©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Sep 24, 2025; 16(9): 111742
Published online Sep 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i9.111742
Published online Sep 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i9.111742
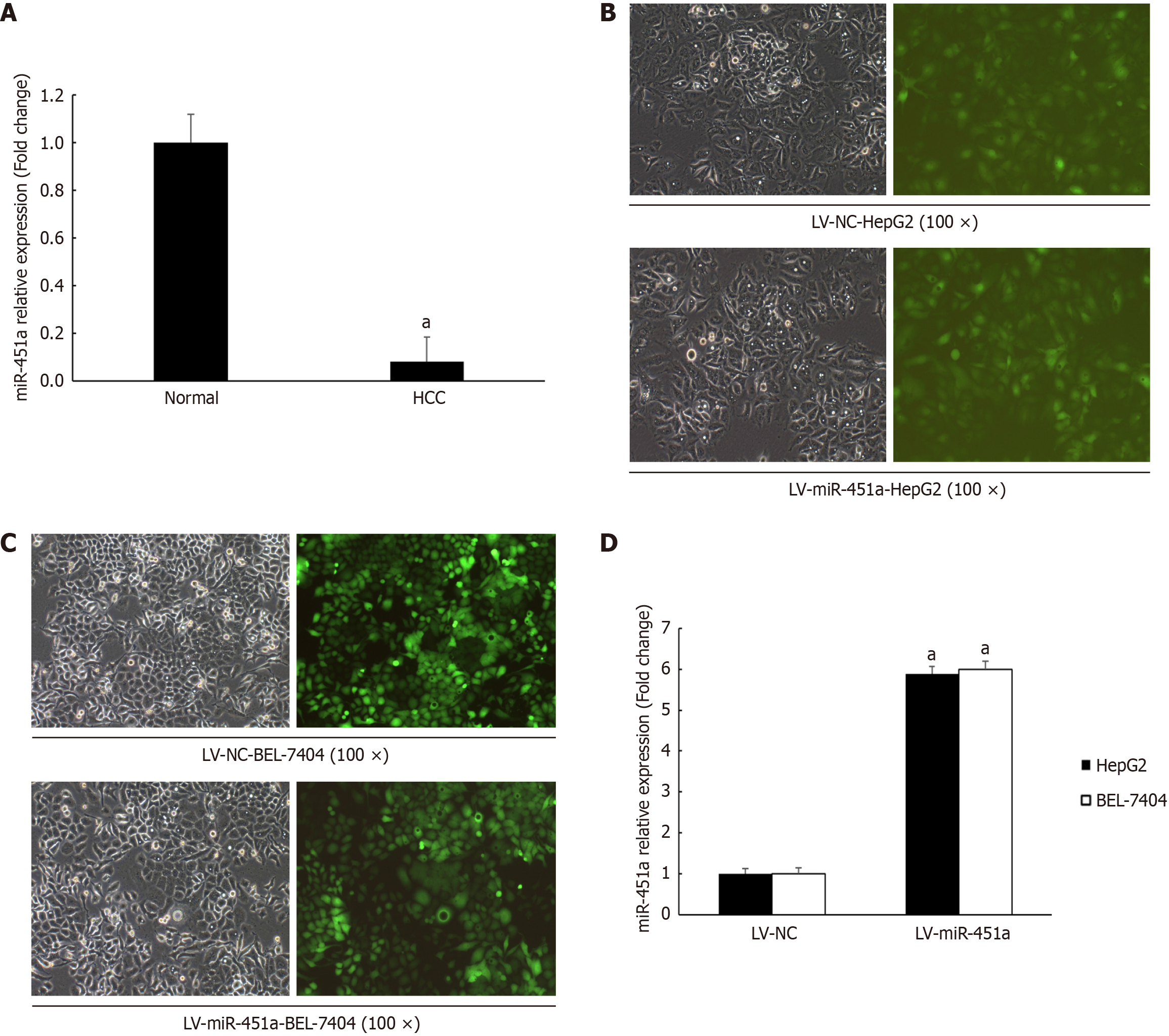
Figure 1 MiR-451a expression in liver cancer tissues and construction of miR-451a stable up-expression cell lines.
A: MiR-451a expression down-regulated in liver cancer tissues; B: Human hepatoblastoma G2 (HepG2) cells transfect with lentivirus-negative control (LV-NC) virus and lentivirus miR-451a (LV-miR-451a) virus, respectively (magnification 100 ×). Figures from left to right are HepG2 cells under bright field, green fluorescence produced by the expressed green fluorescence protein (GFP) fused with the GV369 vector; C: BEL-7404 cells transfect with LV-NC virus and LV-miR-451a virus, respectively (magnification 100 ×). Figures from left to right are BEL-7404 cells under bright field, green fluorescence produced by the expressed GFP fused with the GV369 vector; D: Quantitative real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction result showed that miR-451a significantly up-regulated in HepG2 and BEL-7404 cells after transfecting with LV-miR-451a virus compared with LV-NC group (aP < 0.05). HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HepG2: Human hepatoblastoma G2; LV-miR-451a: Lentivirus miR-451a; LV-NC: Lentivirus-negative control.
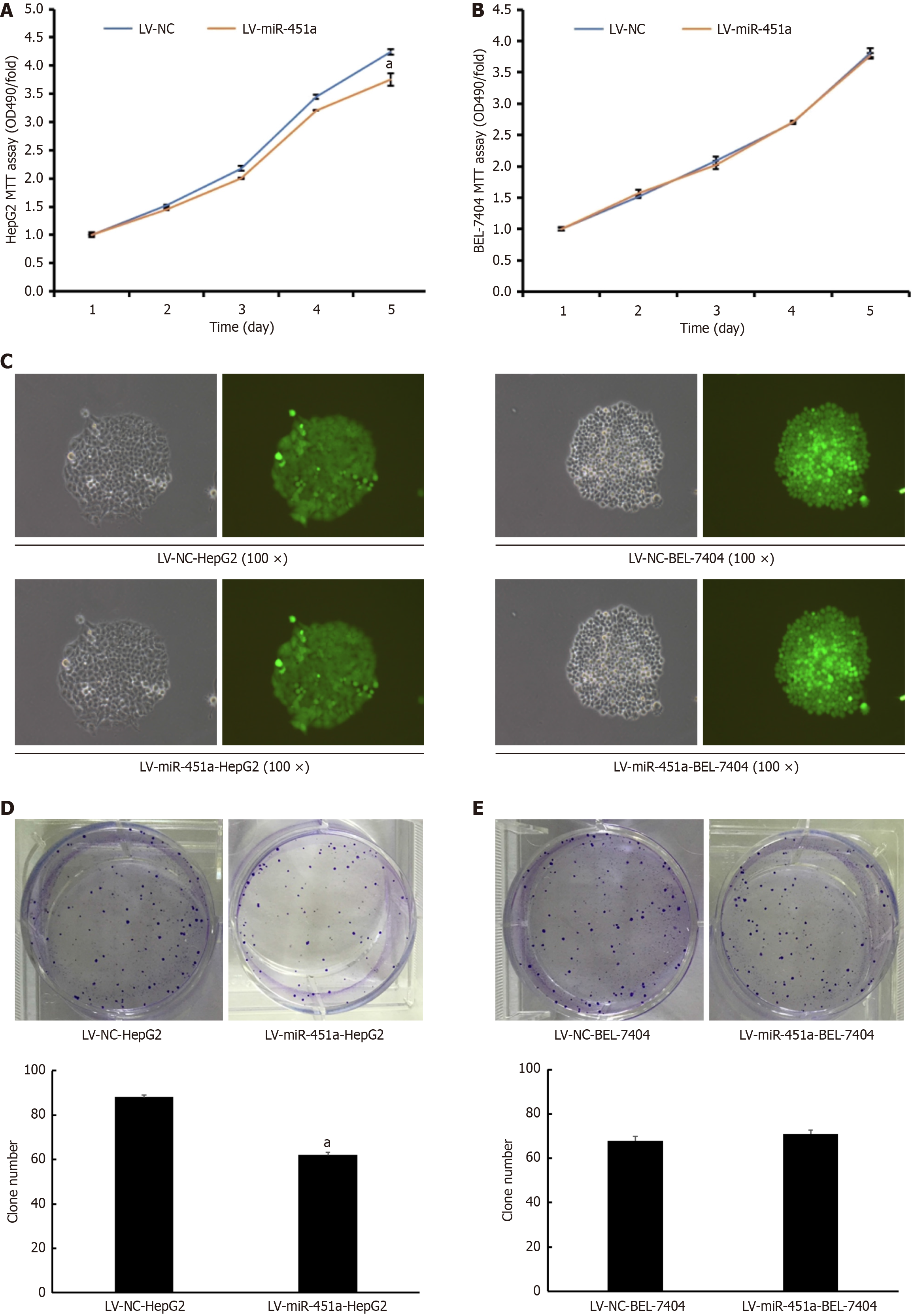
Figure 2 Effects of MiR-451a overexpression on human hepatoblastoma G2 cells and BEL-7404 cells.
A and B: MiR-451a overexpression decreased human hepatoblastoma G2 (HepG2) cell growth but not BEL-7404 cell; C: Green fluorescence indicated the transfection efficiency of HepG2 and BEL-7404 cells in colony formation assay; D and E: Colony formation assay was performed to determine the growth of HepG2 and BEL-7404 cells transfected with lentivirus-negative control or lentivirus miR-451a, respectively (aP < 0.05). HepG2: Human hepatoblastoma G2; LV-miR-451a: Lentivirus miR-451a; LV-NC: Lentivirus-negative control; MTT: Methylthiazolyldiphenyl-tetrazolium.
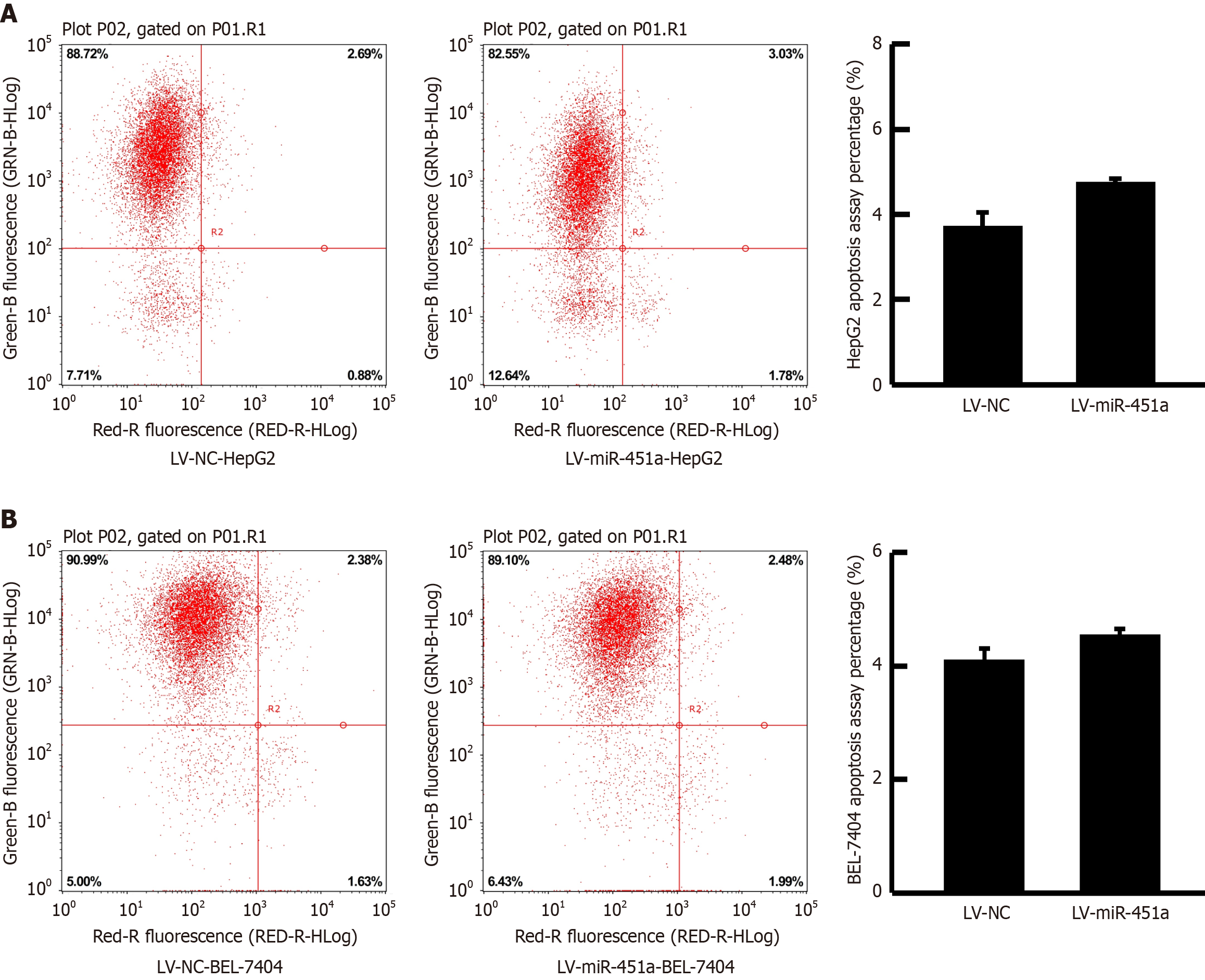
Figure 3 Effects of miR-451a overexpression on apoptosis.
A: Human hepatoblastoma G2 (HepG2); B: BEL-7404. MiR-451a overexpression have no influence in HepG2 and BEL-7404 cell apoptosis. HepG2: Human hepatoblastoma G2; LV-miR-451a: Lentivirus miR-451a; LV-NC: Lentivirus-negative control.
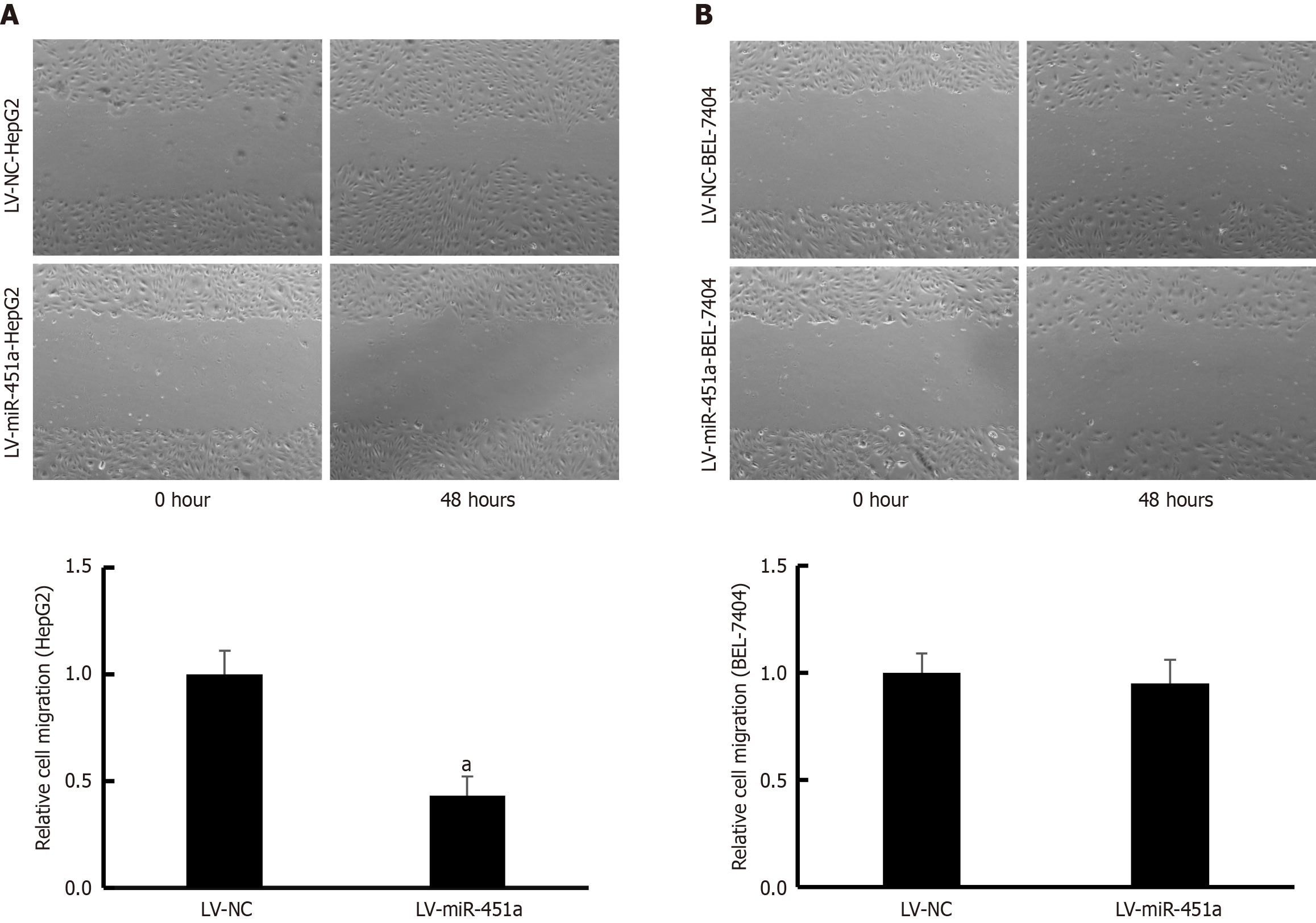
Figure 4 Effect of miR-451a overexpression on cell migration.
A: Human hepatoblastoma G2 (HepG2); B: BEL-7404. MiR-451a overexpression inhibited HepG2 cell migration but not BEL-7404 cell (aP < 0.05). HepG2: Human hepatoblastoma G2; LV-miR-451a: Lentivirus miR-451a; LV-NC: Lentivirus-negative control.
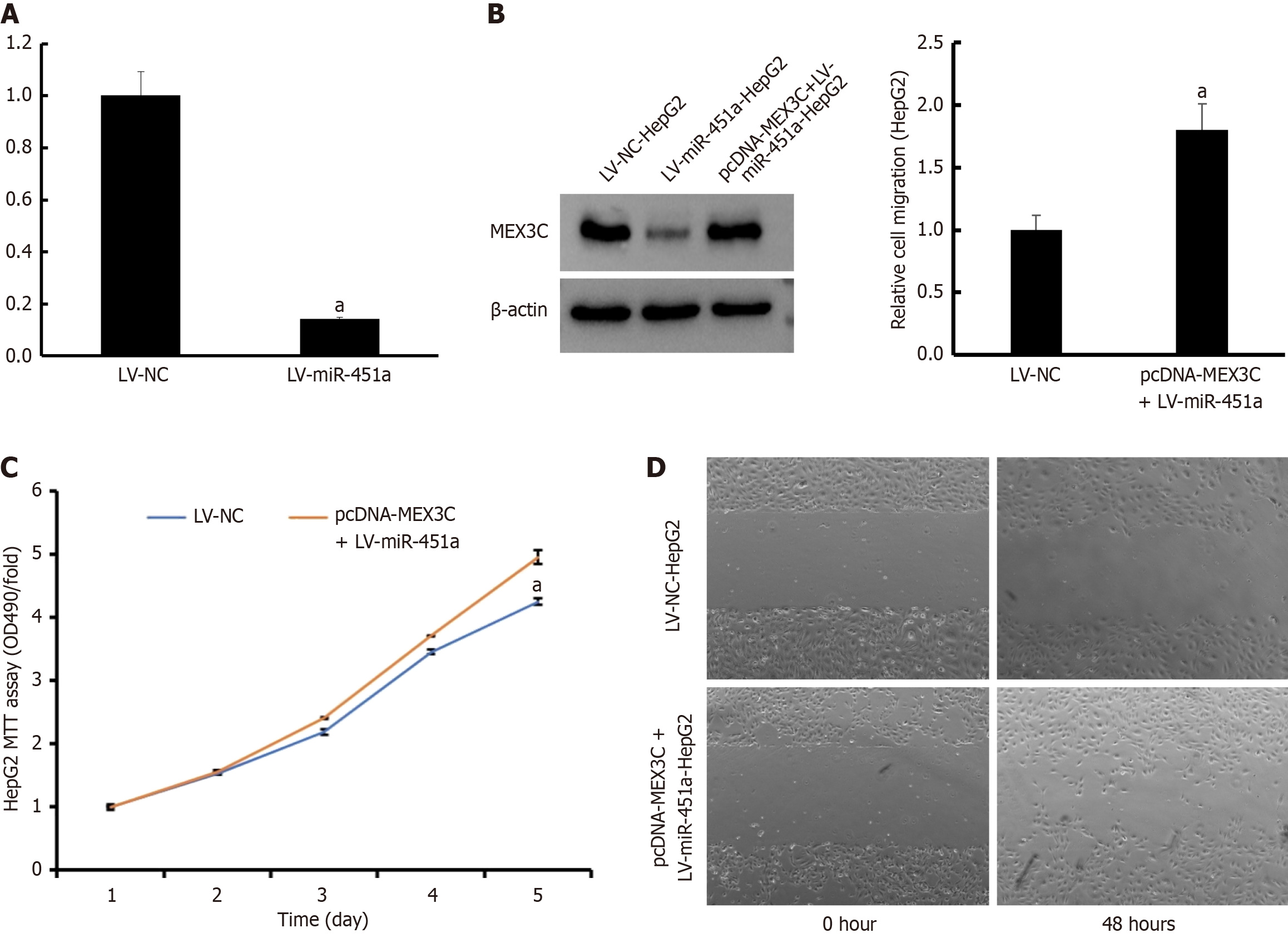
Figure 5 Mex-3 RNA binding family member C overexpression rescued the effects of miR-451a in human hepatoblastoma G2 cell.
A: Re
- Citation: Liu DZ, Wang L, Yang SK, Zhao ZJ, Cui YY, Zhao XK, Zhang F, Guan QH, Zhou L. MiR-451a targets mex-3 RNA binding family member C to regulate human hepatoblastoma G2 cell growth and metastasis. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(9): 111742
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i9/111742.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i9.111742