©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Clin Oncol. Jun 10, 2017; 8(3): 203-213
Published online Jun 10, 2017. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v8.i3.203
Published online Jun 10, 2017. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v8.i3.203
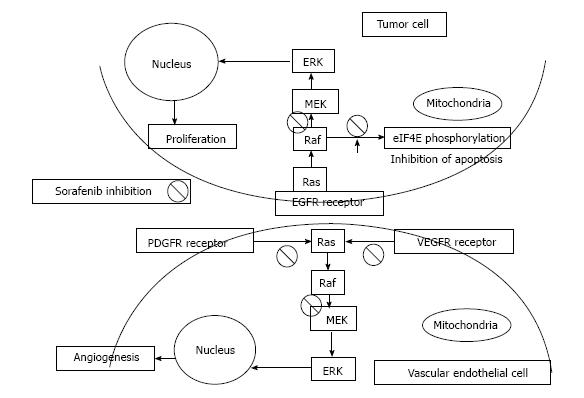
Figure 1 Sorafenib’s mechanism of action.
In tumor cells sorafenib blocks the Raf/MEK/ERK cascade and can lead to apoptosis through various mechanisms, such as inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E phosphorylation. In vascular endothelial cells, it inhibits receptor tyrosine kinases, such as VEGFR and PDGFR. PDGFR: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor; VEGFR: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
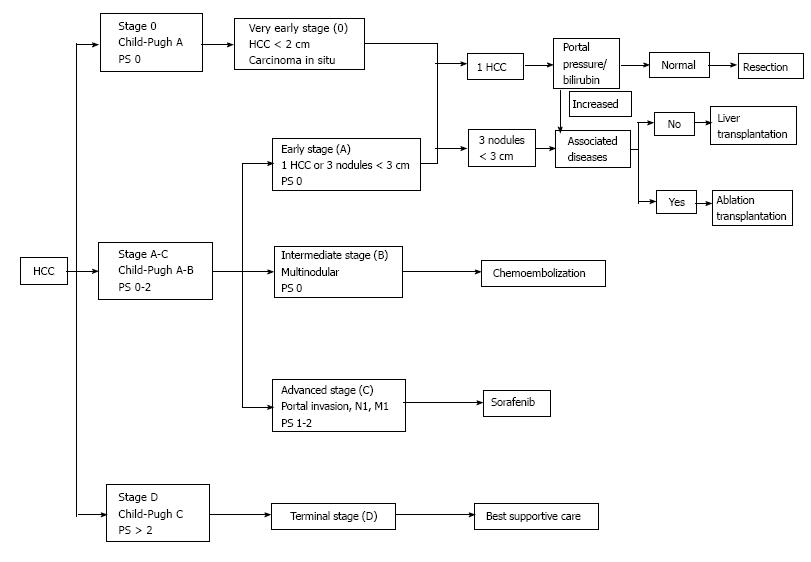
Figure 2 Barcelona clinic liver cancer staging system and treatment algorithm.
PS: Performance status; N: Nodules; M: Metastases; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Ziogas IA, Tsoulfas G. Evolving role of Sorafenib in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Clin Oncol 2017; 8(3): 203-213
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v8/i3/203.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v8.i3.203