©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Jun 24, 2025; 16(6): 104299
Published online Jun 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i6.104299
Published online Jun 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i6.104299
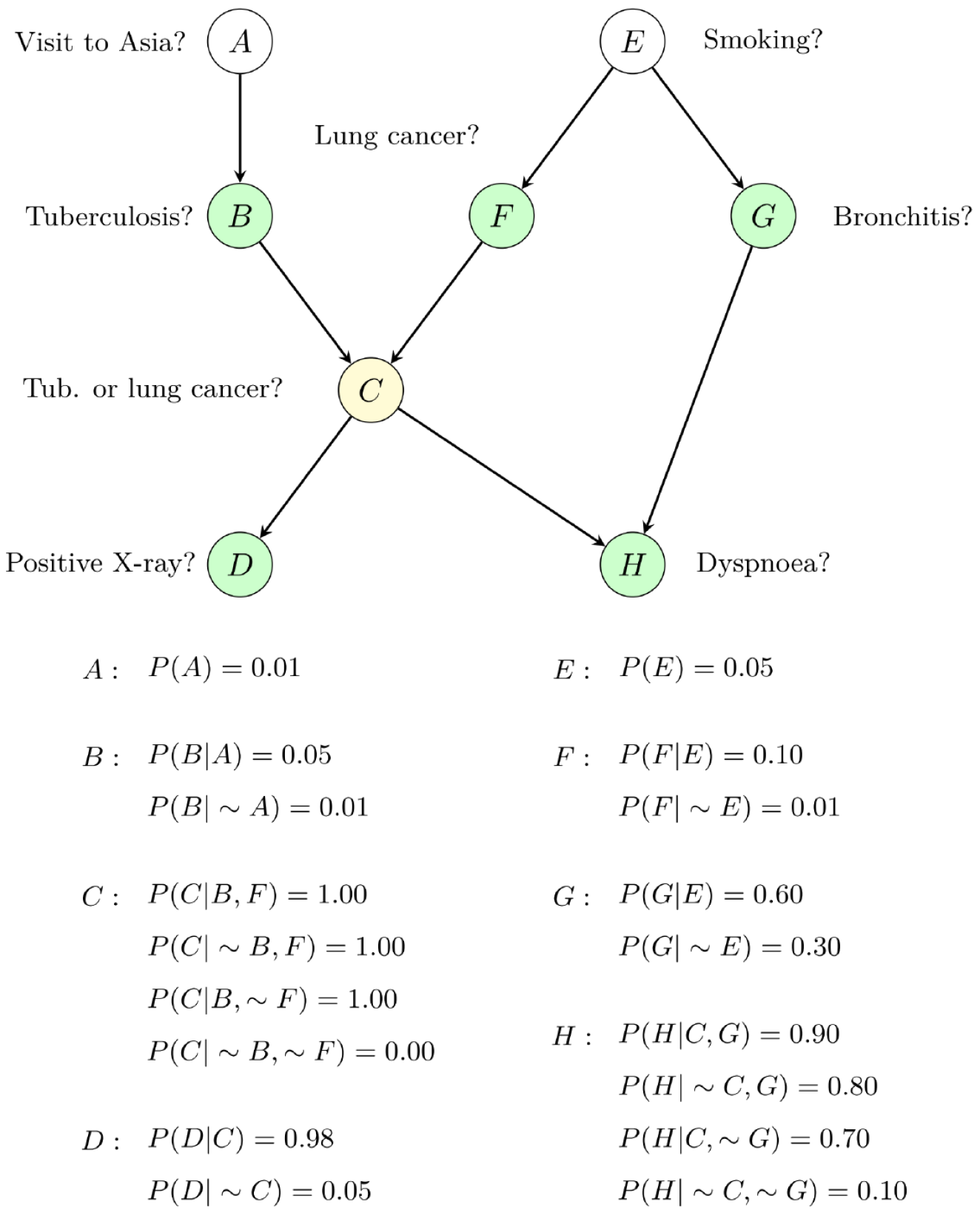
Figure 1 A typical structure of a Bayesian network.
It consists of a directed acyclic graph and the corresponding conditional probability tables. If node C is selected as the target node (yellow node), then the green nodes (B, F, D, H, G) form the Markov blanket of node C, where B and F are parent nodes, D and H are child nodes, and G is a spouse node.
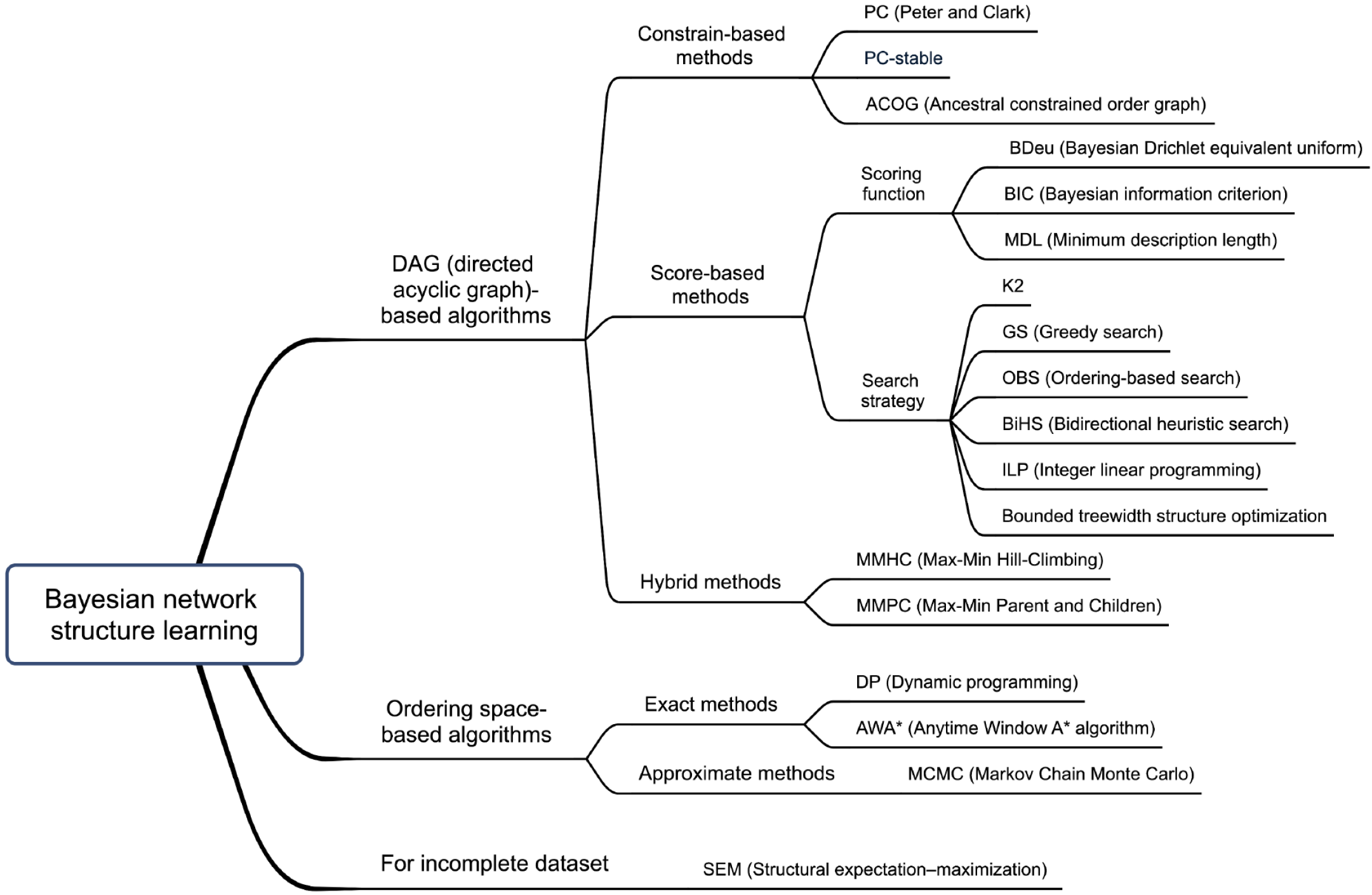
Figure 2 Classification of algorithms related to Bayesian network structure learning.
DAG: Directed acyclic graph; PC: Peter and Clark; ACOG: Ancestral constrained order graph; BDeu: Bayesian Drichlet equivalent uniform; BIC: Bayesian information criterion; MDL: Minimum description length; GS: Greedy search; OBS: Ordering-based search; BiHS: Bidirectional heuristic search; ILP: Integer linear programming; MMHC: Max-Min Hill-Climbing; MMPC: Max-Min Parent and Children; DP: Dynamic programming; AWA*: Anytime Window A* algorithm; MCMC: Markov Chain Monte Carlo; SEM: Structural expectation-maximization.
- Citation: Zhang MN, Xue MJ, Zhou BZ, Xu J, Sun HK, Wang JH, Wang YY. Comprehensive review of Bayesian network applications in gastrointestinal cancers. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(6): 104299
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i6/104299.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i6.104299