©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Crit Care Med. Dec 9, 2025; 14(4): 108370
Published online Dec 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i4.108370
Published online Dec 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i4.108370
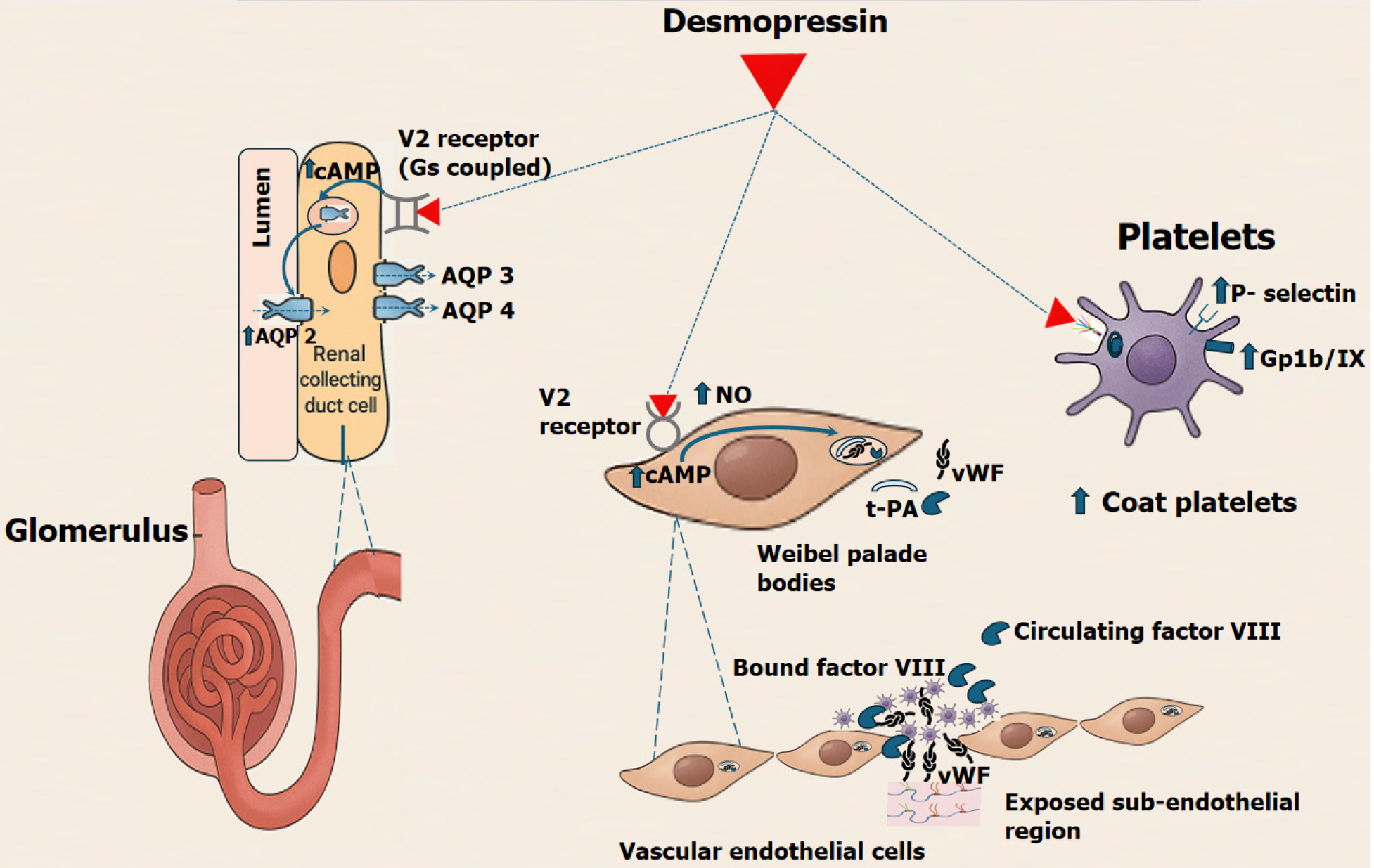
Figure 1 Desmopressin: Mechanisms of action.
Desmopressin exerts its effects primarily through selective activation of vasopressin V2 receptors located on renal tubular and endothelial cells. In the kidney, V2 receptor stimulation increases intracellular cAMP, promoting insertion of aquaporin-2 channels into the apical membrane of collecting duct cells, enhancing water reabsorption and producing an antidiuretic effect. In vascular endothelium, desmopressin induces exocytosis of Weibel-Palade bodies, leading to the release of von Willebrand factor and factor VIII, thereby augmenting platelet adhesion and supporting primary haemostasis. Additionally, desmopressin may stimulate the generation of platelet-derived microparticles with possibility of increased expression of P selectin and Gp1b/IX receptors. It also promotes the formation of collagen and thrombin-activated platelets, a subpopulation of highly procoagulant platelets rich in surface-bound coagulation factors, which further amplifies thrombin generation and fibrin formation. Desmopressin enhances fibrinolytic activity by stimulating endothelial release of tissue plasminogen activator. Moreover, it may induce vasodilation through V2 receptor-mediated activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase, leading to increased nitric oxide production and vascular smooth muscle relaxation. It also promotes endothelial release of tissue plasminogen activator, contributing to a modest enhancement of fibrinolytic activity. NO: Nitric oxide; t-PA: Tissue plasminogen activator.
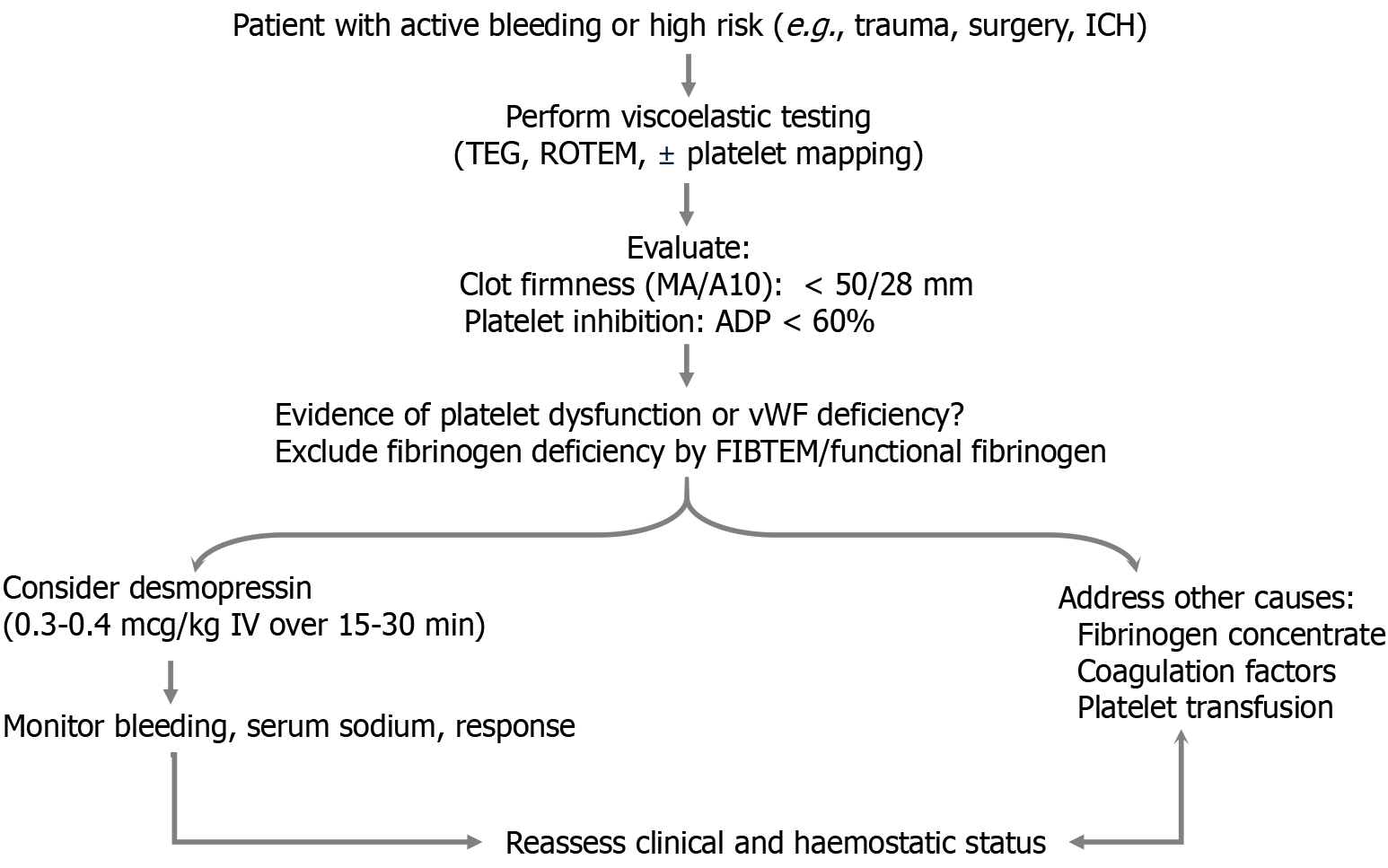
Figure 2 Algorithm for desmopressin use in active or high-risk bleeding.
ADP: Adenosine Diphosphate; A10: Amplitude at 10 minutes; IV: Intravenous; MA: Maximum Amplitude; ROTEM: Rotational Thromboelastometry; TEG: Thromboelastography; vWF: Von Willebrand factor.
- Citation: Vinjamuri S, Tiwari E, Kataria S, Juneja D. Haemostasis and beyond: The expanding role of desmopressin in intensive care. World J Crit Care Med 2025; 14(4): 108370
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v14/i4/108370.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v14.i4.108370