©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Oct 19, 2025; 15(10): 107147
Published online Oct 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i10.107147
Published online Oct 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i10.107147
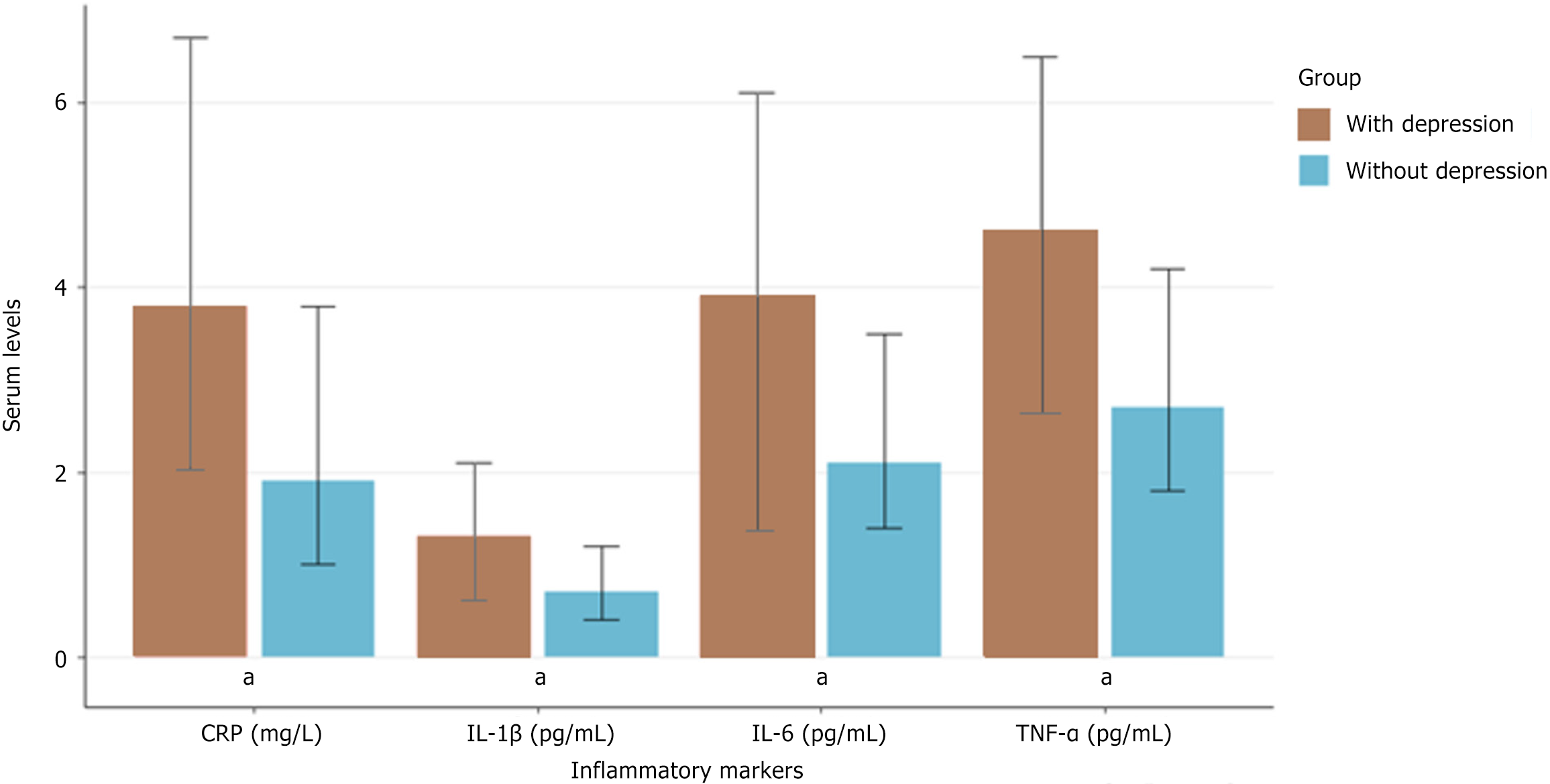
Figure 1 Comparison of inflammatory marker levels between participants with and without depression.
aP < 0.001 for all comparisons. Bar graph showing median (with interquartile range) serum levels of interleukin-6, interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and C-reactive protein in patients with endometriosis-associated chronic pain, classified based on the presence (brown) or absence (blue) of depression. n = 200; Mann-Whitney U-test. CRP: C-reactive protein; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
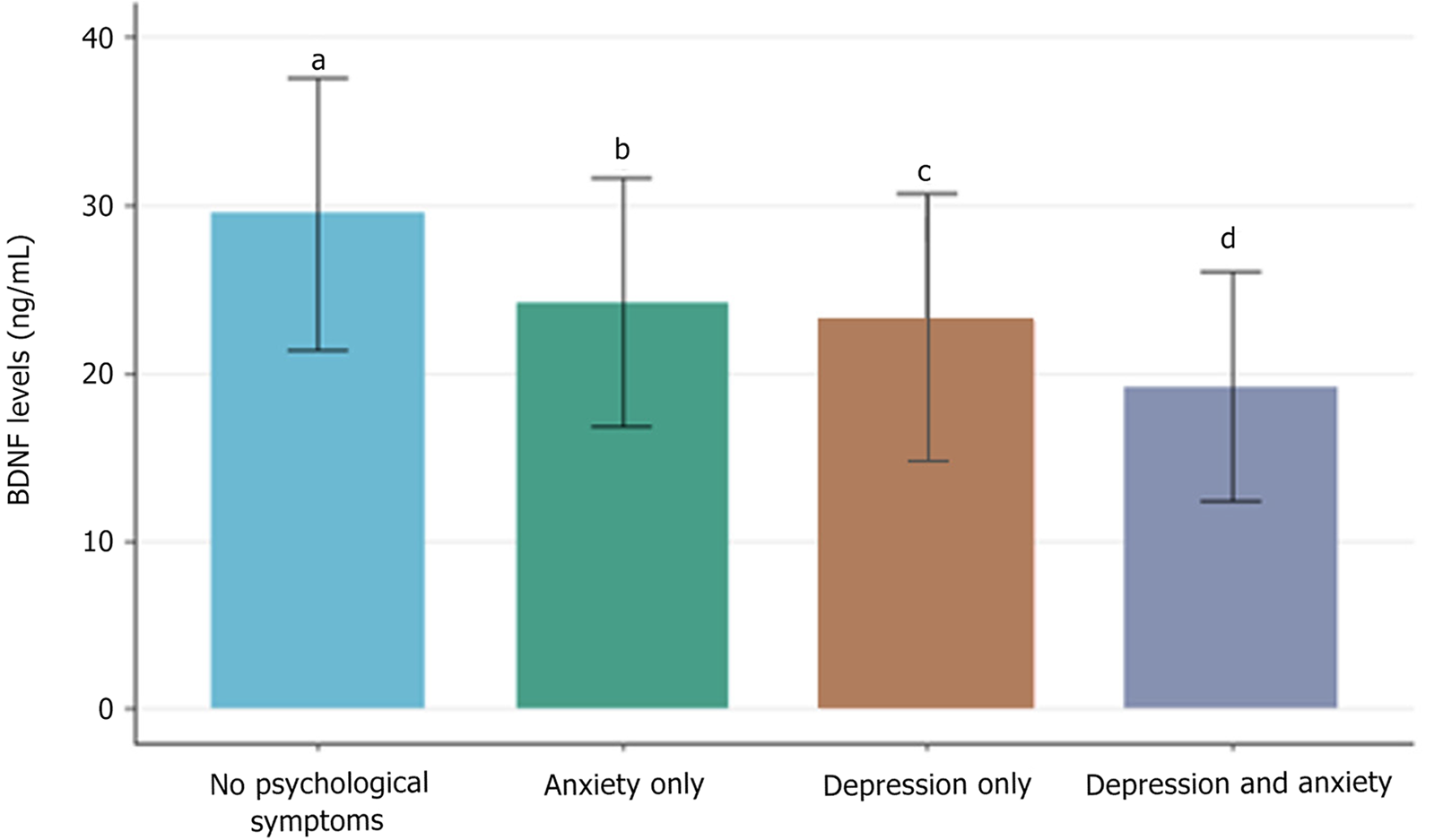
Figure 2 Comparison of brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels between psychological symptom groups.
aP < 0.05 vs anxiety only group; bP < 0.01 vs depression only group; cP < 0.001 vs depression and anxiety group; dP < 0.001 vs all other groups. Bar graph showing mean ± SD serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with endometriosis-associated chronic pain, categorized into four groups: No psychological symptoms (n = 31), anxiety only (n = 35), depression only (n = 18), and comorbid depression and anxiety (n = 67). Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-hoc analysis. BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor.
- Citation: Yang FC, Zhou Y, Zhang SY, Ma R. Depression and anxiety in patients with endometriosis-associated chronic pain: Neuroimmune mechanisms mediated by inflammatory factors. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(10): 107147
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i10/107147.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i10.107147