©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Crit Care Med. Dec 9, 2025; 14(4): 103708
Published online Dec 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i4.103708
Published online Dec 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i4.103708
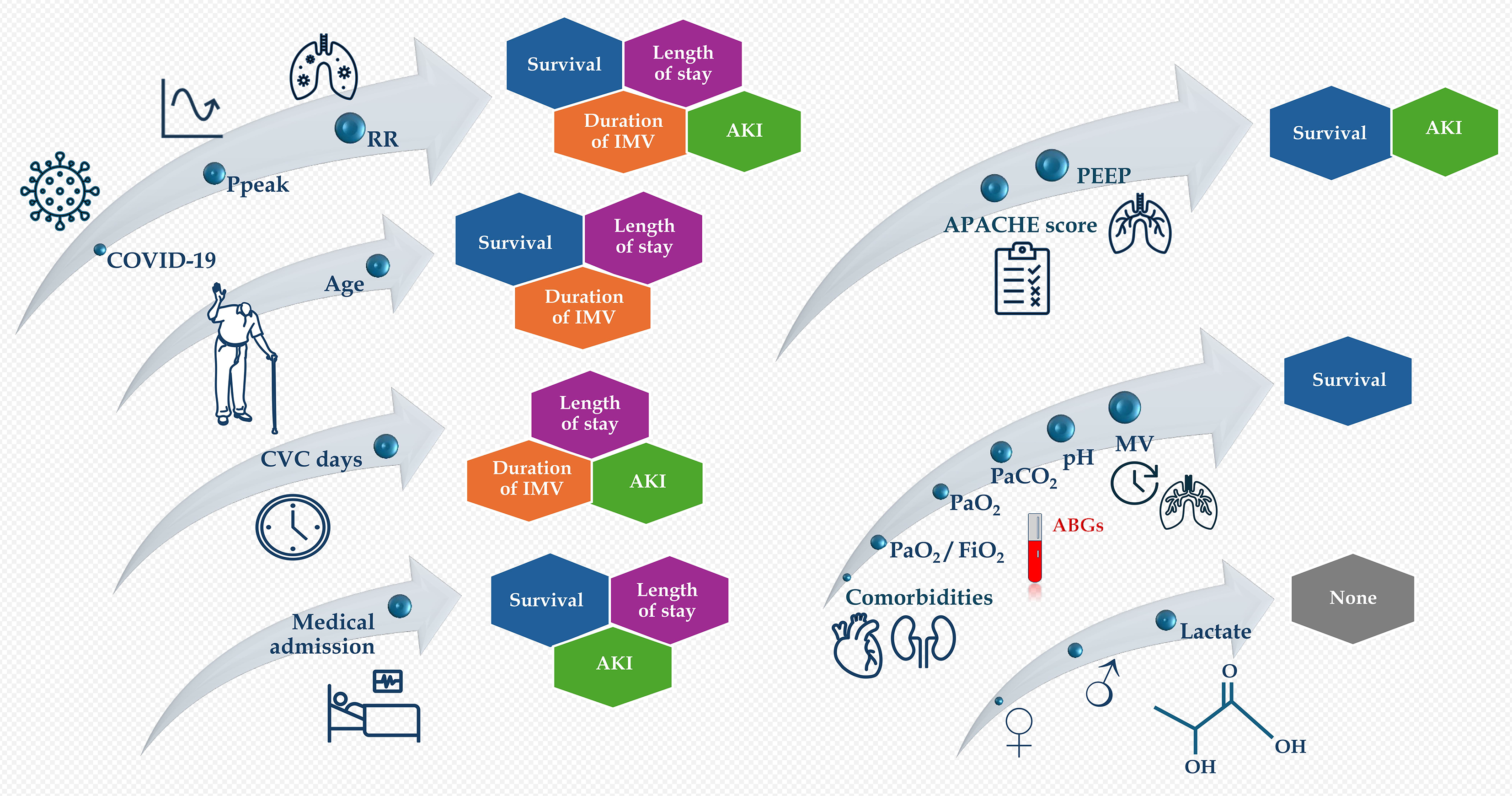
Figure 1 Review of all the correlations of epidemiological and respiratory/arterial blood gas data with the four available outcomes.
Only the presence of coronavirus disease 2019, peak airway pressure, and respiratory rate were correlated to all outcome measures, whereas age, central venous catheter days, and medical reason for admission were correlated to three of the outcome measures. Peak airway pressure and respiratory rate represent interesting targets for intervention to improve outcomes. COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; Ppeak: Peak airway pressure; RR: Respiratory rate; CVC: Central venous catheter; IMV: Invasive mechanical ventilation; AKI: Acute kidney injury; APACHE: Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation; PEEP: Positive end-expiratory pressure; PaO2: Arterial oxygen partial pressure; FiO2: Fraction of inspired oxygen; PaCO2: Arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure; MV: Minute ventilation; ABGs: Arterial blood gases.
- Citation: Papamichalis P, Oikonomou KG, Xanthoudaki M, Papathanasiou SK, Papadogoulas A, Skoura AL, Valsamaki A, Plageras D, Papamichalis M, Katsiafylloudis P, Papapostolou E, Mantzarlis K, Koukoulis A, Mavrommati G, Giannakos P, Chovas A. Length of stay, duration of mechanical ventilation, mortality, and acute kidney injury in acute respiratory failure requiring endotracheal intubation. World J Crit Care Med 2025; 14(4): 103708
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v14/i4/103708.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v14.i4.103708