©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Psychiatry. Feb 19, 2026; 16(2): 111012
Published online Feb 19, 2026. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v16.i2.111012
Published online Feb 19, 2026. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v16.i2.111012
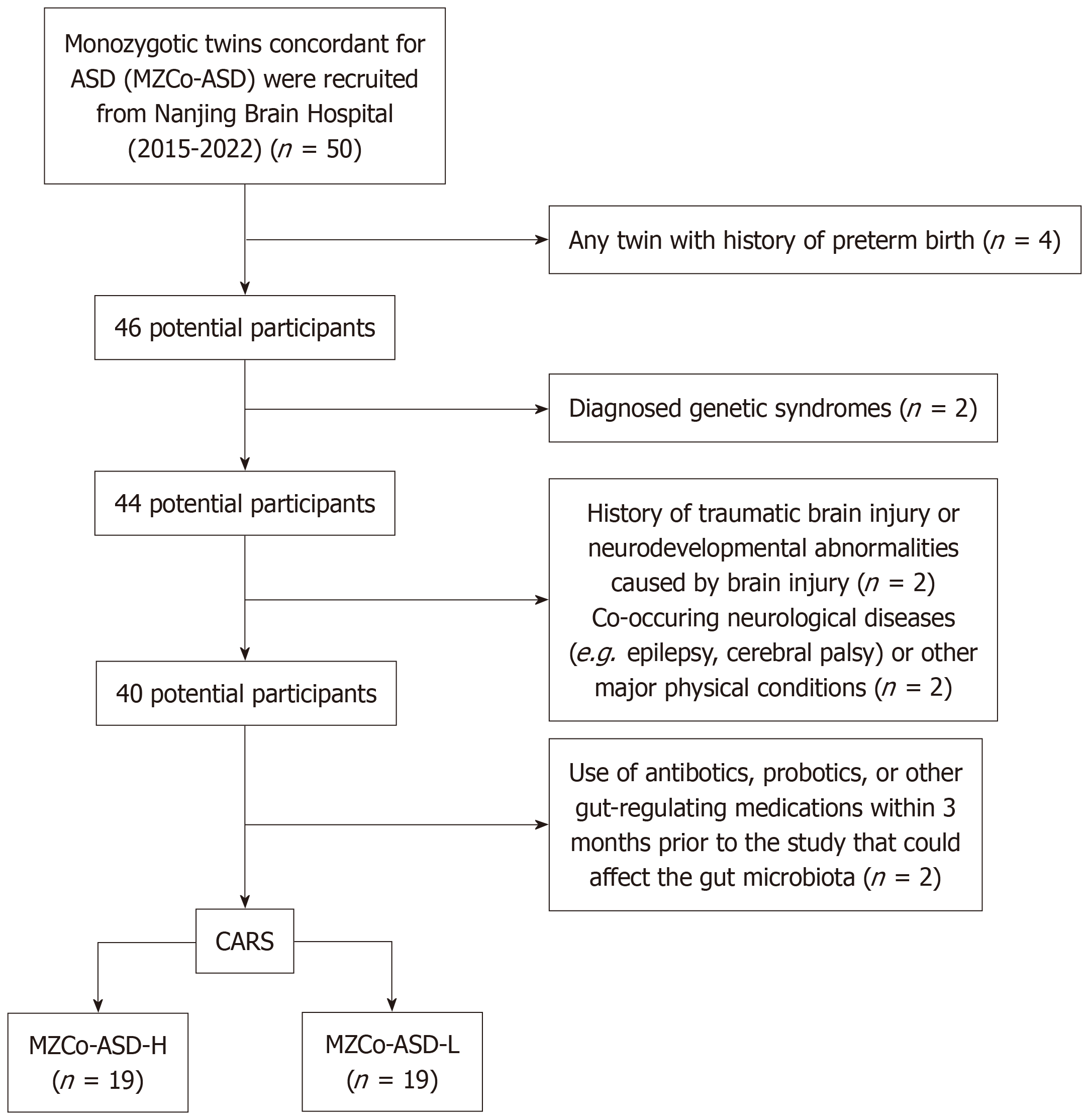
Figure 1 Inclusion and exclusion flowchart.
ASD: Autism spectrum disorder; MZCo-ASD: Monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder; CARS: Childhood Autism Rating Scale; MZCo-ASD-H: Severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder; MZCo-ASD-L: Monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder-mild group.
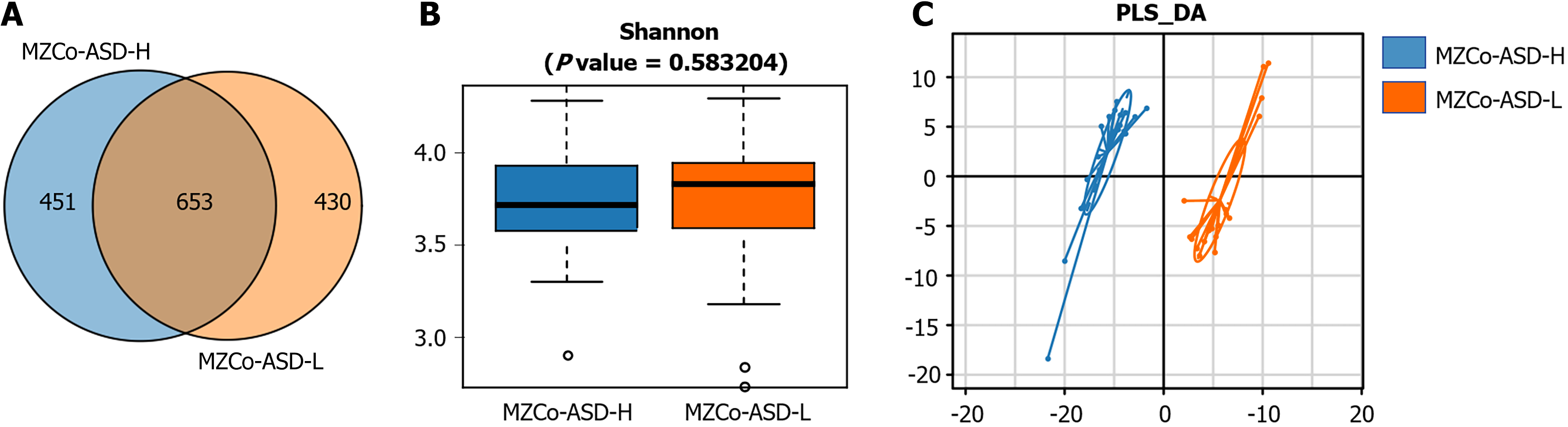
Figure 2 Species composition analysis of severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder and monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder-mild groups.
A: Venn diagram highlights the overlapping area representing shared operational taxonomic unit between the two groups; B: The alpha diversity of the severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder group (blue) and the monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder-mild group (orange); C: The beta diversity of severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder group (blue) and the monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder-mild group (orange). The distance between the two groups reflects their similarity. MZCo-ASD-H: Severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder; MZCo-ASD-L: Monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder-mild group; PLS-DA: Partial least squares discriminant analysis.
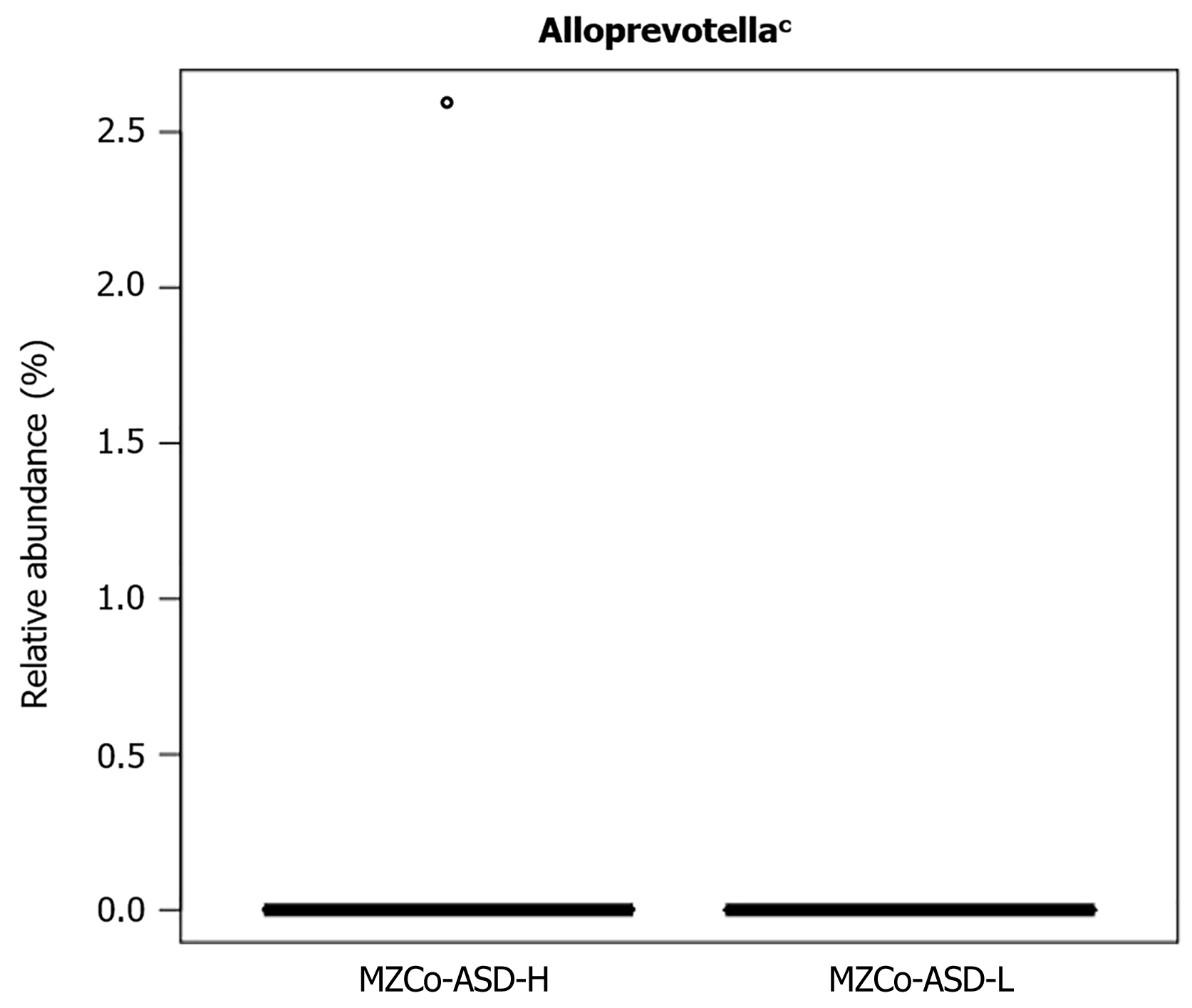
Figure 3 Compares the abundance of different genera of microbial communities between the severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder and monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder-mild groups.
cP < 0.001; MZCo-ASD-H: Severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder; MZCo-ASD-L: Monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder-mild group.
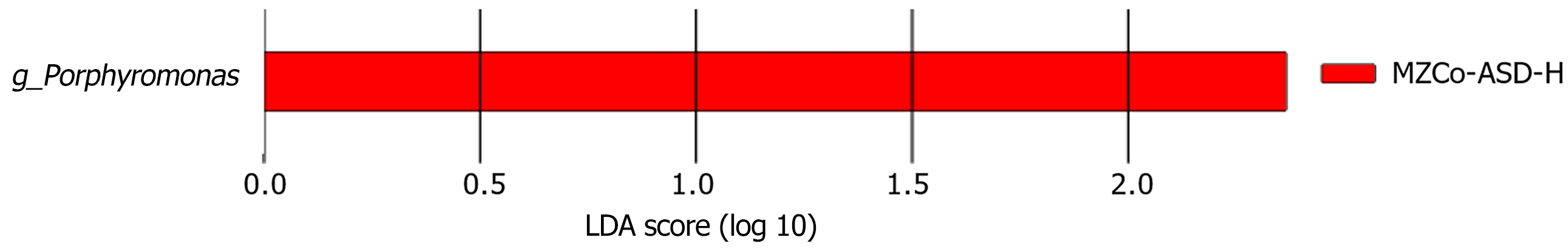
Figure 4 The LDA analysis reveals the significantly enriched species of severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder.
This shows the enriched species of severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder identified through linear discriminant analysis. The horizontal axis displays the linear discriminant analysis score ranging from 0.0 to 2.0, while the vertical axis depicts various taxonomic units. MZCo-ASD-H: Severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder; LDA: Linear discriminant analysis.
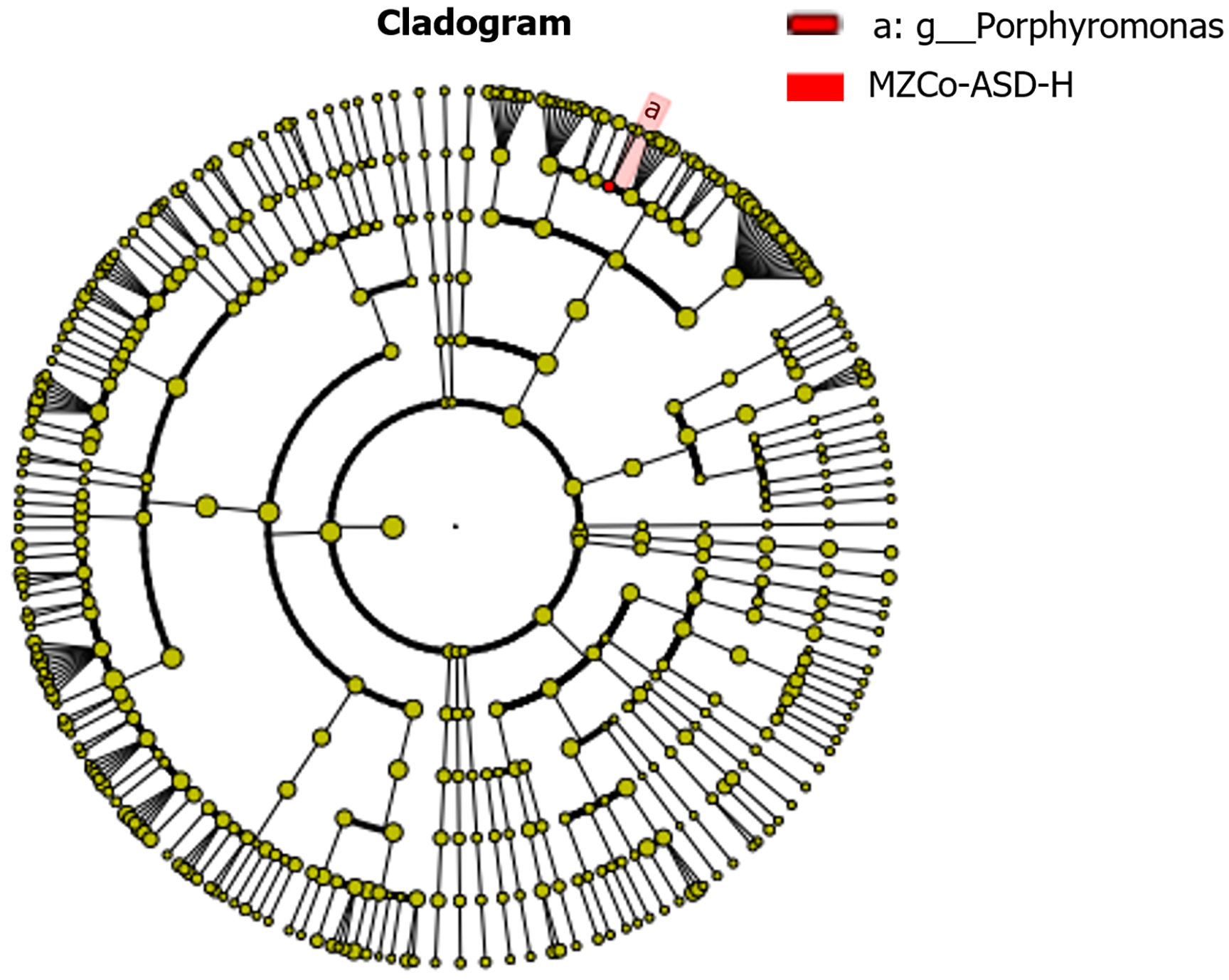
Figure 5 A phylogenetic cladogram that focuses on the genus Porphyromonas.
The phylogenetic cladogram visualized the relationships between microbial communities and the differences among groups. Each dot represents a taxonomic unit, from phylum to genus. Yellow dots indicate nodes with no significant differences, while red dots represent nodes that are significantly more common in the severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder group. The red-highlighted area emphasizes the genus Porphyromonas and its related branches. The cladogram indicates that the genus Porphyromonas has distinct branches and red clusters in the outer circle of the phylogenetic tree. MZCo-ASD-H: Severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder.
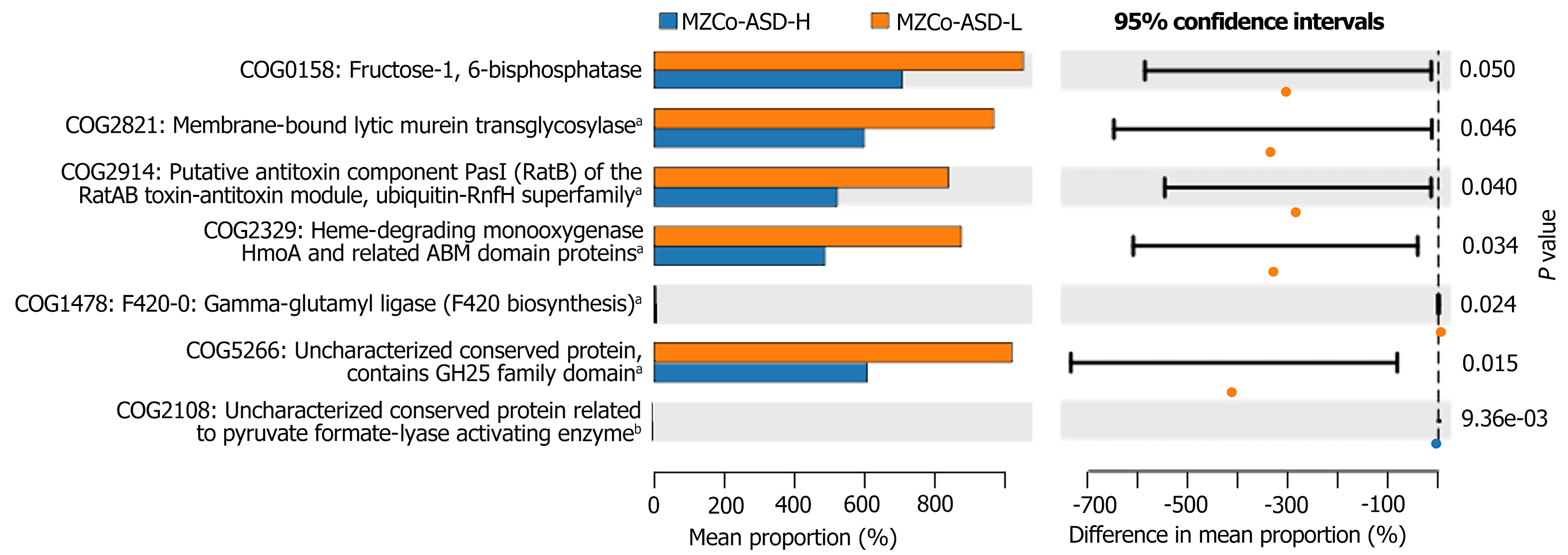
Figure 6 The average differences in Clusters of Orthologous Groups function between the monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder-mild group (in orange) and the severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder group (in blue).
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.05; MZCo-ASD-H: Severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder; MZCo-ASD-L: Monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder-mild group; COG: Clusters of Orthologous Groups; ABM: Antibiotic monooxygenase; F420: Coenzyme F420; GH: Glycoside hydrolase.
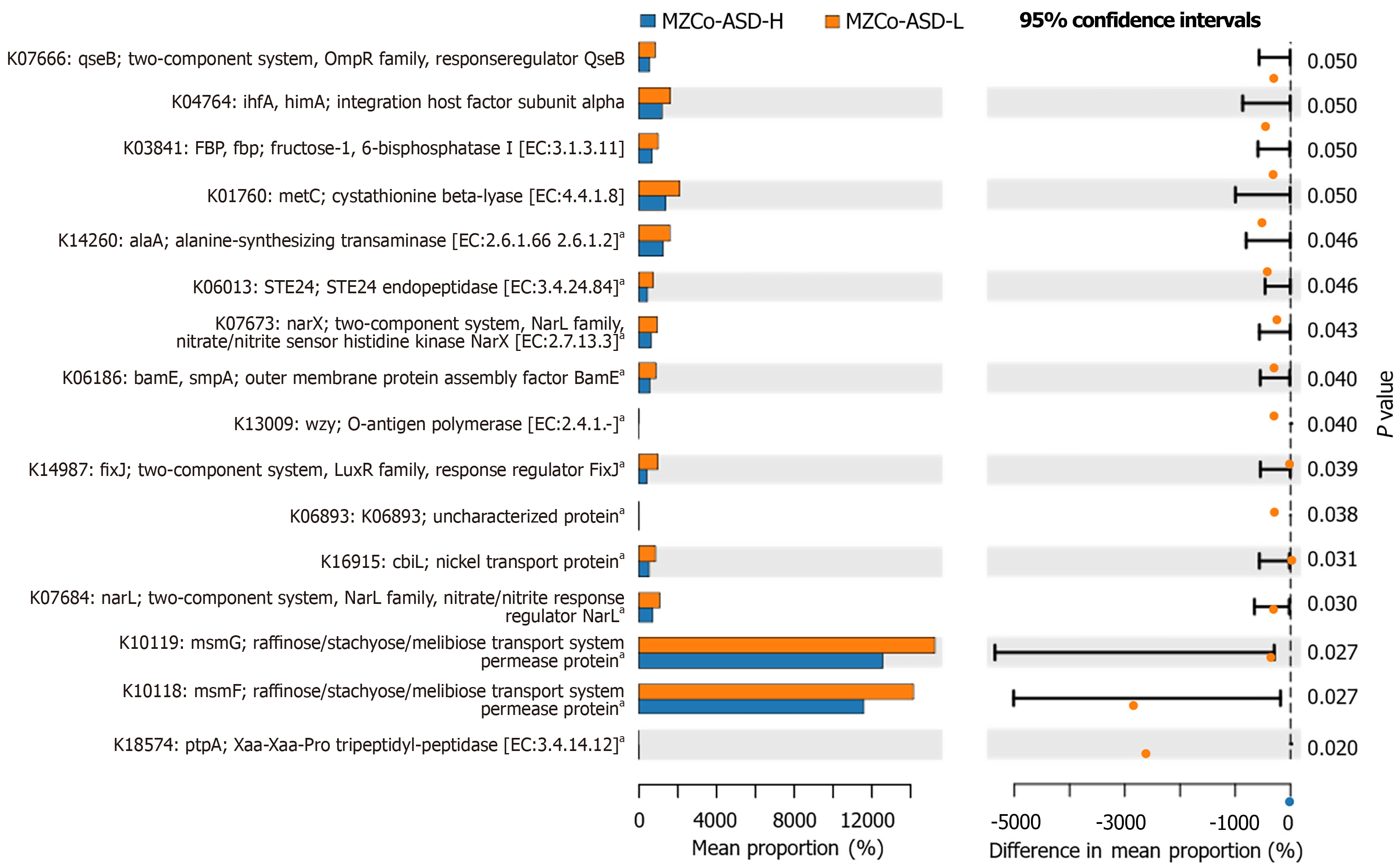
Figure 7 The average differences in knockout function between monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder-mild group (in orange) and the severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder group (in blue).
aP < 0.05; MZCo-ASD-H: Severe monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder; MZCo-ASD-L: Monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorder-mild group; FBP: Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase; EC: Enzyme commission; STE24: Zinc metalloprotease STE.
- Citation: Huang YY, Li CY, Li Y, Fang H, Ke XY. Characteristics and functions of the gut microbiome in monozygotic twins with autism spectrum disorders of varying severity. World J Psychiatry 2026; 16(2): 111012
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v16/i2/111012.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v16.i2.111012