©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Pediatr. Dec 9, 2025; 14(4): 107403
Published online Dec 9, 2025. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i4.107403
Published online Dec 9, 2025. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v14.i4.107403
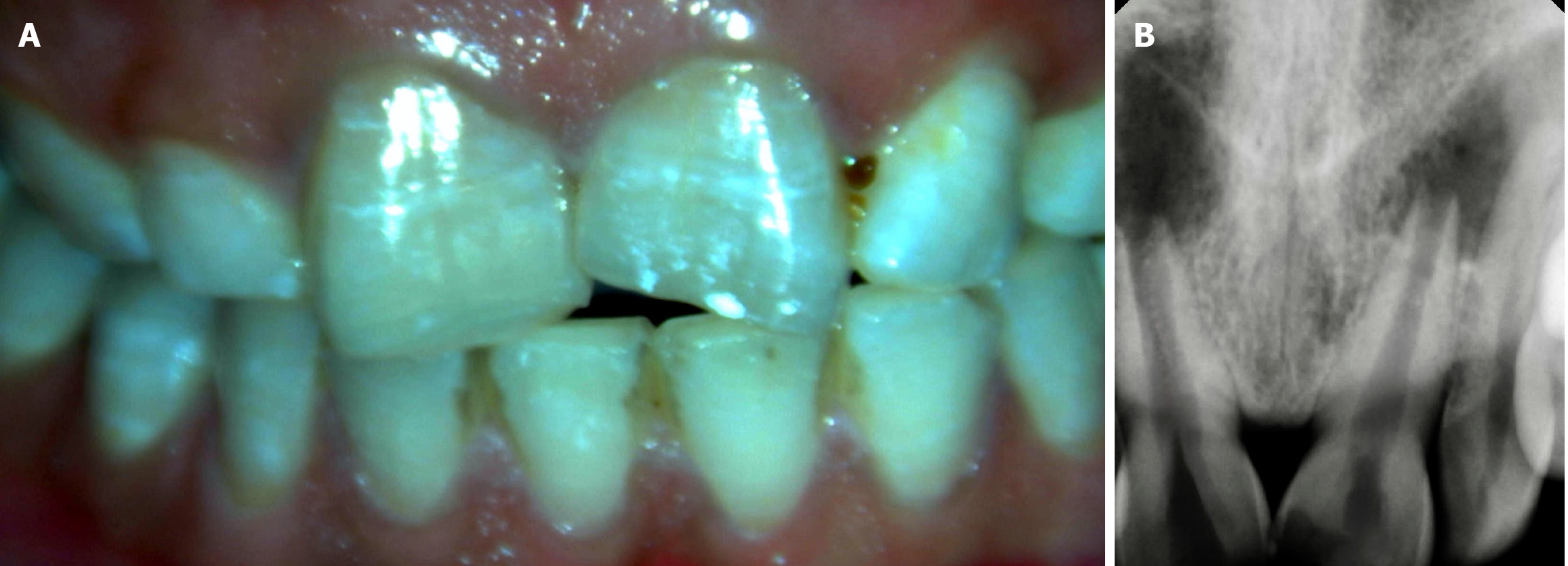
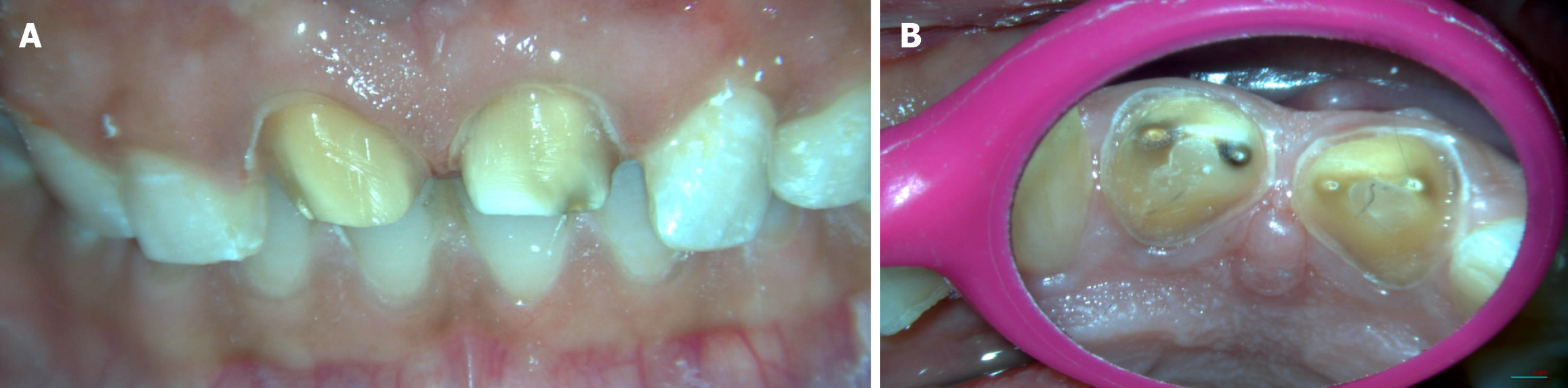
Figure 1 Clinical and radiographic examination.
A: Clinical image wrt 11 and 21; B: Radiograph wrt 11 and 21.
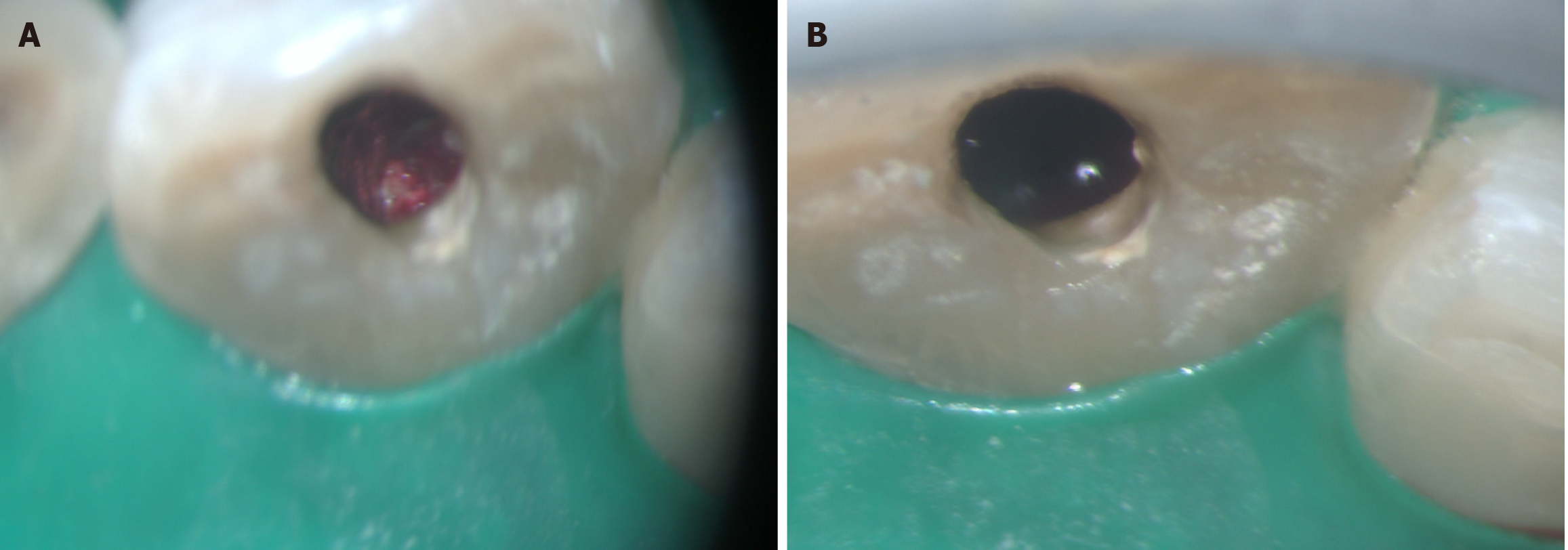
Figure 2 Shows open apex.
A: Wrt 11; B: Wrt 21.
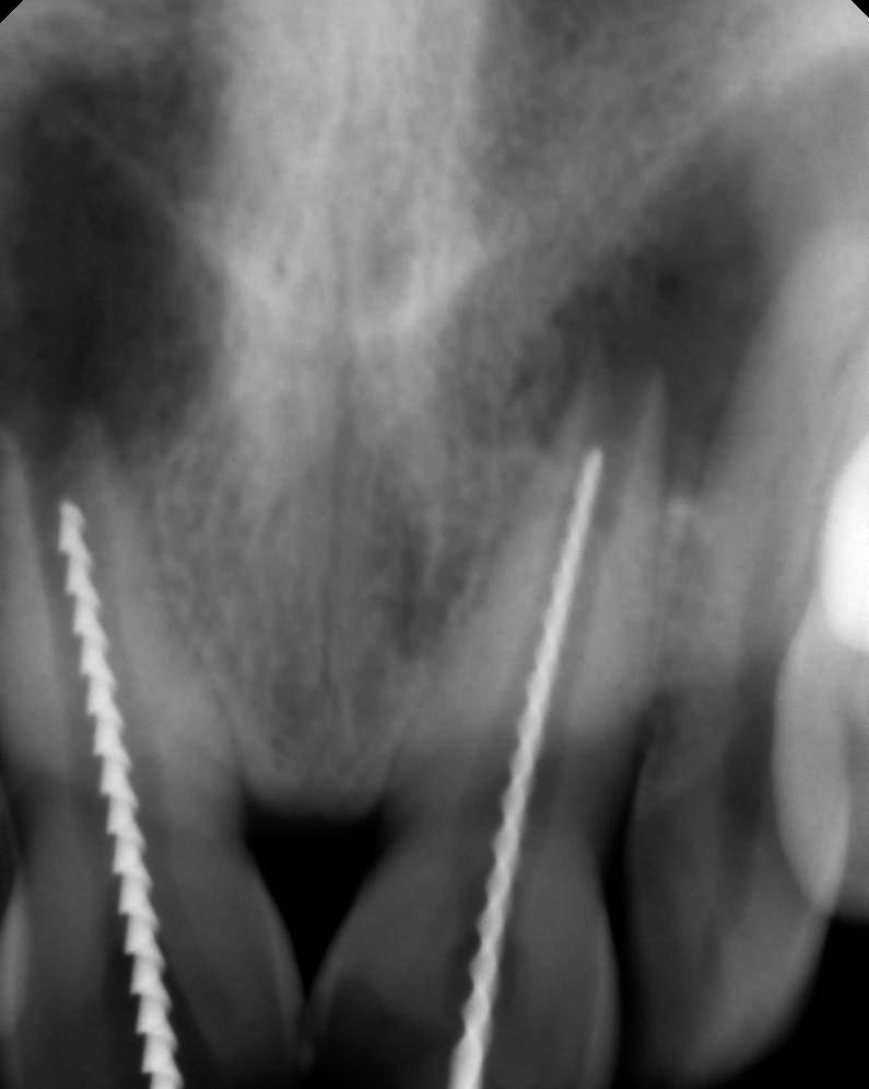
Figure 3 Shows the working length wrt 11 and 21.
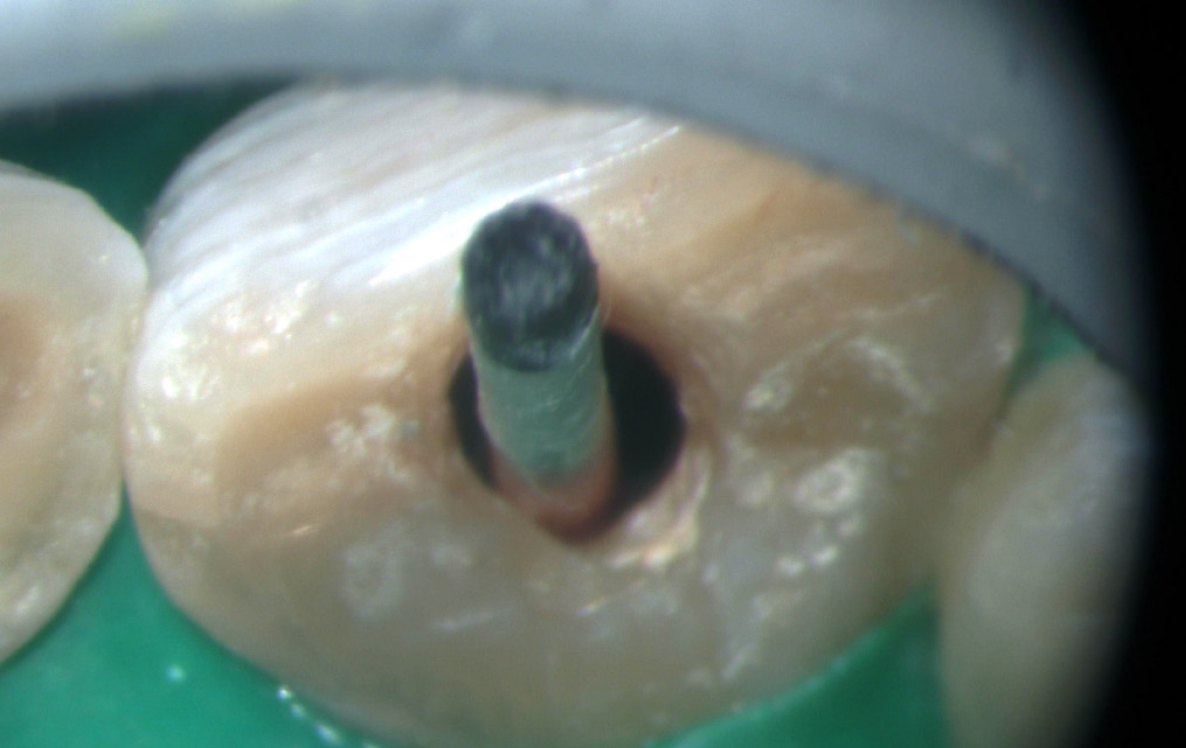
Figure 4 Shows the intracanal medicament (Metapex) wrt 11 and 21.
Figure 5 Shows the canal was dried with paper points.
Figure 6 Shows the resorbable collagen sponge in the canal.
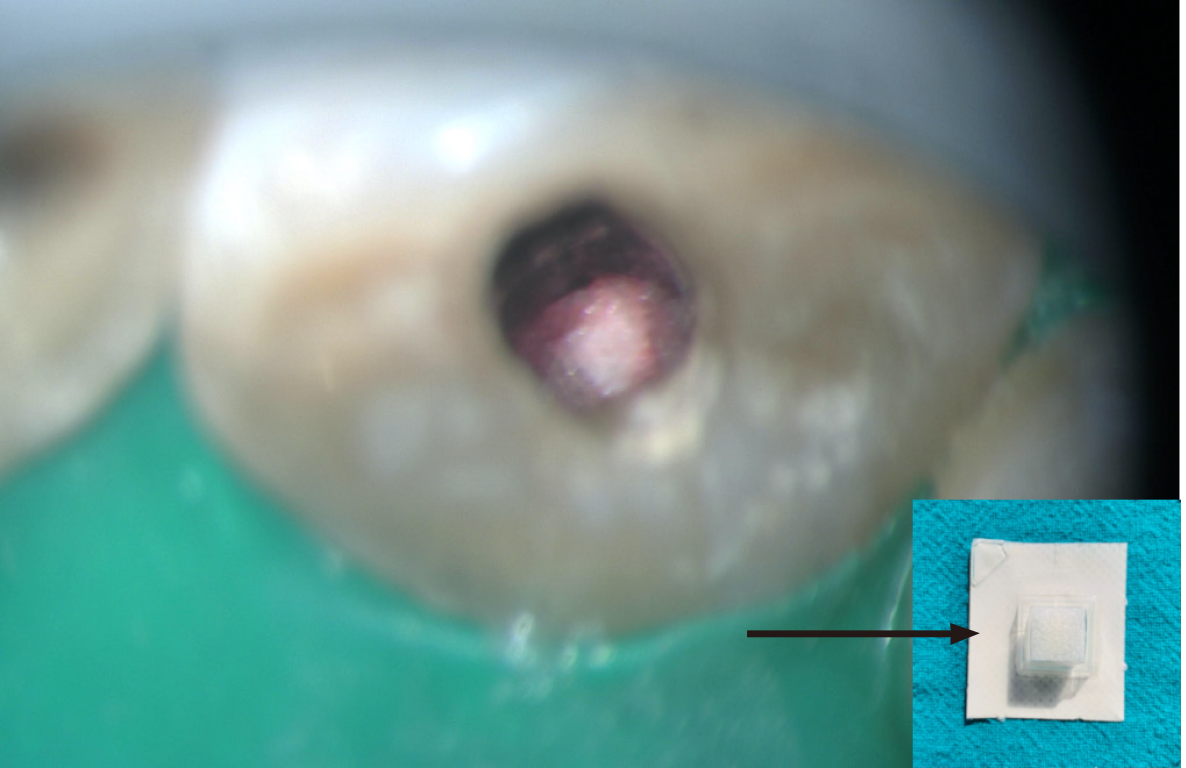
Figure 7 Shows the clinical image mineral trioxide aggregate plug wrt 11.
A: At 16 × magnification; B: At 20 × magnification.
Figure 8 Shows the radiograph of the mineral trioxide aggregate plug.
A: Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) wrt 11; B: MTA wrt 21.
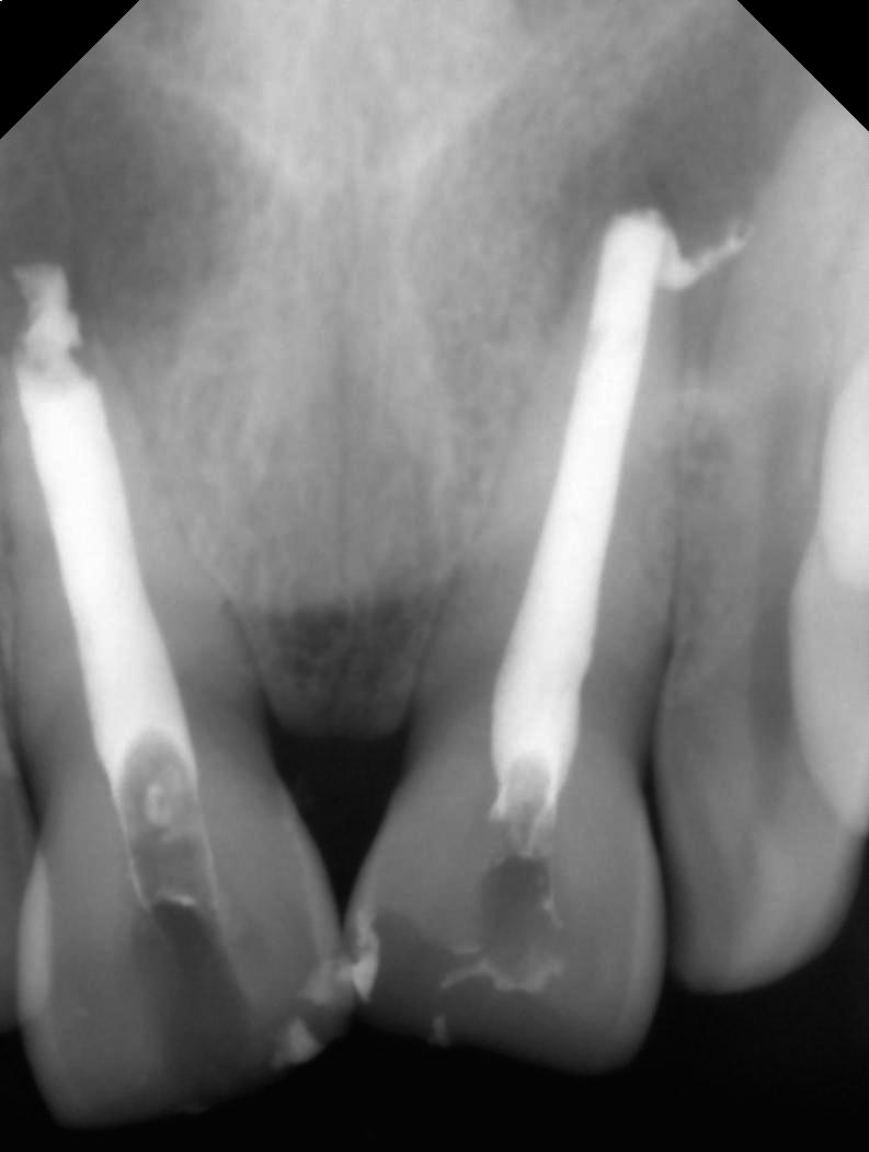
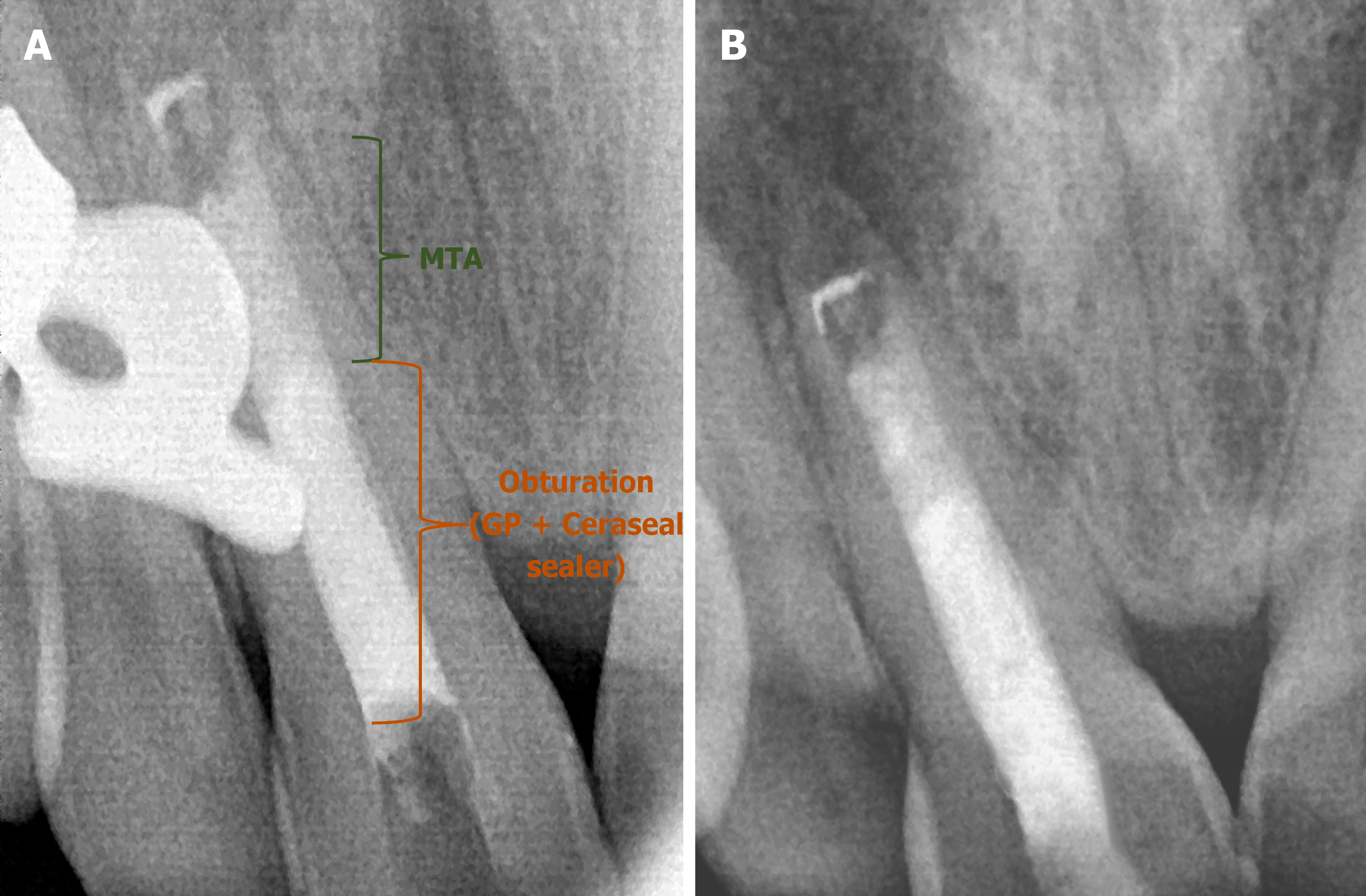
Figure 9 Shows the radiograph wrt 11.
A: Obturation; B: Post-endo composite. MTA: Mineral trioxide aggregate.
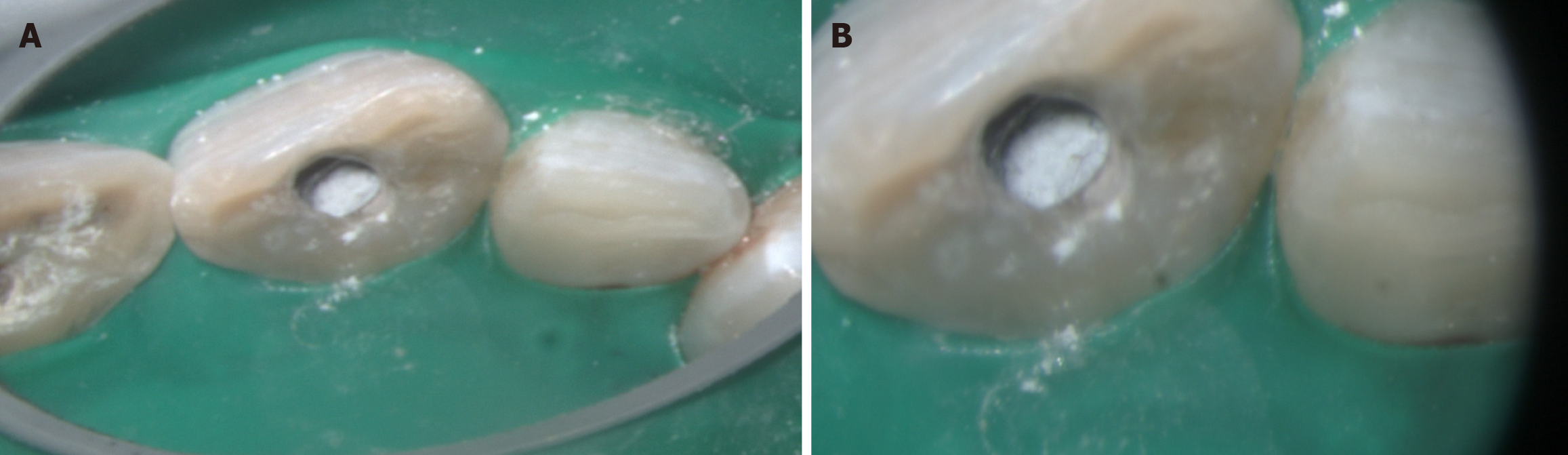
Figure 10 Shows the clinical image of crown preparation.
A: Buccal view; B: Occlusal view.
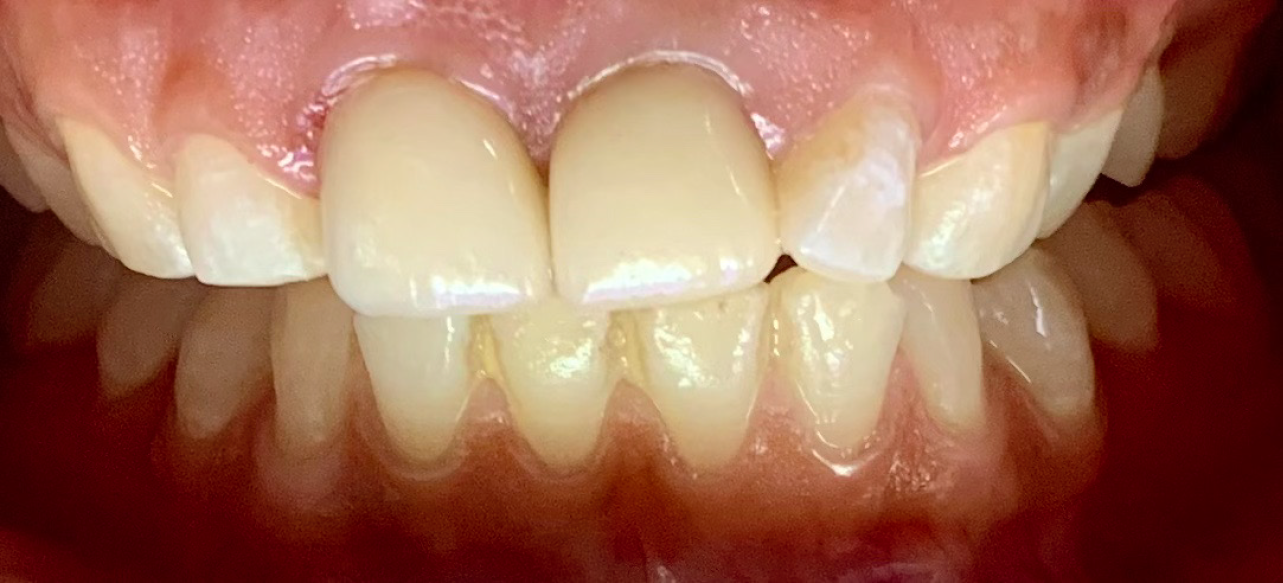
Figure 11 Shows the clinical image of Emax crowns wrt 11 and 21.
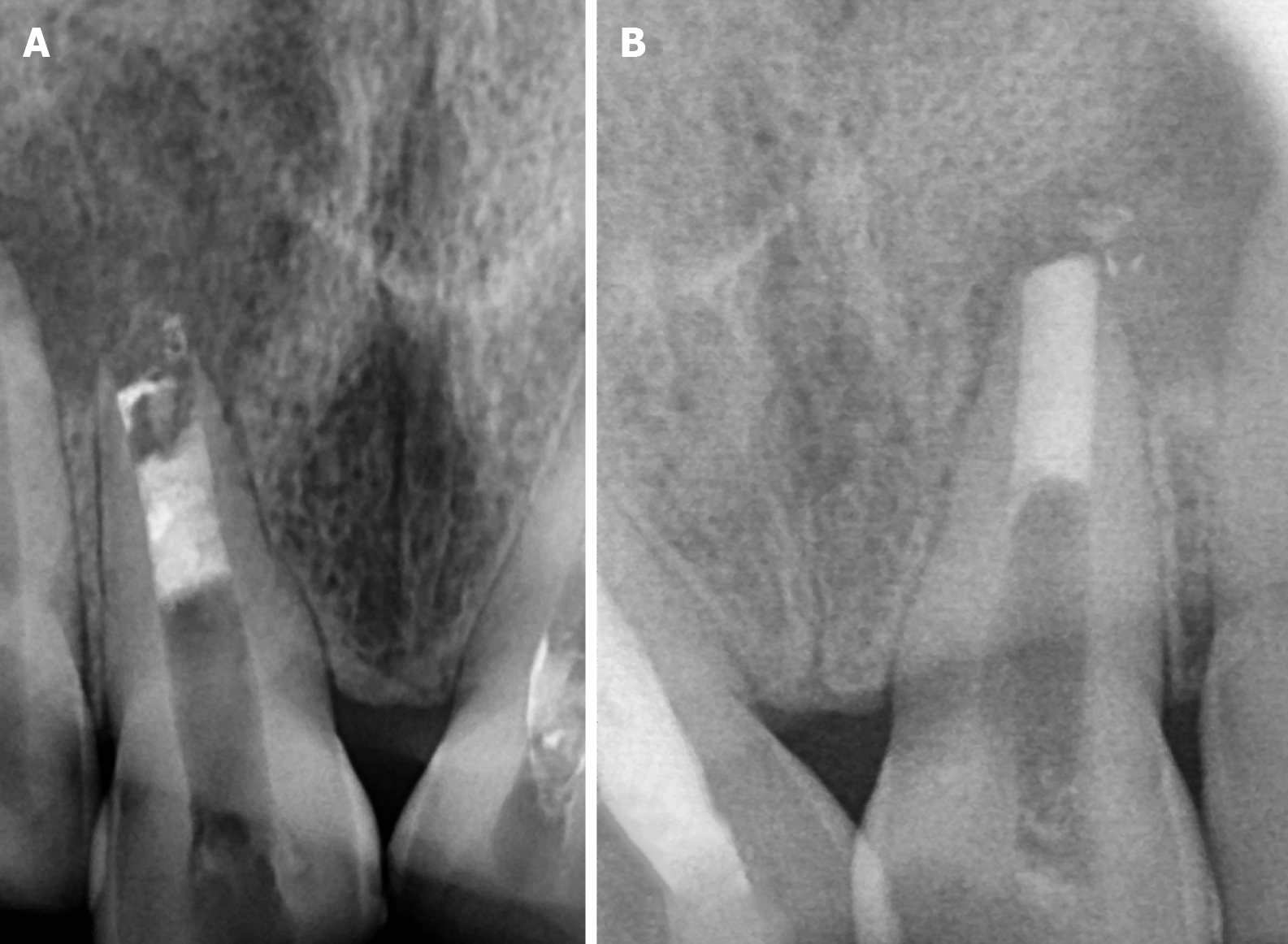
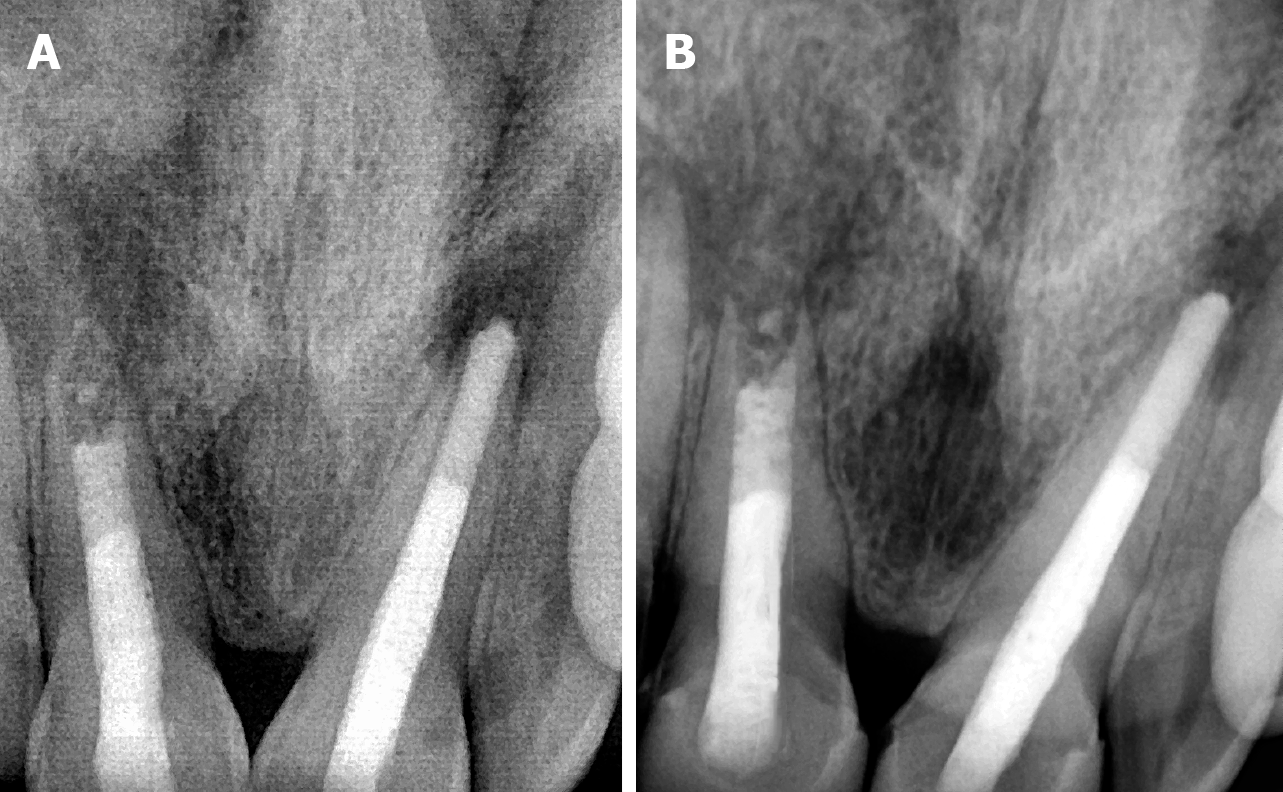
Figure 12 Shows the radiograph showing follow-up.
A: 3-month follow-up; B: 6-month follow-up.
- Citation: Chauhan S, Bhasin P, Chauhan R, Sood A, Lamba J, Yadav P. Microscopic precision with bioceramics apexification: A case report. World J Clin Pediatr 2025; 14(4): 107403
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2808/full/v14/i4/107403.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v14.i4.107403