral medications significantly improved both HIV health-outcomes and life expectancy of HIV infected patients, which led to a significant reduction of suicide rates[26]. However, patients living with HIV/AIDS are still dying in large numbers and, therefore, examining quality-of-life issues remains an important area of research[27]. In particular, individuals with HIV reported profound alterations in day-to-day activities, significant relationships, and health status[28]. Accordingly, several psychometric instruments and health questionnaires have been specifically developed to evaluate quality of life among individuals with HIV.
Based on the current literature, it remains unclear whether or not individuals with HIV and poor quality of life are at a higher risk of depression/suicidality than those with HIV and a higher quality of life. Thus, the present review aimed to investigate the nature of the associations between MDD, quality of life, and suicidal behavior in HIV patients.
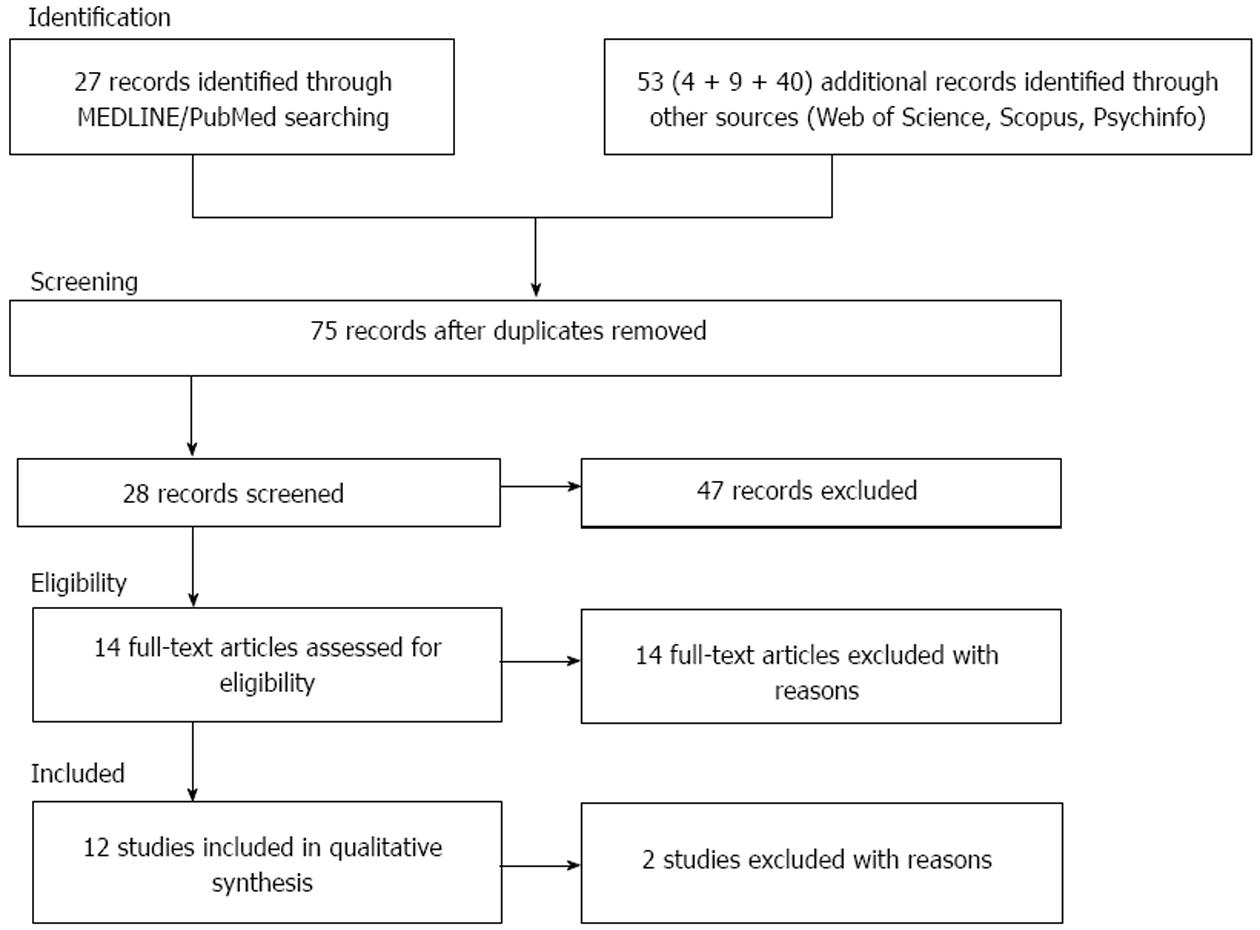
In order to provide a critical review of the associations among depression, suicidality, and quality of life among patients with HIV infection, we performed a detailed search using the largest existing databases (PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, and Psychinfo) to identify all articles and book chapters in English published between January 1995 and January 2015. Specifically, the following search terms were used: “Major depression” OR “Major Depressive Disorder” OR “MDD” AND “Suicidal Behavior” OR “Suicide attempts” OR “Suicide ideation” OR “suicidality” AND “Quality of life” AND “HIV infection.” Full-text articles were evaluated for relevance when a title or abstract appeared to describe a study eligible for inclusion. Abstracts that did not explicitly mention the association between depression, suicidality, and quality of life among individuals living with HIV were excluded. We also excluded meta-analytic studies and reviews. Overall, we identified 36 articles; however, only 12 full-text articles included in our review.
To achieve a high standard of reporting, we have adopted Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses’ (PRISMA) guidelines[29]. The PRISMA Statement consists of a 27-item checklist and a four-phase flow diagram for reporting in systematic reviews. PRISMA includes the broader effort to improve the reporting of different types of health research as well as to improve the quality of research used in decision-making in healthcare.
The combined search strategy yielded a total of eighty articles of which, after a complete analysis, twenty-eight full-text articles were screened and fifty-two were excluded. We excluded articles that were not published in peer reviewed journals, those that were not in English language, articles without abstracts, abstracts that did not explicitly refer to the main topic, and those with unclear data regarding materials and methods and subjects which were analyzed. We assessed fourteen articles for eligibility but two full-text articles were excluded due to low-relevance to the main theme. Therefore, twelve articles fulfilled our inclusion criteria and were included in the present review (Figure 1).
Studies that investigated the prevalence of depression, suicide ideation, suicide thoughts, in patients living with HIV: Nine studies investigated the prevalence of suicide ideation/thoughts and associated risk factors in HIV infected patients. Ogundipe et al[30] found that 13.6% of 295 people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA) reported suicidal ideation.
Moreover, Kinyanda et al[31] demonstrated that the prevalence of moderate to high risk for suicidality (MHS) and lifetime suicide attempts of 618 recruited patients was 7.8% and 3.9%, respectively.
In a sample of 62 randomly selected HIV+ women, Lewis et al[32] investigated the existence and impact of major depression. The researchers also found that activities of daily living (ADL) and the subjective questionnaire of cognitive functioning were useful instruments to assess depression.
In another study, the clinical/behavioral characteristics of 71 patients in northern Taiwan as related to their HIV status have been explored by Lee et al[33]. Based on the main findings, anxiety was reported in 21.0% of patients, depression in 27.2%, memory alterations in 32.7%, and suicide attempts in 32.7%. Atkinson et al[34] also reported that HIV+ individuals (N = 203) reported a significantly higher rate of lifetime MDD than HIV- participants (14% vs 5%). However, both HIV+ and HIV- reported similar rates of current MDD.
Furthermore, Sherr et al[11] demonstrated that the prevalence of suicidal ideation was 31% in a sample of 778 patients living with HIV. Interestingly, heterosexual men and black respondents were twice as likely to experience suicidal ideation when compared to gay men or women and White/Asian respondents. In addition, individuals who did not disclose their HIV status were twice as likely to report suicidal ideation as compared to other subjects.
In another study conducted in a sample of 28 Chinese HIV+ participants and 23 matched HIV- controls, nearly 79% of HIV infected individuals had a significantly higher lifetime rate of major depression relative to 4% of the comparison group[35]. Moreover, 18% of these patients reported active suicidal thoughts.
Haller and Miles[36] also examined suicidality among 190 HIV+ participants and reported that 26% had suicidal thoughts within 30 d of hospitalization, 49% revealed that they had a suicide plan, and 48% indicated they had suicide intent. Further, individuals with suicidal ideation had predominantly MDD (64%).
Finally, Kalichman et al[37] found that in a sample of individuals aged 45 or older and living with HIV/AIDS (N = 113), 27% reported suicidal thoughts.
Studies that investigated the associated risk factors in patients living with HIV: Six studies investigated the relevance of associated risk factors in HIV infected patients. Ogundipe et al[30] identified unemployment, emotional distress, religion, HIV status non-disclosure, and previous suicidal attempt as significant predictors of suicidal ideation in their sample.
In another study, Kinyanda et al[31] reported that significant unique predictors of MHS included female gender, increasing negative life events, a previous psychiatric history, and MDD.
Other articles focused on the importance of associated risk factors in patients diagnosed with HIV. For example, sexual intercourse without condoms during the six previous months were found more frequently in HIV-negative heroin users compared to HIV-positive heroin users[33] whereas higher levels of physical and psychological symptoms independently predicted suicidal ideation[11].
Furthermore, Haller and Miles[36] suggested that individuals with MDD, dysthymia, substance abuse, thought disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or borderline/avoidant personality disorders were more likely to report suicidality.
Interestingly, subjects with suicidal thoughts more frequently used escape and avoidance whereas positive-reappraisal coping strategies were used less frequently[37]. The authors[37] demonstrated the existence of associations among suicidal thoughts and perceived poor social support from friends/family even after controlling for depression.
Studies that analyzed the association between depression, suicidality and quality of life in HIV patients: Eight of the included studies examined the associations between depression, suicidality and quality of life in samples of HIV patients. First, a significant association between suicidal ideation and being unmarried, poor medication and quality of life was found by Ogundipe et al[30] in a sample of 295 PLWHA.
Furthermore, Pompili et al[38] reported that HIV patients with a poorer health-related quality of life (HRQoL) had higher hopelessness levels (these subjects were at high suicide risk) and were more likely to have depression than those with a higher HRQoL. In addition, higher scores on all dimensions of the Temperament Evaluation of Memphis, Pisa, Paris and San Diego-self administered version (TEMPS-A) were reported in patients with a poorer HRQoL relative to those with higher HRQoL. Furthermore, Atkinson et al[34] reported that 203 HIV+ were more likely to have a lifetime substance use diagnoses than HIV- participants (14% vs 6%). They also found that worse daily functioning and life quality as well as unemployment were independently predicted by both depression and HIV status.
Palliative care and quality-of-life issues are still two relevant areas of research in patients with advanced AIDS. Breitbart et al[39] investigated the impact of treatment for depression on the desire for hastened death in a sample of 372 patients with advanced AIDS. They reported a significant association between desire for death and depression; also, desire for death was reduced in those patients who responded to antidepressants medications. However, nearly half of those individuals who received antidepressant medications and/or supportive psychotherapy or counseling showed little or no improvement in depressive symptoms. In another study, Jin et al[35] found that worse daily functioning was independently predicted by both major depression and HIV+ status in a sample of 28 Chinese HIV+ participants and 23 matched HIV- controls.
Furthermore, in a sample of HIV-infected women directly after diagnosis, Krabbendam et al[40] found that the women experienced strong emotions and quality of life impairment, suggesting that high emotional distress may be occurred in specific phases of HIV illness. In addition, Haller and Miles[36] demonstrated a significant association between quality of life variables and suicide ideation in 190 HIV patients. Specifically, leisure/social and family/friends were strongly associated with suicidal ideation in their sample. Finally, higher emotional distress together with poorer HRQoL were found in a sample of individuals living with HIV-AIDS (N = 113) who reported suicide thoughts as compared to those who had not considered suicide[37] (Tables 1 and 2).
| Ref. | Study design | Sample size | Follow-up | Psychometric instruments assessing MDD, suicidality, and quality of life | General fIndings | Limitations | Conclusion |
| Ogundipe et al[30] | Cross-sectional study | 295 PLWHA (102 males and 153 females; mean age 37.3 ± 8.7 yr) | No | GSQ-28, BDI, and WHOQOL-BREF | Overall, 13.6% of PLWHA reported suicidal ideation. A significant association between suicidal ideation and being unmarried, poor medication adherence and altered quality of life has been reported. Unemployment, emotional distress, religion, HIV status non-disclosure and previous suicidal attempts were significant predictors of suicidal ideation among PLWHA | (1) The cross-sectional nature of the study; (2) Subjects have been not assessed for the presence of prior suicide attempts; (3) Participants have been not evaluated during a follow-up period | Suicide should be considered a major health issue in subjects with HIV infection. Specific psychosocial and clinical factors may be useful to identify PLWHA who are at-risk for suicide |
| Pompili et al[38] | Cross-sectional study | 88 outpatients (71 men and 17 women; mean age 42.9 ± 10.3 yr) | No | GMDS, BHS, SHSS, TEMPS-A, and SF-36 | More severe depression and hopelessness have been found between patients with a poorer HRQoL when compared to those with a higher HRQoL. Higher scores on all dimensions of the TEMPS-A were also reported in those with a poorer HRQoL relative to subjects with a higher HRQoL | (1) The small sample size; (2) The cross-sectional nature of the study; (3) Data on HIV severity, illness duration, or age of symptom onset were not collected; (4) Data were collected via self-report and not validated by psychiatric examinations | Patients with a poorer HRQoL were more likely to have depressive affective temperaments, depression and suicide risk than patients with higher HRQoL |
| Kinyanda et al[31] | Cross-sectional study | 618 HIV outpatients (169 male, 449 female; mean age in the 25-44 age band) | No | M.I.N.I., coping style index derived by variables of the MAC, and International HIV Dementia Scale | Prevalence of MHS and life-time attempted suicides resulted 7.8% and 3.9%, respectively. After univariate analyses, female gender, food insecurity, increasing negative life events, high stress score, negative coping style, past psychiatric history, psychosocial impairment, diagnoses of PTSD, GAD, and MDD resulted associated with MHS. After multivariate analyses, only female gender, increasing negative life events, a previous psychiatric history, and MDD were independently associated with MHS | (1) The cross-sectional nature of the study; (2) the small number of subjects with some of the diagnosed psychiatric disorders; (3) the threshold as a cut-off point for MHS has been not validated in the African socio-cultural context; (4) the use of the “risk for suicidality” measure instead of “suicidality” | Both social and psychological stressors may act on previous and current psychiatric morbidities triggering suicidality |
| Lewis et al[32] | Cross-sectional study | 62 HIV-positive women (mean age 35.7 ± 6.6 yr) | No | BDI-FS, MM of the Primary Care Evaluation of Mental Disorders, ADL, and SCQ | ADL and subjective questionnaire of cognitive functioning were useful instruments to measure depression in HIV-positive women | (1) The cross-sectional nature of the present data; (2) The small sample size which may limit the generalization of findings; (3) Participants have been not evaluated during a follow-up period; (4) the sample includes only women | Diagnosis of depression is of great importance, not only clinically, but also to ensure the judicious allocation of scarce medical resources in the regions worst affected by HIV |
| Lee et al[33] | Cross-sectional study | 576 patients (503 male, 73 female; mean age 40.6 ± 9.3 yr) of which 71 were HIV positive, and 514 had hepatitis C | No | A semi-structured questionnaire assessing demographics, quality of life, HIV risk behavior, and psychiatric symptoms,and WHOQOL-BREF | Overall, 21.0% of the subjects reported anxiety, 27.2% depression, 32.7% memory loss, and 32.7% attempted suicide. Based on the main findings, HIV-negative heroin users were more likely to have sexual intercourse without condoms during the six previous months | (1) The sample may be not representative of the Taiwanese heroin users population; (2) It was not possible to validate whether patients replied the questions truthfully | No significant differences were found between the HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients on psychiatric symptoms or quality of life |
| Atkinson et al[34] | Cross-sectional study | 203 HIV-infected former plasma donors and 198 HIV-negative donor controls (122 male, 279 female; mean age 40.2 ± 6.4 yr) | No | WMH-CIDI, BDI-II, MOS-HIV, Modified HIV Stressor Scale, ADL, and Social Support Scale | HIV+ subjects reported a significantly higher rate of lifetime MDD (14% vs 5%) than HIV- participants. Both HIV+ and HIV- reported similar rates of current MDD. HIV+ were more likely to have lifetime substance use diagnoses than HIV- (14% vs 6%). Importantly, worse daily functioning and life quality as well as unemployment were independently predicted by both depression and AIDS | (1) Rates of depression may be underestimated by the used psychometric measures; (2) Recurrence of MDD episodes and bipolar disorder cases have not been examined; (3) The sample is derived by an agrarian setting; (4) The preliminary nature of the findings | High lifetime rates of MDD and suicidality were found in this HIV-infected agrarian cohort presumably due to the existence of a pre-HIV mood disorder, direct effects of HIV, social stigma, negative impact of HIV/AIDS on employment together with the perception that HIV is a terminal condition |
| Sherr et al[11] | Cross-sectional study | 778 HIV-positive clinic attenders (183 heterosexual women, 76 heterosexual men, 496 gay/bisexual; mean age 40.5 yr) | No | Suicidal ideation reported using a self-report item based on feelings in the preceding week, levels of optimism in relation to treatment and infectiousness, MSAS short-form, and EuroQol-5D | Suicidal ideation was reported by 31% of patients. Heterosexual men and black respondents were twice more likely to have suicidal ideation relative to gay men or women and White/Asian respondents, respectively. Also, those with lack of disclosure were twice more likely to have suicidal ideation than those without. Higher physical and psychological symptoms independently predicted suicidal ideation | (1) The cross-sectional study design; (2) Subjects have been not evaluated for the presence of previous suicide attempts; (3) Participants have been not tested during a follow-up period | Suicidal ideation rates among HIV-positive clinic attenders were high |
| Jin et al[35] | Cross-sectional study | 28 HIV+ participants and 23 matched HIV- controls (38 male, 13 female; mean age 35.4 ± 6.7 yr) | No | CIDI Depression Module, BDI-I, Module E of the CIDI assessing lifetime suicidality, ADL | Overall, 79%of HIV-infected subjects had a lifetime rate of major depression relative to 4% of the comparison group. 9% of patients received treatment for depression, but 18% showed active suicidal thoughts. Worse daily functioning was independently predicted by both depression and HIV+ status | (1) The small sample size that may limit the generalization of the present findings; (2) The effects of gender could be not separated; (3) The sample was selected for feasibility purposes | High rates of major depression and suicidality have been found in HIV-infected Chinese subjects |
| Ref. | Study design | Sample size | Follow-up | Quality of life instruments | General findings | Limitations | Conclusion |
| Breitbart et al[39] | Follow-up study | 372 patients with advanced AIDS, of which 42 were re-assessed at the follow-up (280 men, 92 female; mean age 44.4 ± 9.4 yr) | 2-mo follow-up | Depression module of the SCID, HIV version, Ham-D, SAHD, DDRS, no specific psychometric instruments were used to measure quality of life | A significant association between desire for death and depression was found but desire for death was reduced in those patients who responded to antidepressants medications. However, approximately half of subjects who received antidepressant medications and/or supportive psychotherapy or counseling demonstrated little or no improvement in depressive symptoms | (1) The study was not a controlled clinical trial of antidepressant therapy; (2) Systematic bias (e.g., with more refractory patients being less likely to remain in the study) may be not excluded; (3) The failure to find significant differences about the proportion of patients with a high desire for hastened death may reflect the limited power of these analyses | Depressed patients who were successfully treated with antidepressant medications reported a significant reduction of desire for death |
| Haller et al[36] | Cross-sectional study | 190 HIV patients (129 male, 61 female; mean age 37.3 ± 7.4 yr) | No | UM-CIDI, MCMI-III, Suicide Screener (seven-item structured interview), quality of life derived by HIV-PARSE | Overall, 26% of subjects reported suicide thoughts within 30 d of admission, 49% a suicide plan, and 48% a suicide intent. Individuals with suicidal ideation had predominantly MDD (64%), drug dependence (52%), and depressive personality disorder (50%). After regression analyses, those with MDD, dysthymia, substance abuse, thought disorder, PTSD, and borderline/avoidant personality disorders were more likely to have suicidality. Concerning the quality of life variables which were measured, leisure/social and family/friends were strongly associated with suicidal ideation | (1) The cross-sectional nature of the findings; (2) No specific psychometric instruments were used. | Subjects with substance use disorders, unstable interpersonal relations, and a restricted social environment may be considered at-risk individuals and need to be regularly screened for suicidality |
| Kalichman et al[37] | Cross-sectional study | 113 HIV-AIDS subjects (mean age 53, age range 47-69) | No | Beck Depression Index, and WOC | Subjects who reported suicide thoughts (27%) have also higher emotional distress and poorer health-related quality of life relative to those who had not considered suicide. Furthermore, escape and avoidance were more frequently used whereas positive-reappraisal coping strategies were less frequently used by those with suicide thoughts. An association between suicide thoughts and the perception of reduced social support from friends and family was also reported. The mentioned differences remained even after controlling for symptoms of depression | (1) The small sample size; (2) The cross-sectional nature of the findings. These factors may limit the generalization of the findings | Relevant emotional distress and suicide thoughts were experienced by subjects in midlife and older individuals with HIV-AIDS |
| Krabbendam et al[40] | Cross-sectional study | 24 HIV women (mean age 32 yr with a range of 20-49 yr) | No | In depth interviews using a qualitative semi-structured approach providing insights into feelings, perceptions, beliefs | Strong emotions and quality of life impairment were experienced by HIV-infected women directly after diagnosis. It has been suggested that one counseling session was not effective | (1) The small sample size and the cross-sectional nature of the findings may seriously limit the generalization of the present findings; (2) Counseling given once was reported to be not effective | Continuous counseling may be provided by support groups. Importantly, the counselors may be used as examples |
The present mini-review aimed to investigate the associations among MDD, quality of life, and suicidal behavior.
First, our findings indicated that the prevalence of a current MDD diagnosis varied from 14.0% to 27.2% according to the selected samples[33,34]; however, as high as 79% of HIV patients reported a lifetime diagnosis of MDD[35]; Second, the prevalence of suicidal ideation ranged from 13.6% to 31.0%; whereas, the prevalence of attempted suicide ranged from 3.9% to 32.7%[11,30,31,33]; Third, various associated risk factors for depression and suicide were found to be important in HIV patients[11,30,31,33,36,37].
Other recent studies[41-43] confirmed this high but more variable prevalence of MDD in HIV patients ranging between 18% to 81% at some stage of the illness according to the different populations which were investigated, the different study designs as well as the different diagnostic criteria which were used.
As reported by Hirsch Allen et al[44], depression may be evaluated both dimensionally as well as categorically and this is the first source of variability.
In addition, MDD in HIV patients may vary according to several variables such as the population of interest, main research hypotheses as well as comparisons with other studies/populations. Importantly, depressive symptoms that do not meet diagnostic criteria may be also associated with significant psychosocial impairment and disability[44]. Moreover, the role of somatic symptoms related to depression may be frequently neglected in HIV infected patients due to their frequent overlapping with somatic complaints directly related to the disease.
Overall, clinicians should carefully consider that screening, diagnosing, and quantifying depressive symptoms represent three different but equally critical/challenging tasks when managing depressed HIV infected patients.
MDD often contributes to the negative psychological effects of HIV, increases emotional distress, and exerts a critical impact on adherence to treatment over time in HIV-infected individuals[45]. Clinicians encounter a challenging task in diagnosing MDD in HIV patients given the complex nature of this association. One of the most debated issues is whether or not MDD is a manifestation of HIV brain disorder or, conversely, MDD should be considered the primary disorder that may be exacerbated by the presence of HIV. Interestingly, some authors hypothesized that MDD and its clinical presentation should be considered an adjustment reaction to the diagnosis of HIV infection[41].
Moreover, the presence of depression may significantly impair the number and activity of lymphocytes in HIV-positive patients dramatically reducing the role of natural killer cells, which increases the mortality in this population[41,42,46]. Del Guerra et al[43] have suggested that HIV may predispose patients to the onset of MDD through the interaction between the following neurobiological mechanisms: (1) Chronic increase of inflammatory cytokines and abnormal activation of microglia and astrocytes; (2) Consistent reduction of monoamine levels; (3) Neurotoxicity; and (4) Reduction of neurotrophic factors and subsequent impaired neuroplasticity processes, and psychosocial factors.
Our findings indicate a significant association between suicide ideation/thoughts and poor quality of life in HIV patients[30,36,37,40]. Moreover, results also suggest that depression was significantly associated with[38,39] or predicted a poor quality of life in HIV patients[34,35]. According to population-based studies[47], an higher prevalence of suicide in subjects with HIV may be found relative to the general population, and comorbid mood disorders may be identified in more than half of subjects. Among HIV infected individuals, those with AIDS were more likely to report current suicidal ideation, lifetime suicidal thoughts, and suicide plans compared to those without AIDS. This may be explained by the fact that individuals diagnosed with AIDS usually have a poorer HRQoL than those with HIV infection. Also, the presence of severe depressive symptoms in these patients was a significant predictor of daily functioning together with unemployment, and life quality[34,48]. Moreover, depressive symptoms may be independent predictors of significant impairment in daily functioning and quality of life regardless of the effects of HIV, as suggested by Jin et al[35]. The negative consequences of MDD on daily functioning and employment have also been found in previous studies[49]. Taken together, these findings suggest the clinical relevance of early detection and adequate MDD treatment, particularly in those individuals who are severely medically ill.
The present review should be considered in the light of limitations. First, some included studies may reflect the authors’ choice according to their expertise and may include small sample sizes, which limit the generalization of the findings; Second, most studies were cross-sectional in nature and did not allow for causal interpretations of the associations between depression, quality of life, and suicidality in HIV patients; Third, some studies predominantly investigated the presence of suicide ideation instead of considering the impact of prior suicide attempts on the quality of life of HIV patients; Fourth, some studies were limited by the possible underestimation of MDD and suicidal behavior rates given the use of self-reported psychometric instruments and the limited power of some analyses to find significant differences regarding the proportion of patients with depression and suicidality.
The prevalence of depression and suicidal ideation are consistent in patients with HIV, suggesting the importance of early detection for both these conditions in this population. Also, significant associations have been reported among MDD, suicidal ideation, and poor quality of life in HIV populations. However, further studies are necessary to elucidate this complex association.
It has been reported that individuals living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are at risk for both depression and suicidality. Most of individuals diagnosed with HIV suffer from one or more comorbid psychiatric disorders and experience a poorer health-related quality of life compared to individuals without comorbidities.
It is quite unclear whether or not subjects with HIV and poor quality of life are at higher risk of depression/suicidality compared with HIV and higher quality of life.
Among patients with HIV the prevalence of major depressive disorder (MDD), suicidal ideation, and attempted suicides ranged from 14.0% to 27.2%, from 13.6% to 31.0%, and from 3.9% to 32.7%, respectively. A significant association has been reported among MDD, suicidal ideation, and poor quality of life in HIV populations.
Further additional studies are needed to elucidate the exact nature of the association between MDD, suicidality, and quality of life in HIV patients. The early detection and adequate treatment of these conditions is absolutely recommended in clinical practice, in particular in those individuals who are severely medically ill.
PRISMA: The PRISMA Statement consists of a 27-item checklist and a four-phase flow diagram for reporting in systematic reviews in the effort to improve the reporting of different types of health research and the quality of research used in decision-making in healthcare. Hopelessness: Hopelessness may be defined as a negative perspective concerning the future, loss of motivation, and expectations. Hopelessness predisposes patients with psychiatric disorders to suicidal behavior and has been identified as an important risk factor for suicide; TEMPS-A: (Temperament Evaluation of Memphis, Pisa, Paris and San Diego) The TEMPS-A is a self-rating questionnaire consisting of 109 items for men and 110 for women assessing subaffective trait expressions as they were conceptualized in Greek medicine and in German psychiatry.
The review has great clinical implication as well.
| 1. | Hall HI, Song R, Rhodes P, Prejean J, An Q, Lee LM, Karon J, Brookmeyer R, Kaplan EH, McKenna MT. Estimation of HIV incidence in the United States. JAMA. 2008;300:520-529. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1011] [Cited by in RCA: 999] [Article Influence: 55.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Bing EG, Burnam MA, Longshore D, Fleishman JA, Sherbourne CD, London AS, Turner BJ, Eggan F, Beckman R, Vitiello B. Psychiatric disorders and drug use among human immunodeficiency virus-infected adults in the United States. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58:721-728. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 892] [Cited by in RCA: 936] [Article Influence: 37.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Sherbourne CD, Hays RD, Fleishman JA, Vitiello B, Magruder KM, Bing EG, McCaffrey D, Burnam A, Longshore D, Eggan F. Impact of psychiatric conditions on health-related quality of life in persons with HIV infection. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:248-254. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 183] [Cited by in RCA: 182] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Blashill AJ, Perry N, Safren SA. Mental health: a focus on stress, coping, and mental illness as it relates to treatment retention, adherence, and other health outcomes. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2011;8:215-222. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 90] [Cited by in RCA: 104] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Lima VD, Geller J, Bangsberg DR, Patterson TL, Daniel M, Kerr T, Montaner J, Hogg RS. The effect of adherence on the association between depressive symptoms and mortality among HIV-infected individuals first initiating HAART. AIDS. 2007;21:1175-1183. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Ickovics JR, Hamburger ME, Vlahov D, Schoenbaum EE, Schuman P, Boland RJ, Moore J. Mortality, CD4 cell count decline, and depressive symptoms among HIV-seropositive women: longitudinal analysis from the HIV Epidemiology Research Study. JAMA. 2001;285:1466-1474. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 656] [Cited by in RCA: 671] [Article Influence: 26.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Rounsaville BJ, Tierney T, Crits-Christoph K, Weissman MM, Kleber HD. Predictors of outcome in treatment of opiate addicts: evidence for the multidimensional nature of addicts’ problems. Compr Psychiatry. 1982;23:462-478. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Marlatt GA, Gordon , editors . Relapse prevention. New York: Guilford press 1985; . |
| 9. | Havard A, Teesson M, Darke S, Ross J. Depression among heroin users: 12-Month outcomes from the Australian Treatment Outcome Study (ATOS). J Subst Abuse Treat. 2006;30:355-362. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 86] [Cited by in RCA: 91] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Lonnqvist J. Physical illness and suicide. Suicide-An unnecessary death. Martin Dunitz: London, UK 2001; 93-98. |
| 11. | Sherr L, Lampe F, Fisher M, Arthur G, Anderson J, Zetler S, Johnson M, Edwards S, Harding R. Suicidal ideation in UK HIV clinic attenders. AIDS. 2008;22:1651-1658. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 72] [Cited by in RCA: 77] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Bellini M, Bruschi C. HIV infection and suicidality. J Affect Disord. 1996;38:153-164. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Kelly B, Raphael B, Judd F, Perdices M, Kernutt G, Burnett P, Dunne M, Burrows G. Suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, and HIV infection. Psychosomatics. 1998;39:405-415. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 82] [Cited by in RCA: 69] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Préau M, Bouhnik AD, Peretti-Watel P, Obadia Y, Spire B. Suicide attempts among people living with HIV in France. AIDS Care. 2008;20:917-924. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Simoni JM, Nero DK, Weinberg BA. Suicide attempts among seropositive women in New York City. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155:1631-1632. [PubMed] |
| 16. | Cooperman NA, Simoni JM. Suicidal ideation and attempted suicide among women living with HIV/AIDS. J Behav Med. 2005;28:149-156. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 83] [Cited by in RCA: 83] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Lawrence ST, Willig JH, Crane HM, Ye J, Aban I, Lober W, Nevin CR, Batey DS, Mugavero MJ, McCullumsmith C. Routine, self-administered, touch-screen, computer-based suicidal ideation assessment linked to automated response team notification in an HIV primary care setting. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50:1165-1173. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 87] [Cited by in RCA: 85] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Schlebusch L, Vawda N. HIV-infection as a self-reported risk factor for attempted suicide in South Africa. Afr J Psychiatry (Johannesbg). 2010;13:280-283. [PubMed] |
| 19. | Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with HIV/AIDS. Work Group on HIV/AIDS. American Psychiatric Association. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:1-62. [PubMed] |
| 20. | Shirey KG, editor . Suicide and HIV. Mental Health Practitioner’s Guide to HIV. Springer New York: New York 2013; 405-407. |
| 21. | Sherr L, Clucas C, Harding R, Sibley E, Catalan J. HIV and depression--a systematic review of interventions. Psychol Health Med. 2011;16:493-527. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 241] [Cited by in RCA: 229] [Article Influence: 15.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Rabkin JG. HIV and depression: 2008 review and update. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2008;5:163-171. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 249] [Cited by in RCA: 240] [Article Influence: 13.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Li X, Ma Y, Li SK. The Social Support System of AIDS Patients. Chin Med Philos (Humanist Soc Med Ed). 2007;28:334. |
| 24. | Zhou YR. “If you get AIDS... you have to endure it alone”: understanding the social constructions of HIV/AIDS in China. Soc Sci Med. 2007;65:284-295. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 56] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Elmore K. Southern discomfort: AIDS stigmatization in Wilmington, North Carolina. Southeast Geogr. 2006;46:215-230. |
| 26. | Passaes CP, Sáez-Cirión A. HIV cure research: advances and prospects. Virology. 2014;454-455:340-352. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 91] [Cited by in RCA: 93] [Article Influence: 7.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Selwyn PA, Rivard M. Palliative care for AIDS: challenges and opportunities in the era of highly active anti-retroviral therapy. J Palliat Med. 2003;6:475-487. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Alciati A, Gallo L, Monforte AD, Brambilla F, Mellado C. Major depression-related immunological changes and combination antiretroviral therapy in HIV-seropositive patients. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2007;22:33-40. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339:b2535. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18665] [Cited by in RCA: 18058] [Article Influence: 1062.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 30. | Ogundipe OA, Olagunju AT, Adeyemi JD. Suicidal ideation among attendees of a West African HIV clinic. Arch Suicide Res. 2015;19:103-116. [PubMed] |
| 31. | Kinyanda E, Hoskins S, Nakku J, Nawaz S, Patel V. The prevalence and characteristics of suicidality in HIV/AIDS as seen in an African population in Entebbe district, Uganda. BMC Psychiatry. 2012;12:63. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 71] [Article Influence: 5.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Lewis EL, Mosepele M, Seloilwe E, Lawler K. Depression in HIV-positive women in Gaborone, Botswana. Health Care Women Int. 2012;33:375-386. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Lee TS, Shen HC, Wu WH, Huang CW, Yen MY, Wang BE, Chuang P, Shih CY, Chou YC, Liu YL. Clinical characteristics and risk behavior as a function of HIV status among heroin users enrolled in methadone treatment in northern Taiwan. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2011;6:6. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Atkinson JH, Jin H, Shi C, Yu X, Duarte NA, Casey CY, Franklin DR, Vigil O, Cysique L, Wolfson T. Psychiatric context of human immunodeficiency virus infection among former plasma donors in rural China. J Affect Disord. 2011;130:421-428. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Jin H, Hampton Atkinson J, Yu X, Heaton RK, Shi C, Marcotte TP, Young C, Sadek J, Wu Z, Grant I. Depression and suicidality in HIV/AIDS in China. J Affect Disord. 2006;94:269-275. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Haller DL, Miles DR. Suicidal ideation among psychiatric patients with HIV: psychiatric morbidity and quality of life. AIDS Behav. 2003;7:101-108. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Kalichman SC, Heckman T, Kochman A, Sikkema K, Bergholte J. Depression and thoughts of suicide among middle-aged and older persons living with HIV-AIDS. Psychiatr Serv. 2000;51:903-907. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 180] [Cited by in RCA: 162] [Article Influence: 6.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Pompili M, Pennica A, Serafini G, Battuello M, Innamorati M, Teti E, Girardi N, Amore M, Lamis DA, Aceti A. Depression and affective temperaments are associated with poor health-related quality of life in patients with HIV infection. J Psychiatr Pract. 2013;19:109-117. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Breitbart W, Rosenfeld B, Gibson C, Kramer M, Li Y, Tomarken A, Nelson C, Pessin H, Esch J, Galietta M. Impact of treatment for depression on desire for hastened death in patients with advanced AIDS. Psychosomatics. 2010;51:98-105. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Krabbendam AA, Kuijper B, Wolffers IN, Drew R. The impact of counselling on HIV-infected women in Zimbabwe. AIDS Care. 1998;10 Suppl 1:S25-S37. [PubMed] |
| 41. | Arseniou S, Arvaniti A, Samakouri M. HIV infection and depression. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;68:96-109. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 133] [Cited by in RCA: 159] [Article Influence: 13.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Almeida SM. Cognitive impairment and major depressive disorder in HIV infection and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2013;71:689-692. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Del Guerra FB, Fonseca JL, Figueiredo VM, Ziff EB, Konkiewitz EC. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated depression: contributions of immuno-inflammatory, monoaminergic, neurodegenerative, and neurotrophic pathways. J Neurovirol. 2013;19:314-327. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 66] [Article Influence: 5.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Hirsch Allen AJ, Forrest JI, Kanters S, O’Brien N, Salters KA, McCandless L, Montaner JS, Hogg RS. Factors associated with disclosure of HIV status among a cohort of individuals on antiretroviral therapy in British Columbia, Canada. AIDS Behav. 2014;18:1014-1026. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 45. | Battegay M, Haerry DH, Fehr J, Staehelin C, Wandeler G, Elzi L. [Psychosocial aspects on the treatment of HIV-infection]. Ther Umsch. 2014;71:509-513. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Ironson G, O’Cleirigh C, Fletcher MA, Laurenceau JP, Balbin E, Klimas N, Schneiderman N, Solomon G. Psychosocial factors predict CD4 and viral load change in men and women with human immunodeficiency virus in the era of highly active antiretroviral treatment. Psychosom Med. 2005;67:1013-1021. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 47. | Keiser O, Spoerri A, Brinkhof MW, Hasse B, Gayet-Ageron A, Tissot F, Christen A, Battegay M, Schmid P, Bernasconi E. Suicide in HIV-infected individuals and the general population in Switzerland, 1988-2008. Am J Psychiatry. 2010;167:143-150. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 83] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 48. | Leserman J. Role of depression, stress, and trauma in HIV disease progression. Psychosom Med. 2008;70:539-545. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 434] [Cited by in RCA: 445] [Article Influence: 24.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 49. | Murray C, Lopez A, editors . The global burden of disease: summary. Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA 1996; . |
P- Reviewer: Balazs J, Lopez-Jornet P S- Editor: Ji FF L- Editor: A E- Editor: Yan JL
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/