©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Virol. Dec 25, 2025; 14(4): 111810
Published online Dec 25, 2025. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v14.i4.111810
Published online Dec 25, 2025. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v14.i4.111810
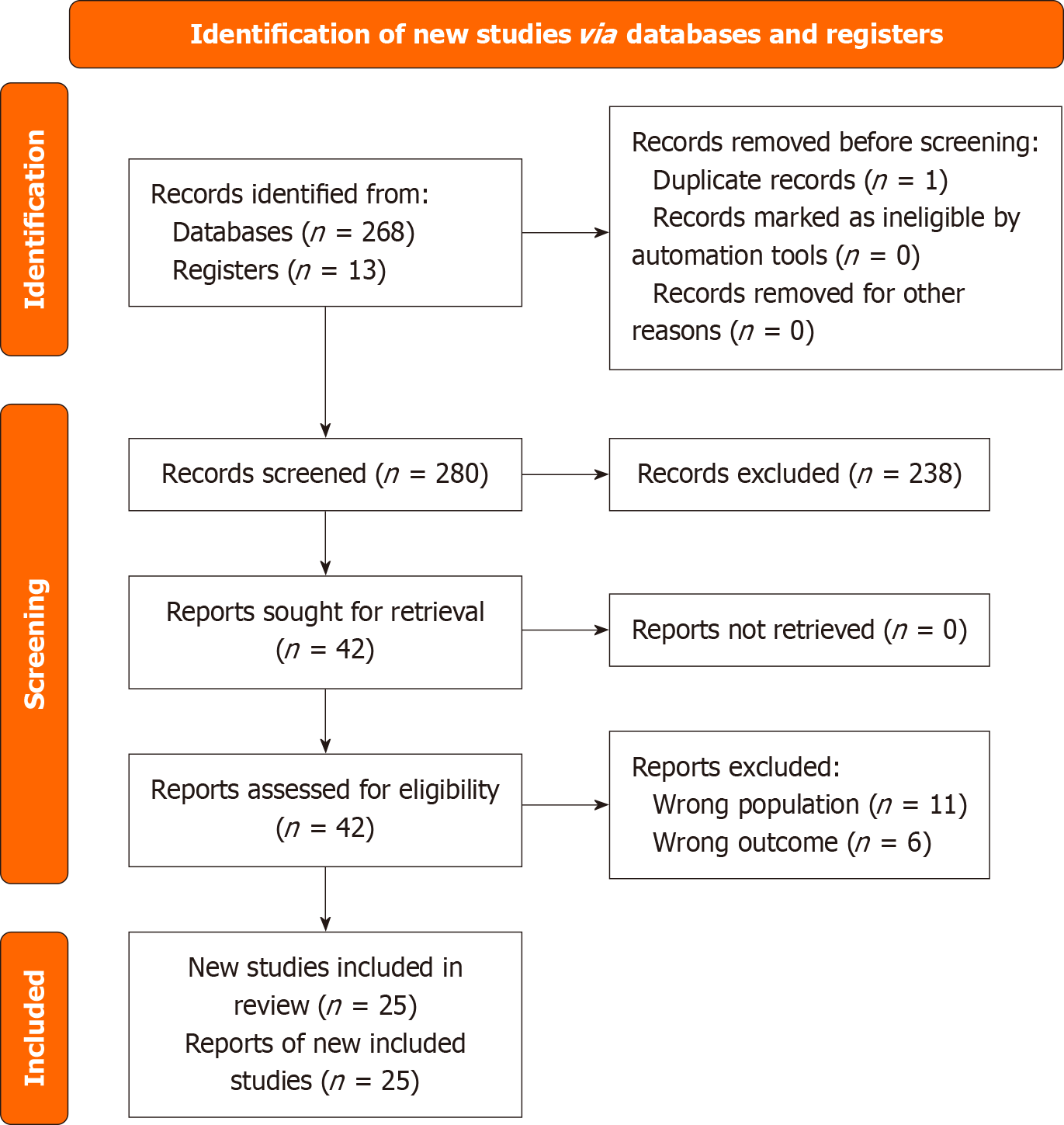
Figure 1 PRISMA flow diagram of study selection.
Flowchart illustrating the systematic review process. A total of 280 records were screened after removing 1 duplicate. Of these, 42 full text reports were assessed for eligibility, and 25 studies met the inclusion criteria. 17 reports were excluded due to wrong population (11) or outcome (6).
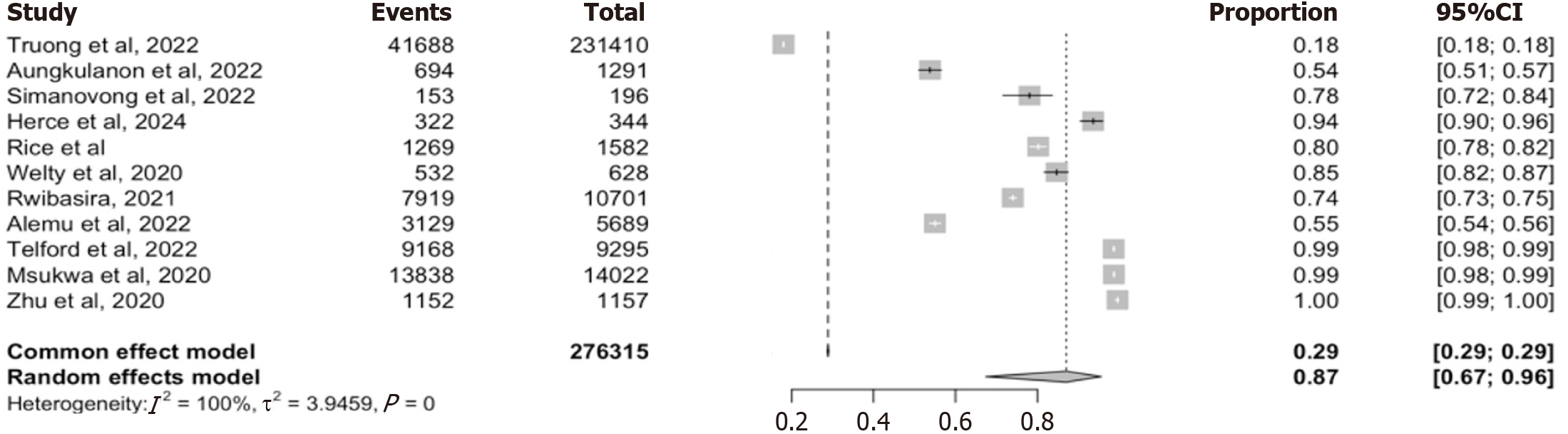
Figure 2 Pooled recency testing coverage among newly diagnosed people living with human immunodeficiency virus in low- and middle-income countries.
Forest plots showing the proportion of newly diagnosed individuals who received a rapid test for recent infection across 11 studies. Estimates are pooled using a random effects model. Substantial heterogeneity observed (I2 = 100%).
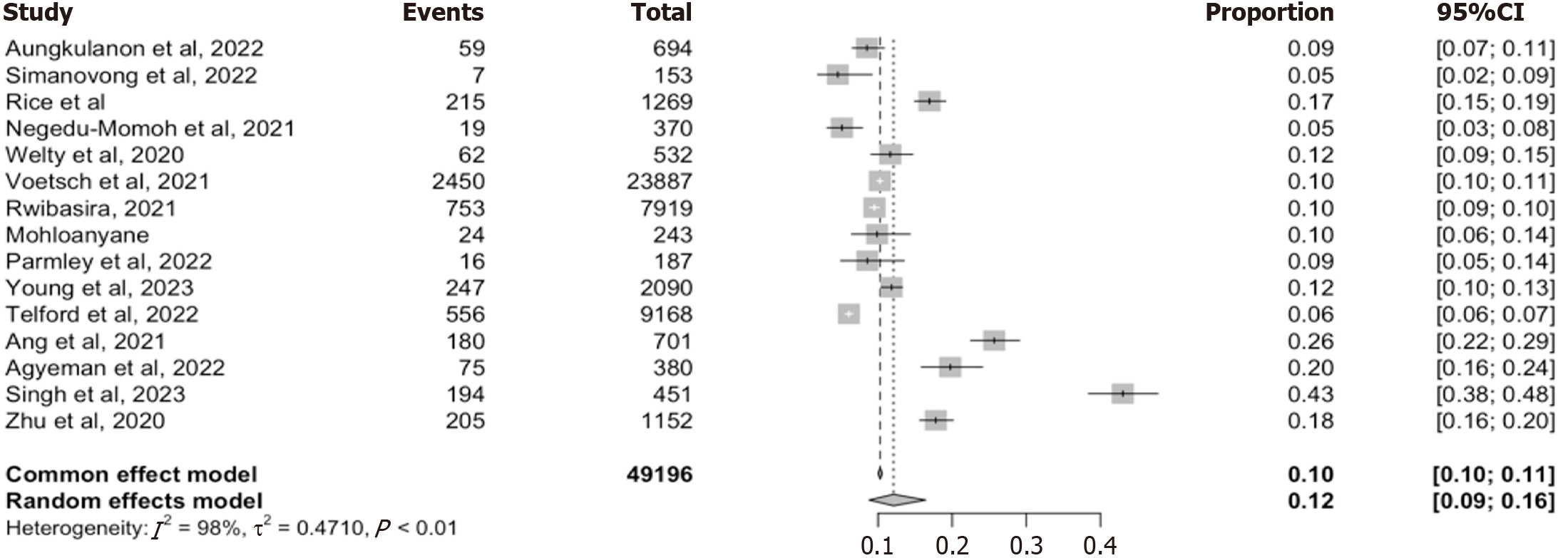
Figure 3 Pooled prevalence of preliminary-recent human immunodeficiency virus infection across included studies.
Forest plots summarizing the proportion of individuals identified as recently infected using recent infection testing algorithm assays in 15 studies. The pooled estimates is generated using a random effect model. Heterogeneity was high (I2 = 98%).
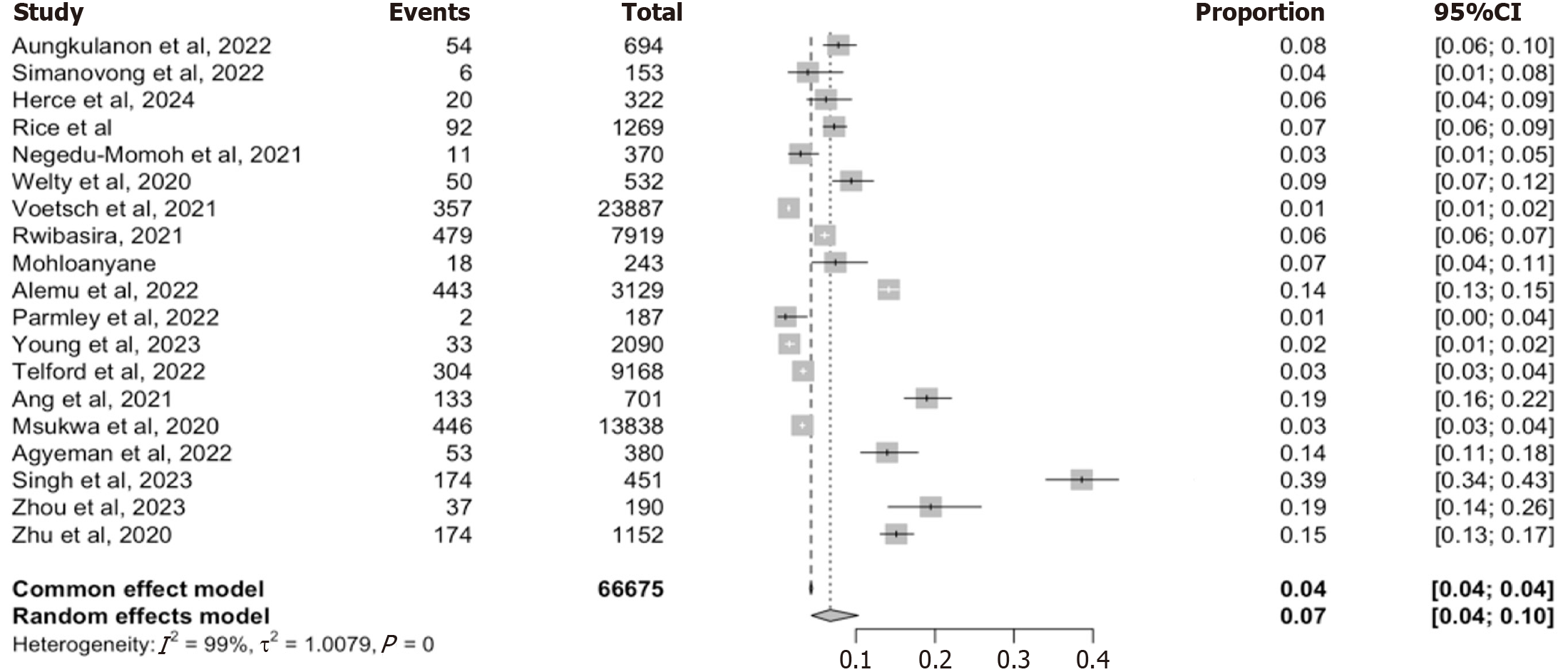
Figure 4 Pooled Prevalence of recent infection testing algorithm - recent human immunodeficiency virus Infection based on World Health Organization - algorithm.
Forest plots showing the prevalence of recent infection using recent infection testing algorithm (rapid testing for recent infection + viral load ≥ 1000 copies/mL from 18 studies. Estimates are derived using random-effects and fixed-effect models with I2 equal 99%.
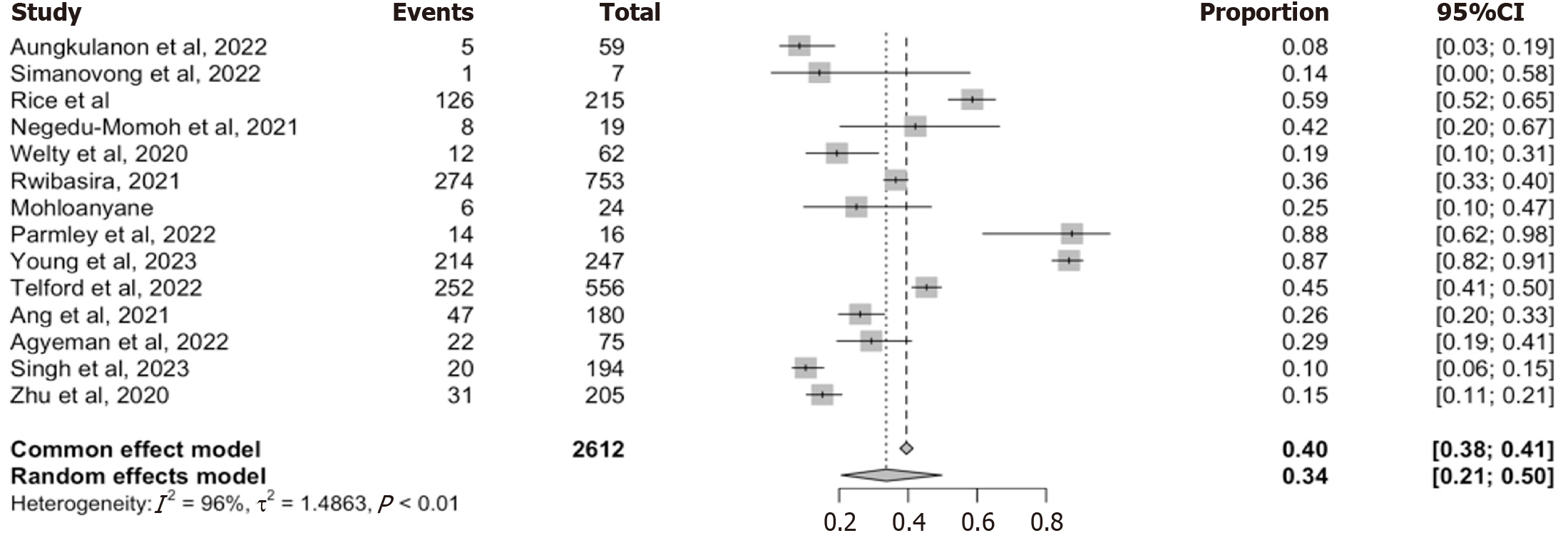
Figure 5 Reclassification rate of individuals initially classified as recent by rapid testing for recent infection.
Forest plots of 14 studies reporting the proportion of rapid testing for recent infection - recent cases reclassified as long-term after viral load confirmation. Random-effects estimates with substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 96%).
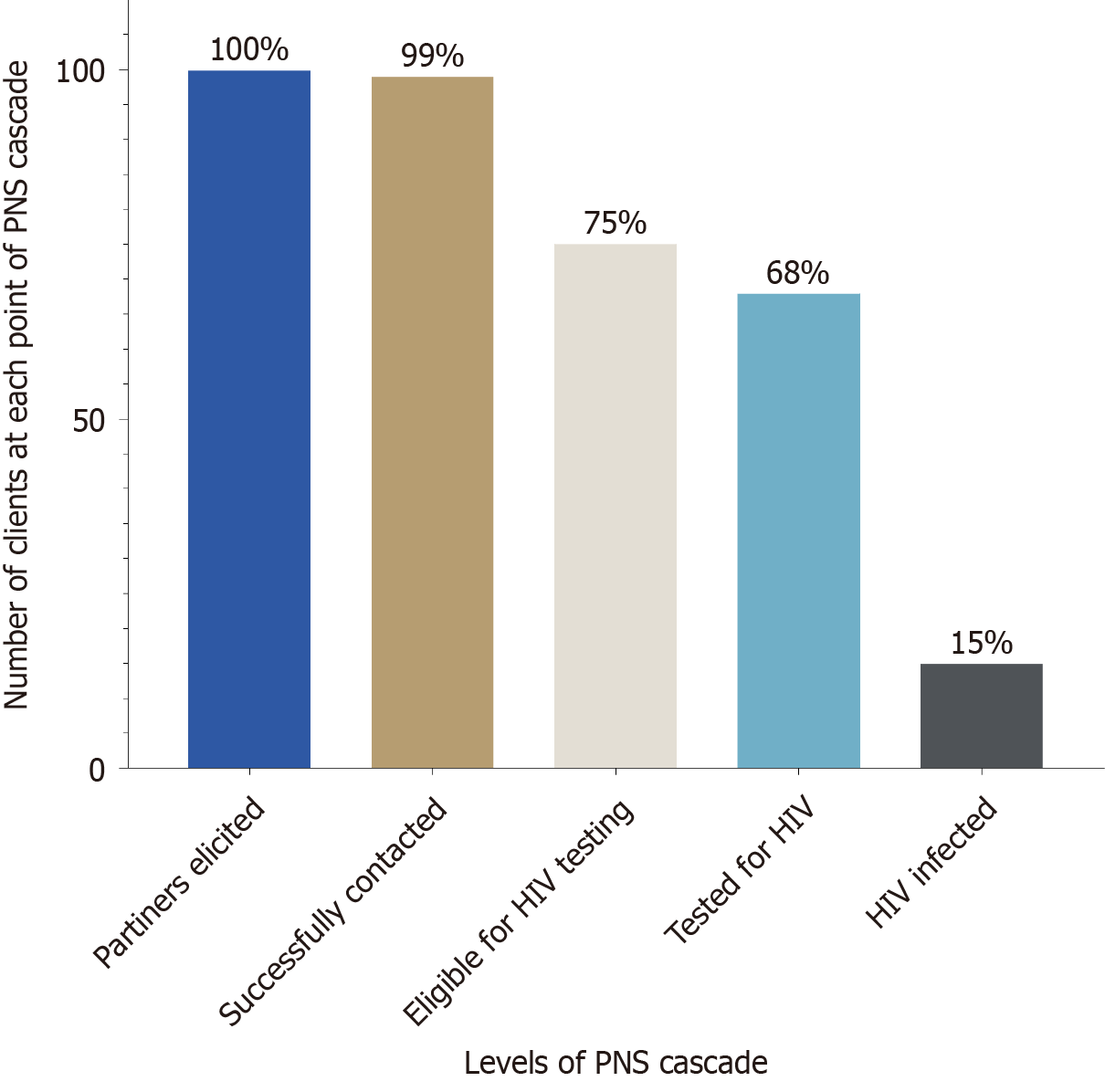
Figure 6 Partner notification services among patients of newly diagnosed individuals.
Bar charts showing the proportion of partners successfully contacted (99%), deemed eligible for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) testing (75%), tested (68%) and diagnosed HIV-positive (15%) across 5 studies. The cascade highlights strong partner reach but notable drop-offs at eligibility and testing stages with a high positivity yield among those tested. HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus; PNS: Partner notification services.
- Citation: El-Imam IA, Peter TA, Fussi HF, Ally ZM, Bakari HM, Mbwana MS, Chenya UK, Mpimo BK, Ally HM, Ramadhani HO. Human immunodeficiency virus recency testing coverage and partner-notification-services among people-living with human immunodeficiency virus in low- and middle-income countries. World J Virol 2025; 14(4): 111810
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v14/i4/111810.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v14.i4.111810