©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Crit Care Med. Dec 9, 2025; 14(4): 105547
Published online Dec 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i4.105547
Published online Dec 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i4.105547
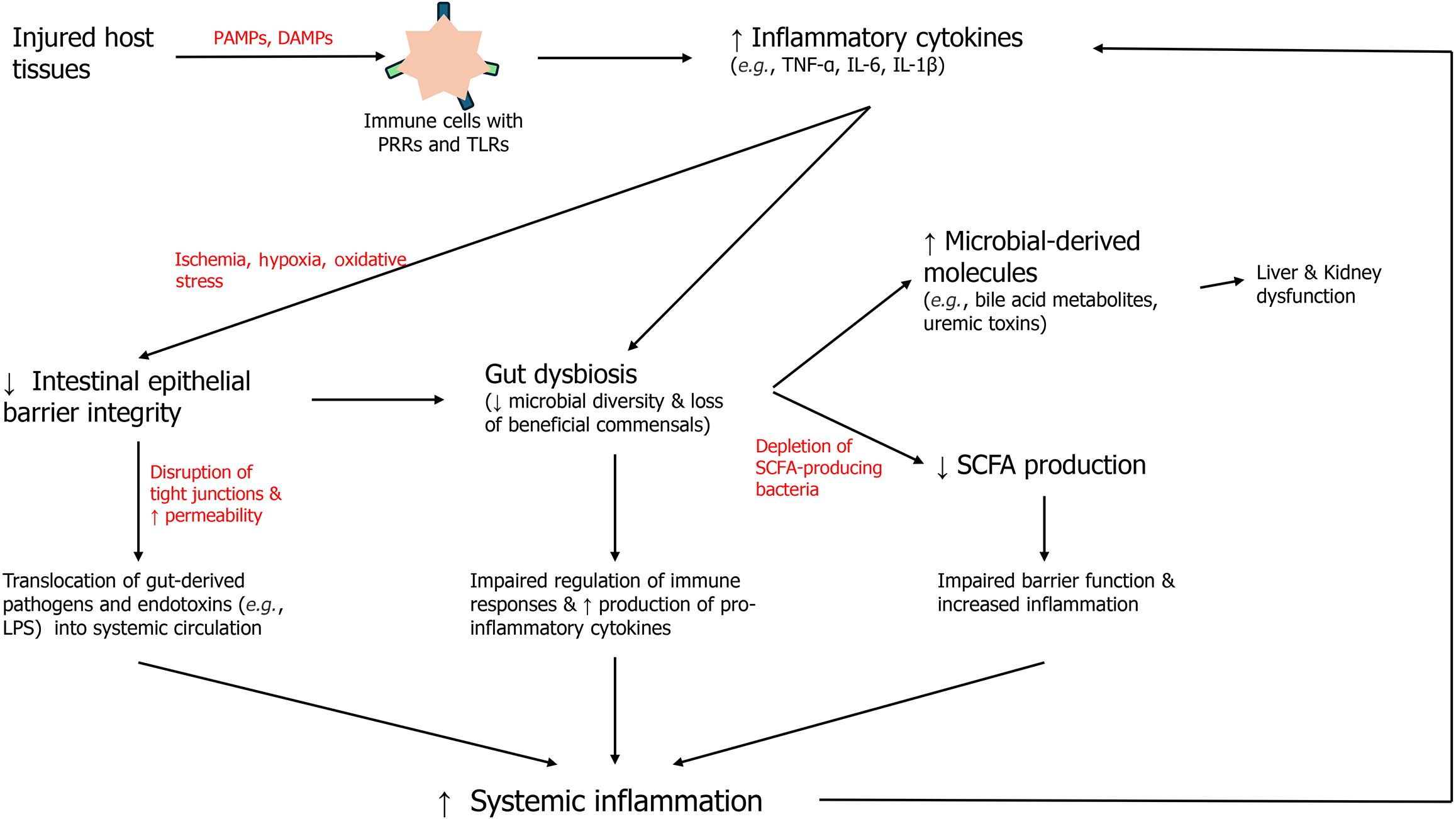
Figure 1 Interplay between disrupted gut barrier integrity, microbial translocation, reduced short chain fatty acid production, and the resulting pro-inflammatory cascade that exacerbates multi-organ dysfunction through microbial-derived metabolites and cytokine release.
SCFA: Short chain fatty acid; PAMPs: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; DAMPs: Damage-associated molecular patterns; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL: Interleukin; LPS: Lipopolysaccharides.
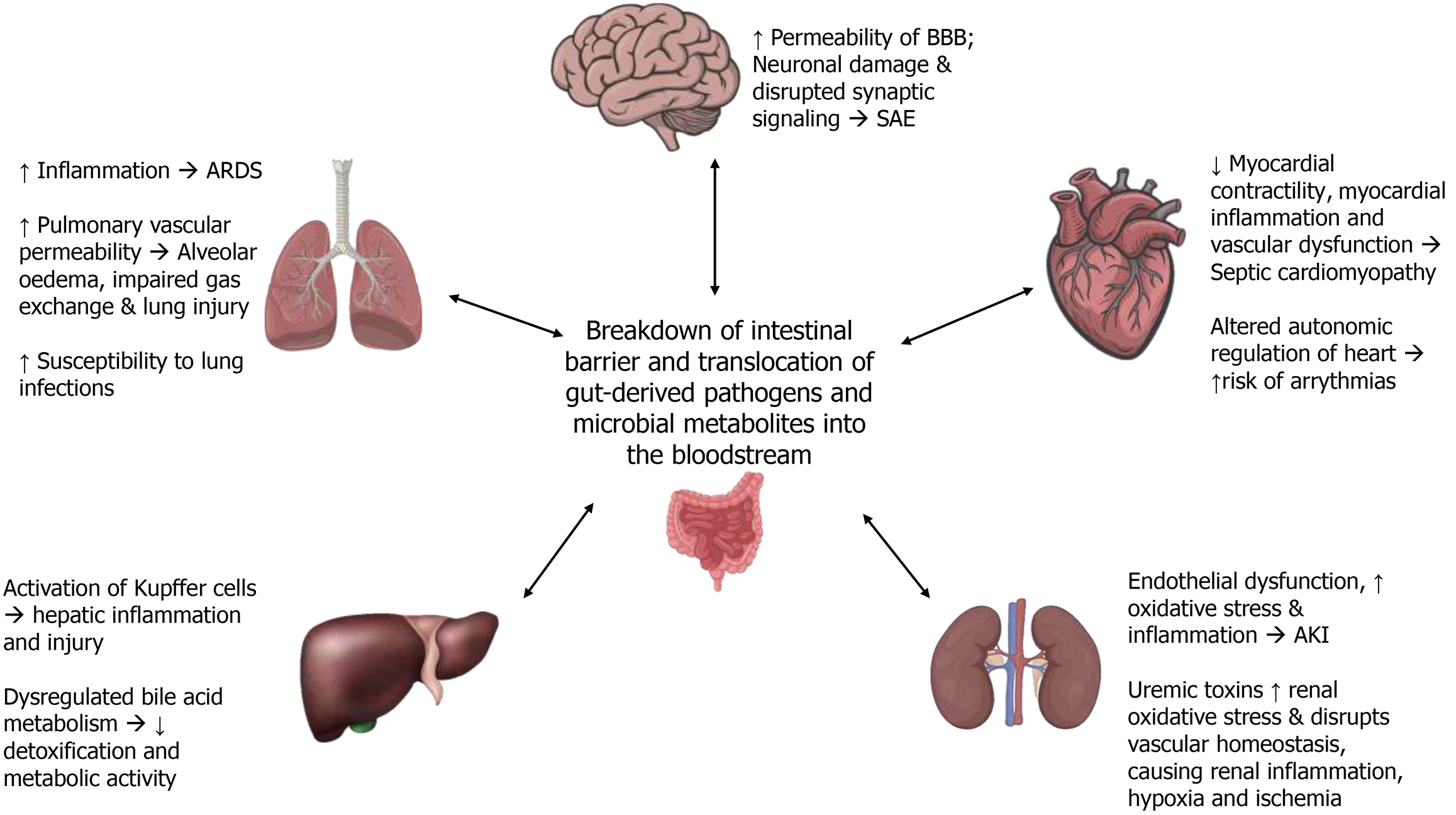
Figure 2 Impact of gut-organ axes in sepsis on multi-organ dysfunction affecting the lungs, brain, heart, kidneys, and liver.
ARDS: Acute respiratory distress syndrome; SAE: Sepsis-associated encephalopathy; AKI: Acute kidney injury.
- Citation: Wang JDJ, Suan E, Li SS, Shelat VG. Sepsis and the diverse organ-gastrointestinal tract axis. World J Crit Care Med 2025; 14(4): 105547
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v14/i4/105547.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v14.i4.105547