©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Dec 24, 2025; 16(12): 111175
Published online Dec 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i12.111175
Published online Dec 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i12.111175
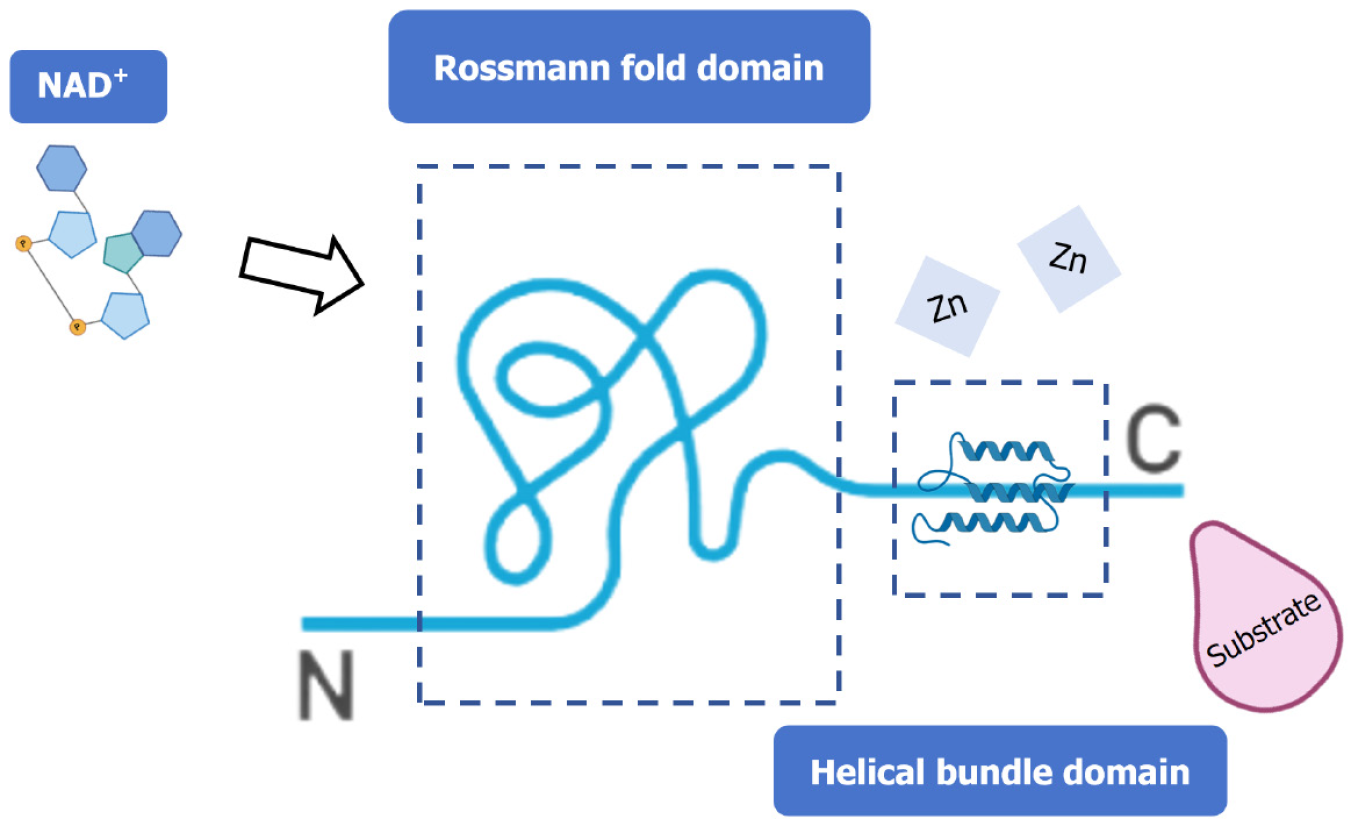
Figure 1 Structure of sirtuin 3.
The conserved enzymatic core of sirtuin 3 comprises a Rossmann fold domain, a catalytic zinc finger motif, and a substrate-binding region.
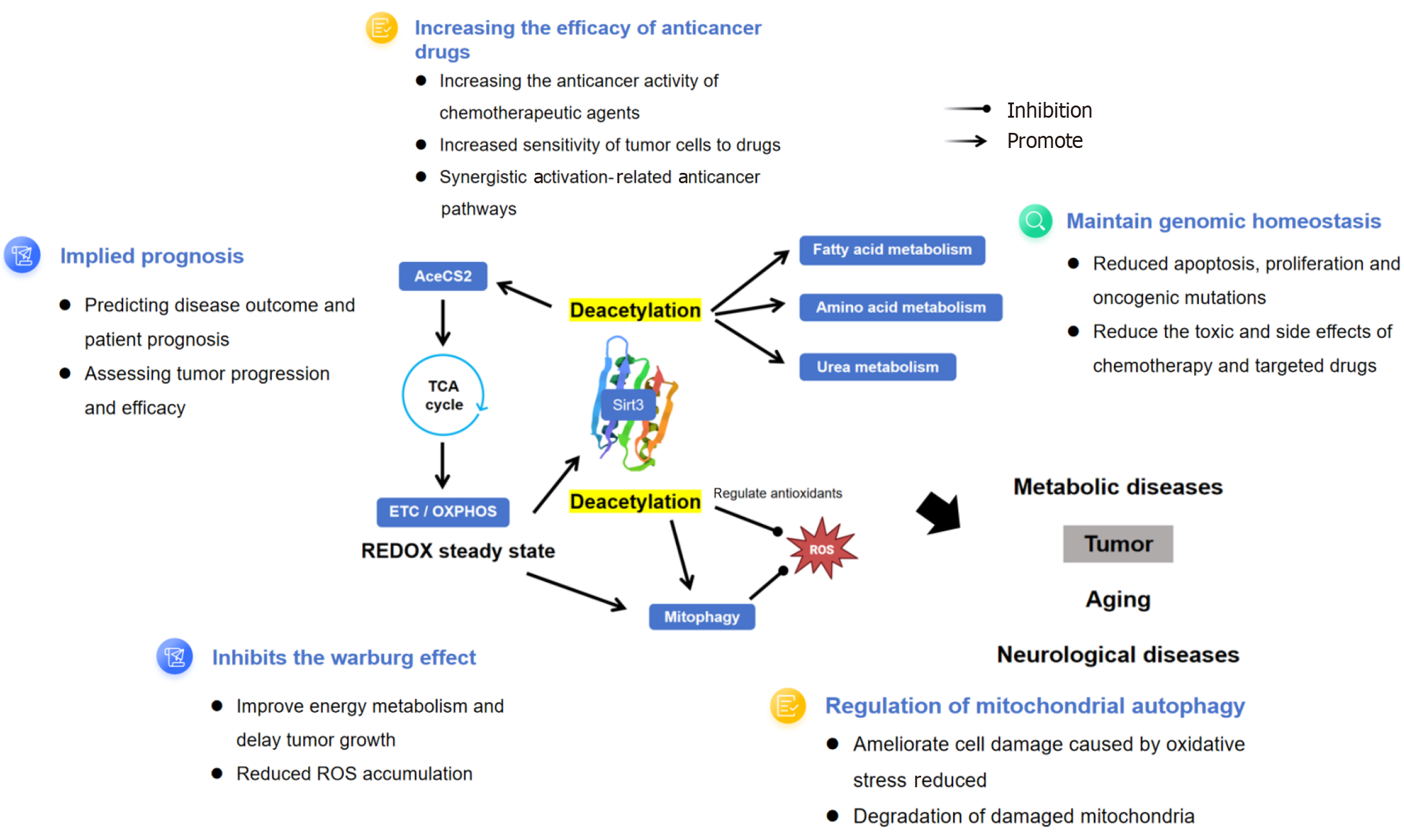
Figure 2 Function of sirtuin 3 and its potential application in the prevention and treatment of cancer.
AceCS2: Acetyl-CoA synthetase 2; ETC: Electron transport chain; REDOX: Oxidation/reduction; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid.
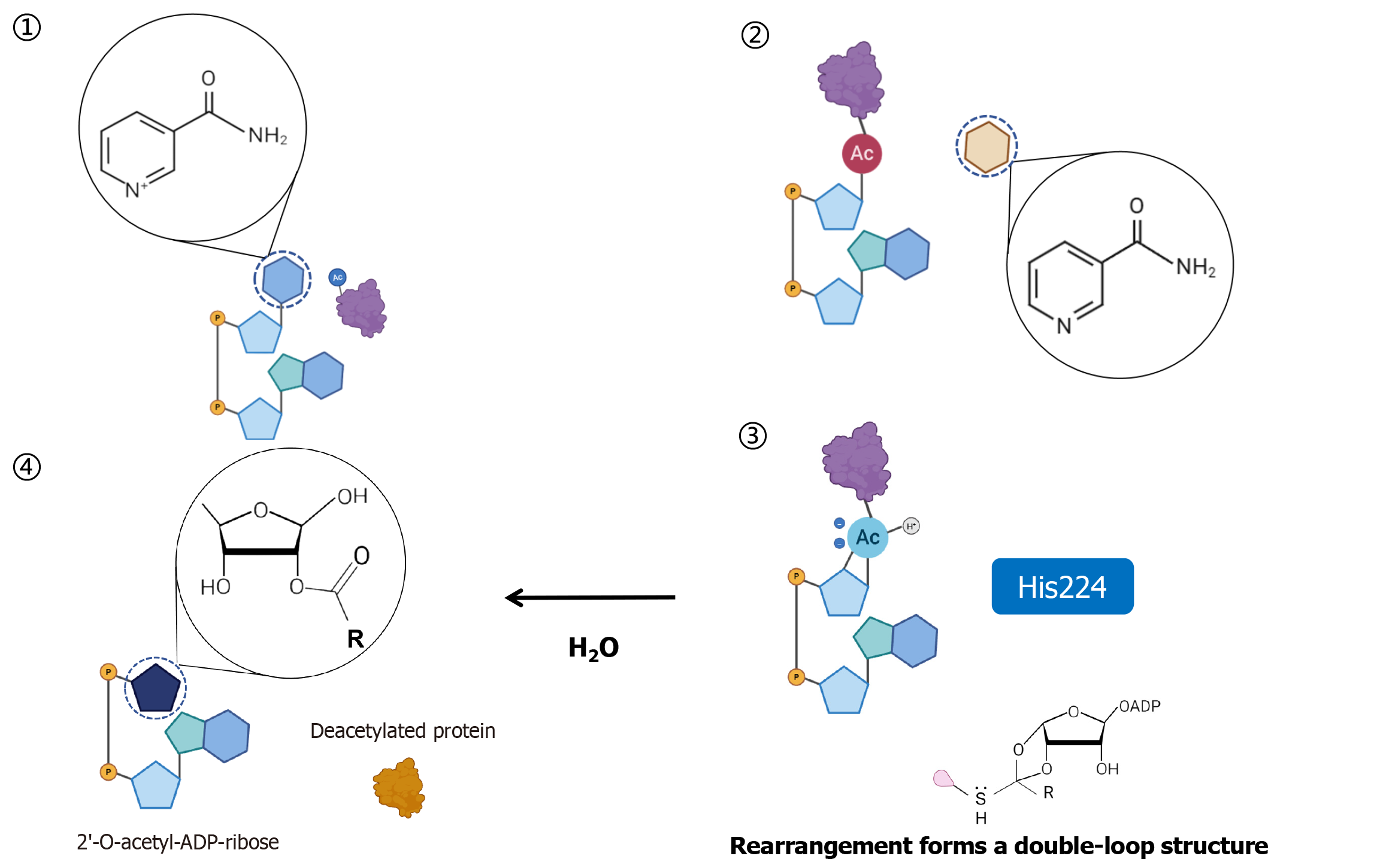
Figure 3 Sirtuin 3 modification deacetylates its substrate in an NAD+-dependent manner.
His224: Histidine residue.
Figure 4 Conventional negative and positive regulatory mechanism of sirtuin 3.
A: Conventional negative regulatory mechanism of sirtuin 3 (SIRT3). In the hypoxic microenvironment, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) selectively activates glycolysis-related enzymes and inhibits mitochondrial SIRT3 to block the tricarboxylic acid cycle – a hallmark of the classic "Warburg effect". This process drives local reactive oxygen species accumulation and amplifies inflammatory cascades, worsening hypoxia and creating a negative feedback loop targeting SIRT3. Notably, activating SIRT3 can suppress hypoxia-induced HIF-1α overexpression through specific mechanisms, thereby disrupting the sustained activation of this closed negative regulatory loop; B: Conventional positive regulatory mechanism of SIRT3. SIRT3-AMP-activated protein kinase-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α-SIRT3 positive feedback loop represents a key pathway for SIRT3's positive regulation. AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; FoxO3a: Forkhead box protein O3a; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SIRT3: Sirtuin 3; SUMO: Small ubiquitin-related modifier; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid; PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α.
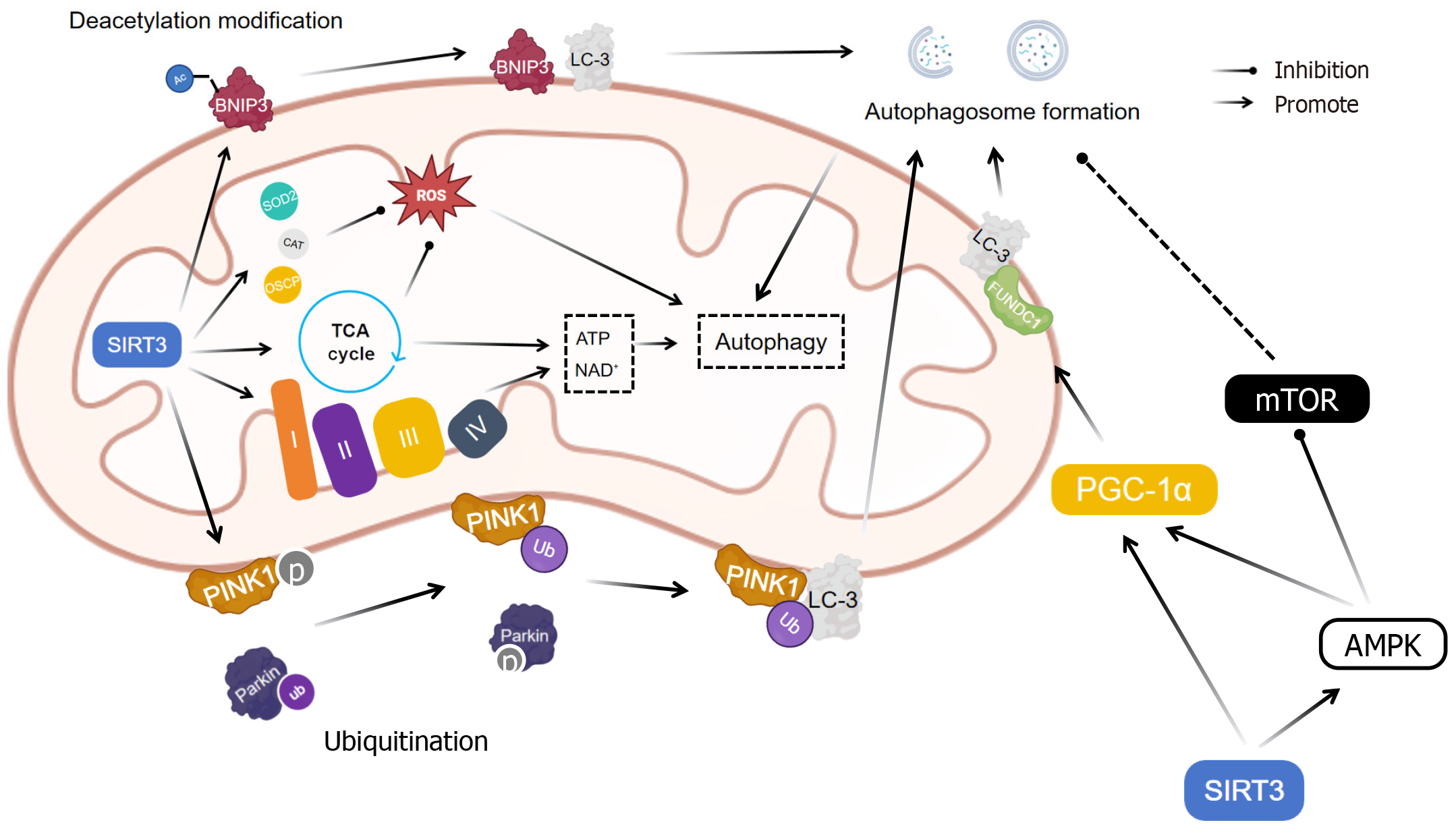
Figure 5 Mechanisms of sirtuin 3 regulation of mitophagy.
AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; BNIP3: BCL2-interacting protein 3; CAT: Catalase; LC-3: Light chain 3; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; OSCP: Oligomycin sensitivity conferral protein; PINK1: Phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced putative kinase 1; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SIRT3: Sirtuin 3; SOD2: Superoxide dismutase 2; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid; PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α.
- Citation: Zhao HY, Yu CY, Ye XT, Qian ST, Huang Y, Liu QS. Relevance and application of sirtuin 3-activated mitophagy in gastric cancer treatment. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(12): 111175
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i12/111175.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i12.111175