©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Crit Care Med. Dec 9, 2025; 14(4): 105600
Published online Dec 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i4.105600
Published online Dec 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i4.105600
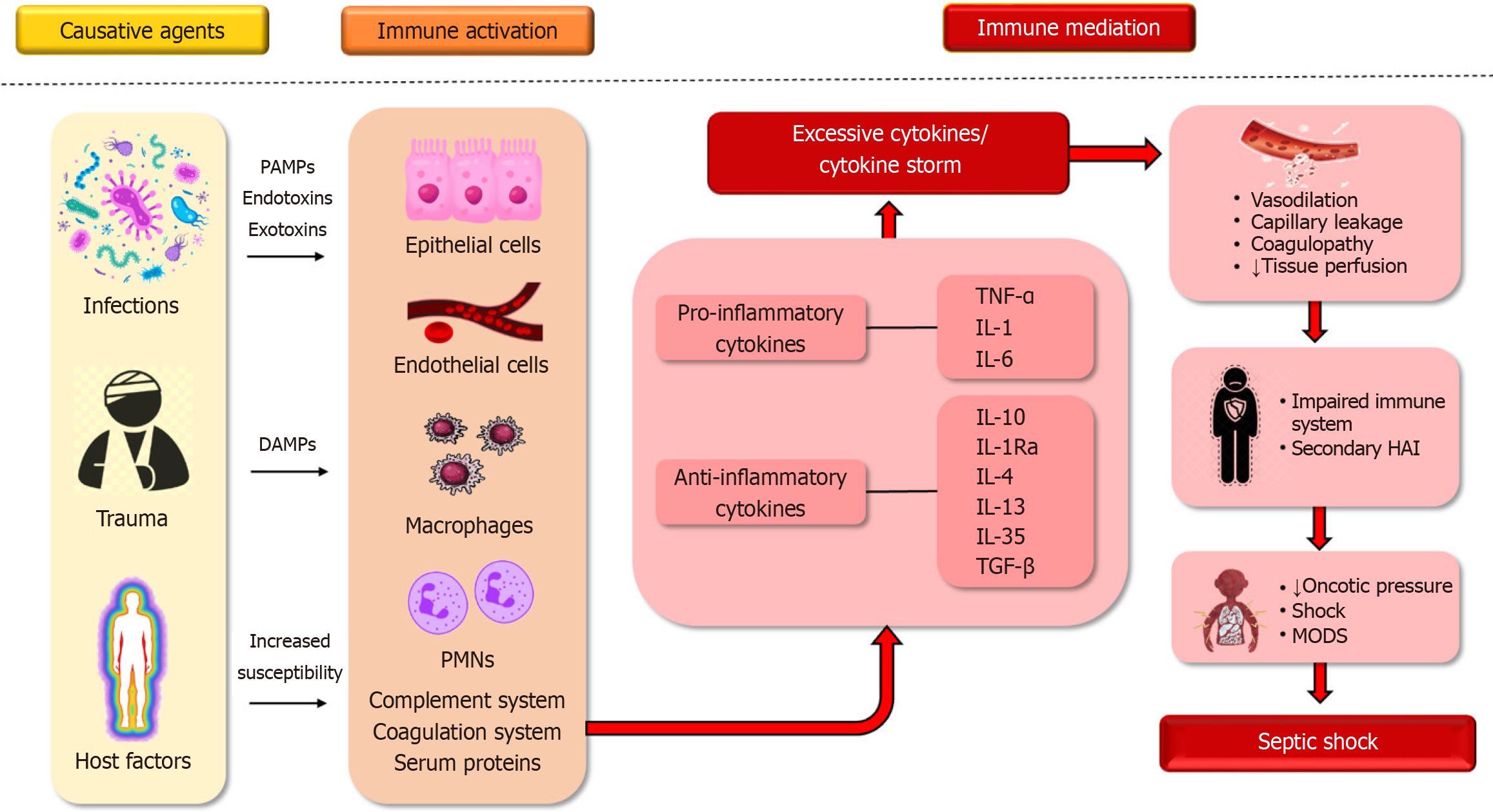
Figure 1 Pathophysiology of septic shock.
PAMPs: Pathogen-associated molecular Patterns; DAMPs: Damage-associated molecular patterns; PMN: Polymorphonuclear neutrophils; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; TGF: Transforming growth factor; HAI: Healthcare-associated infections; MODS: Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome.
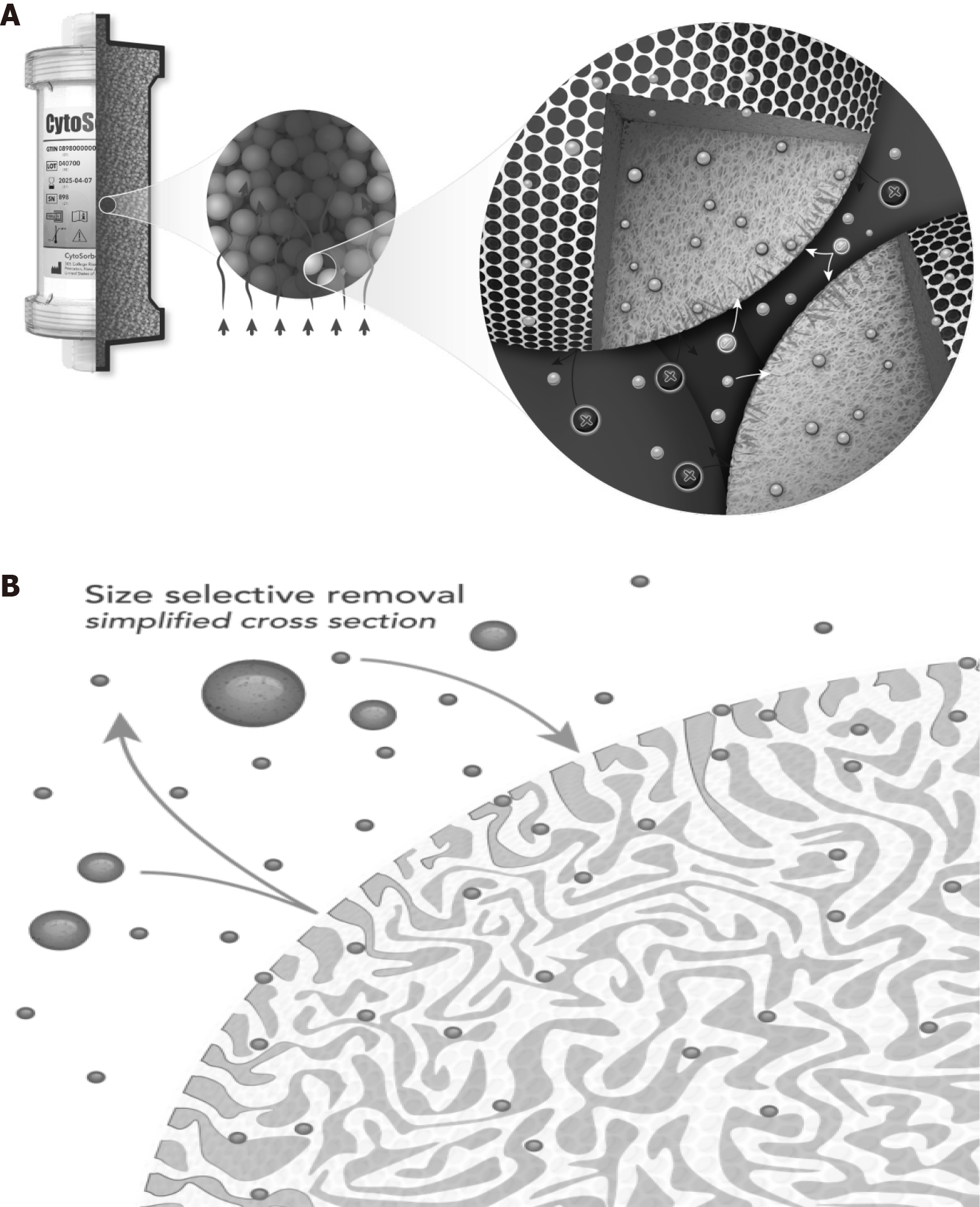
Figure 2 Key features of the cytoSorb therapy.
A: CytoSorb adsorber-bead based technology; B: CytoSorb size selective removal.
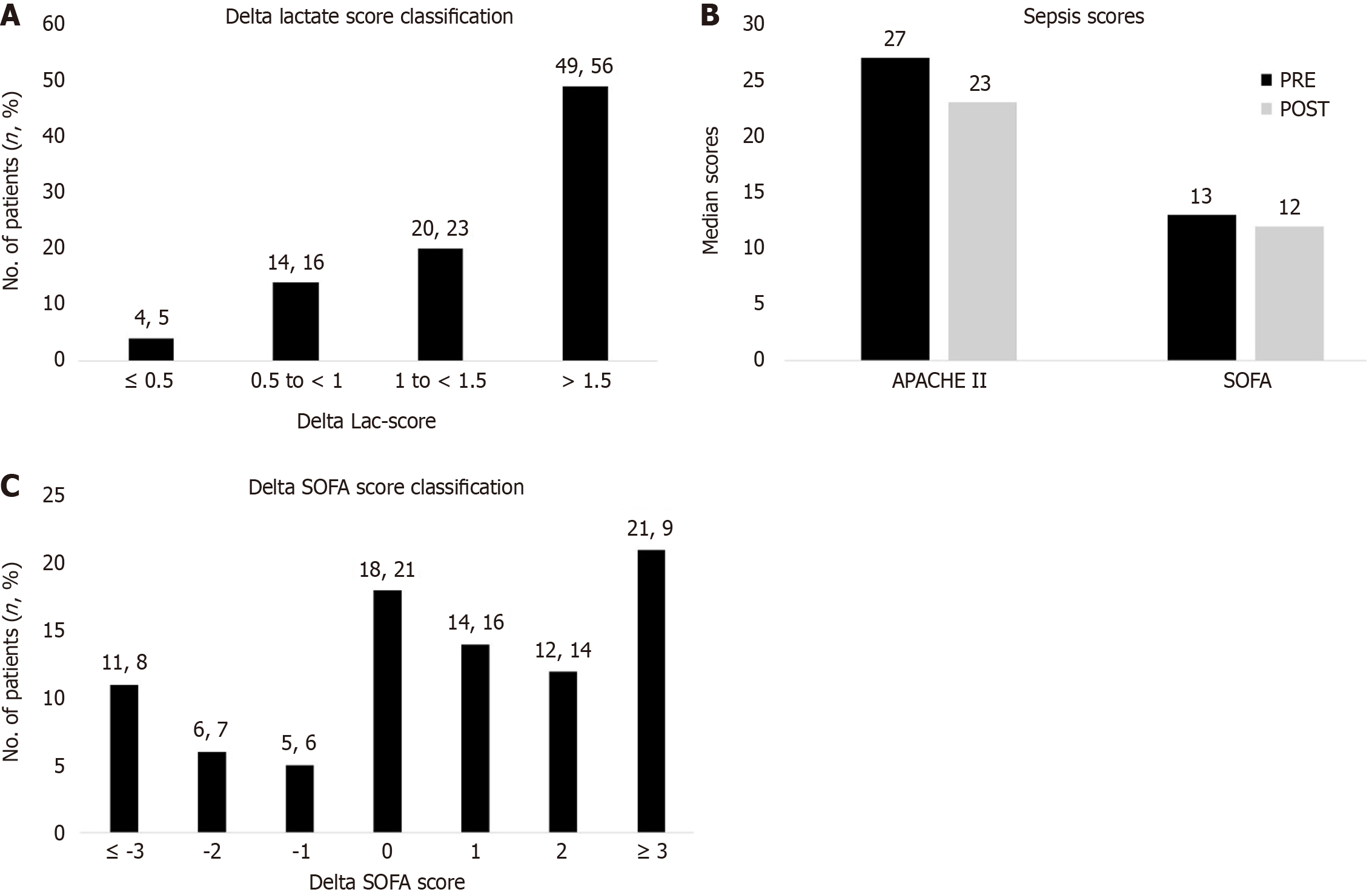
Figure 3 Sepsis severity and prognosis.
A: Delta lactate score classification; B: Comparison of sepsis scores; C: Delta sepsis associated organ failure score classification. SOFA: Sepsis Associated Organ Failure; APACHE II: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation; PRE: Values recorded pre/before CytoSorb; POST: Values recorded post/after CytoSorb.
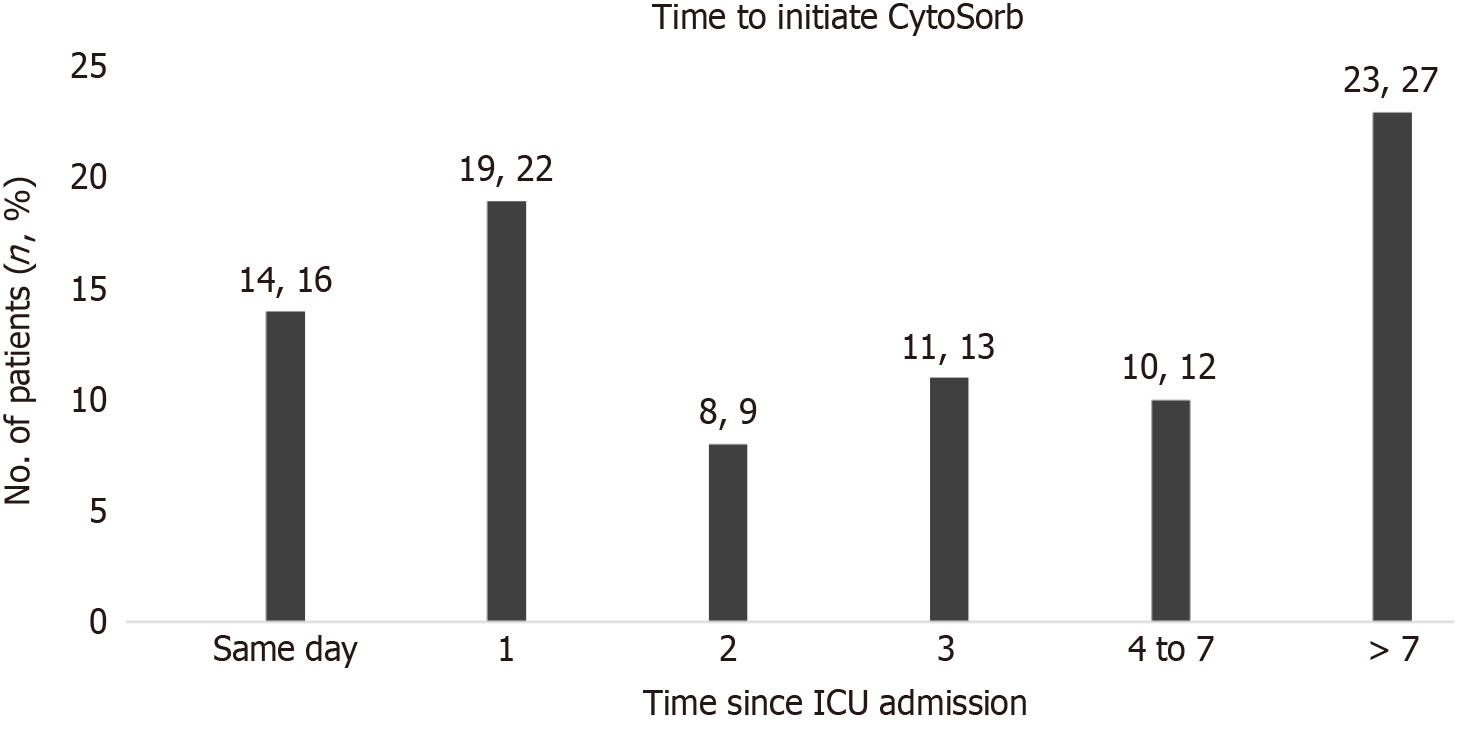
Figure 4 Time to initiate CytoSorb after intensive care unit admission.
ICU: Intensive care unit.
- Citation: Shah MS, Sharma VV, Patel SJ, Ansari AS. Retrospective evaluation of efficacy of CytoSorb® therapy in septic shock patients in a tertiary care intensive care unit. World J Crit Care Med 2025; 14(4): 105600
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v14/i4/105600.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v14.i4.105600