©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. Nov 24, 2025; 16(11): 110453
Published online Nov 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i11.110453
Published online Nov 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i11.110453
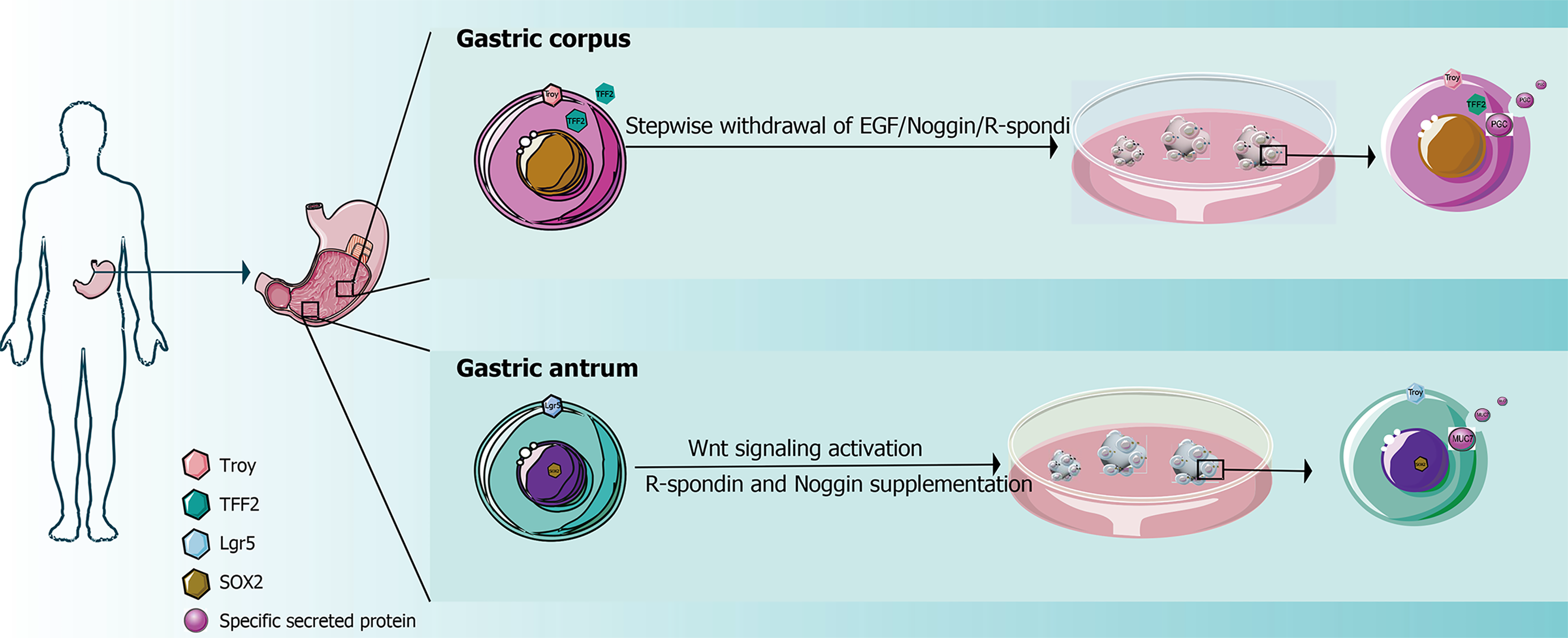
Figure 1 Region-specific modeling using gastric organoids.
TFF2: Trefoil factor 2; Lgr5: Leucine-rich-repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5; SoX2: SRY-box transcription factor 2; EGF: Epidermal growth factor.
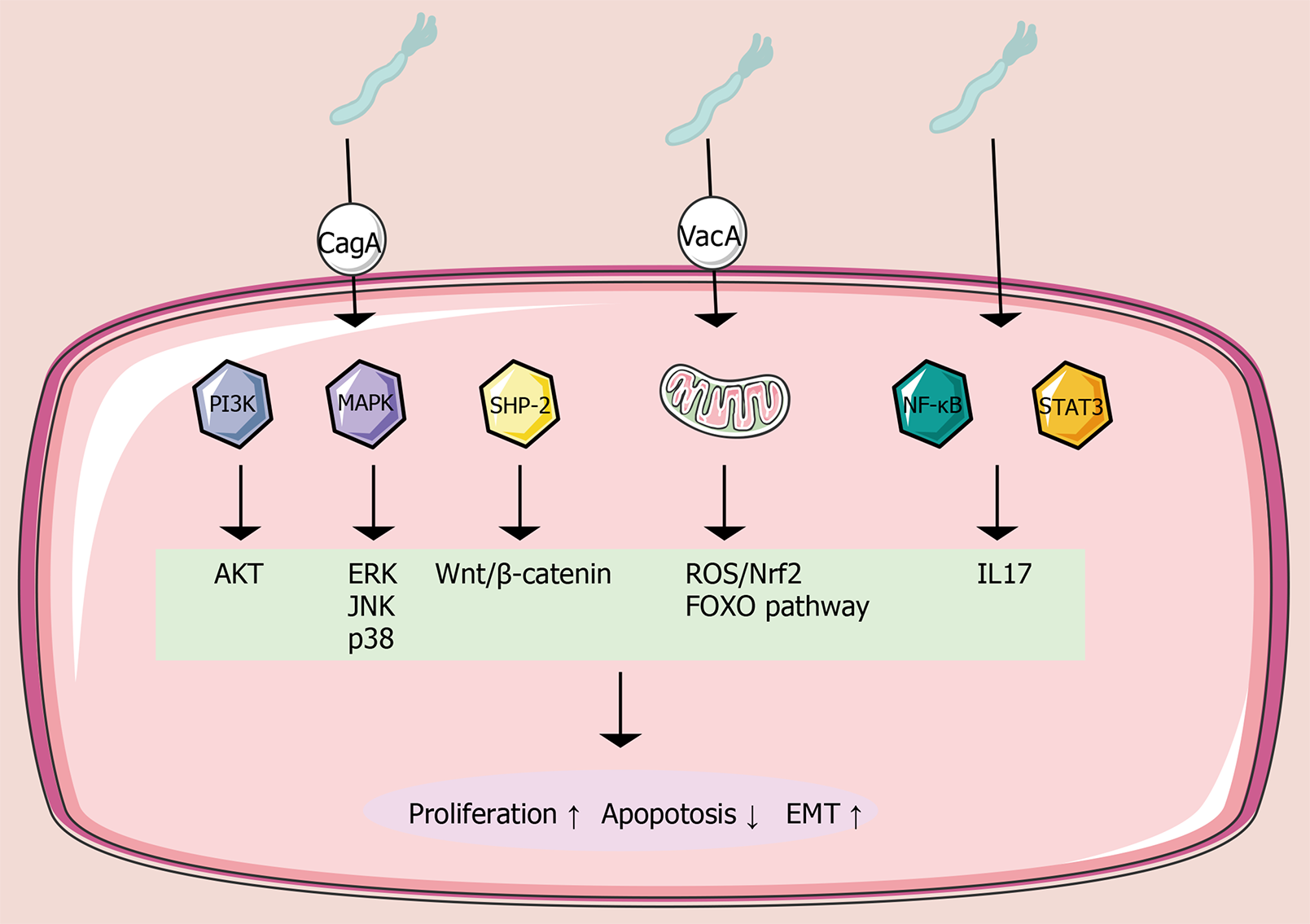
Figure 2 Role of Helicobacter pylori in inflammation-cancer transition.
P13K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; CagA: Cytotoxin-associated protein A; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; VacA: Vacuolating cytotoxin A; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2; FOXO: Forkhead box O; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; IL: Interleukin; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
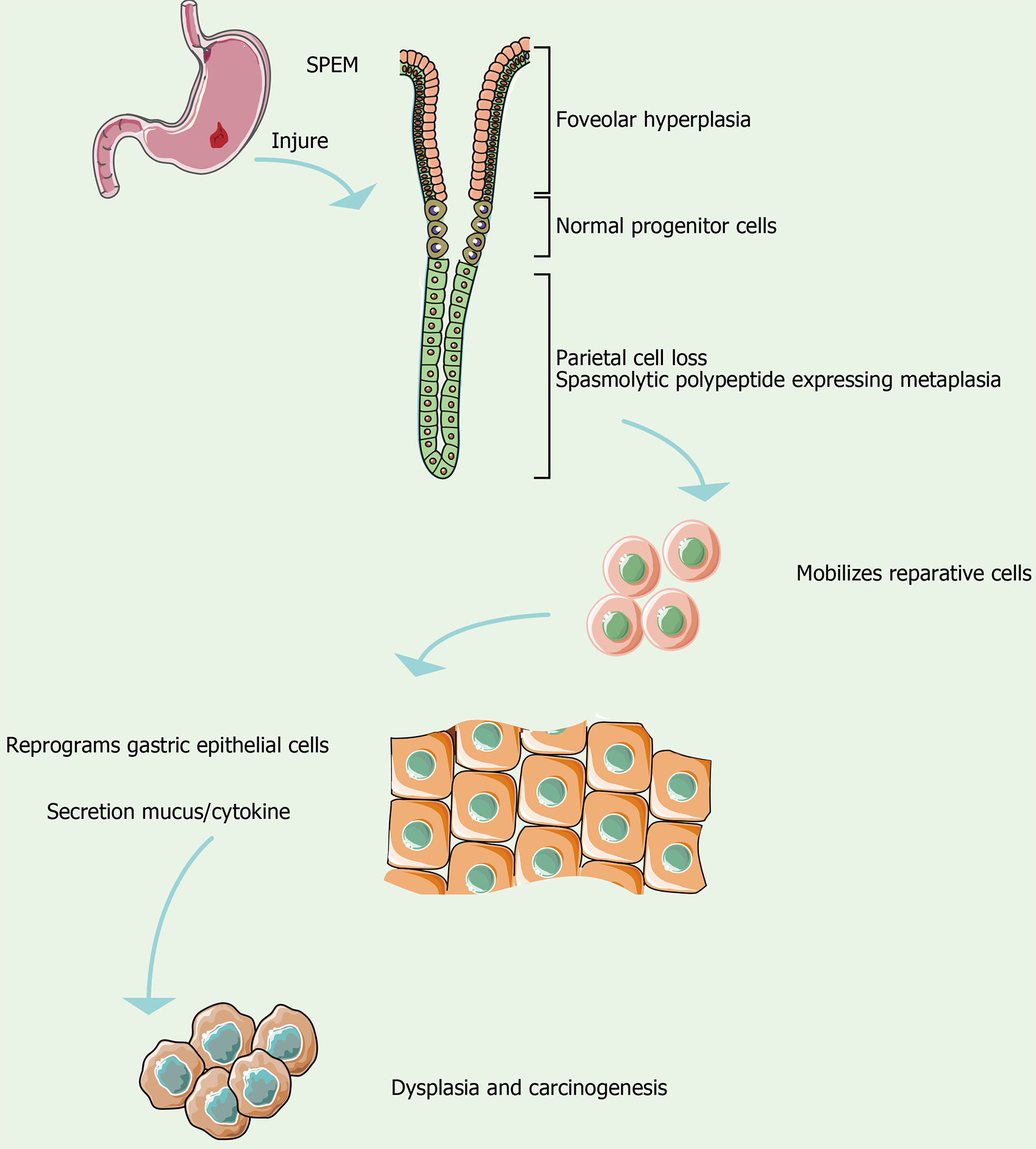
Figure 3 Spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia in inflammation-cancer transition.
SPEM: Spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia.
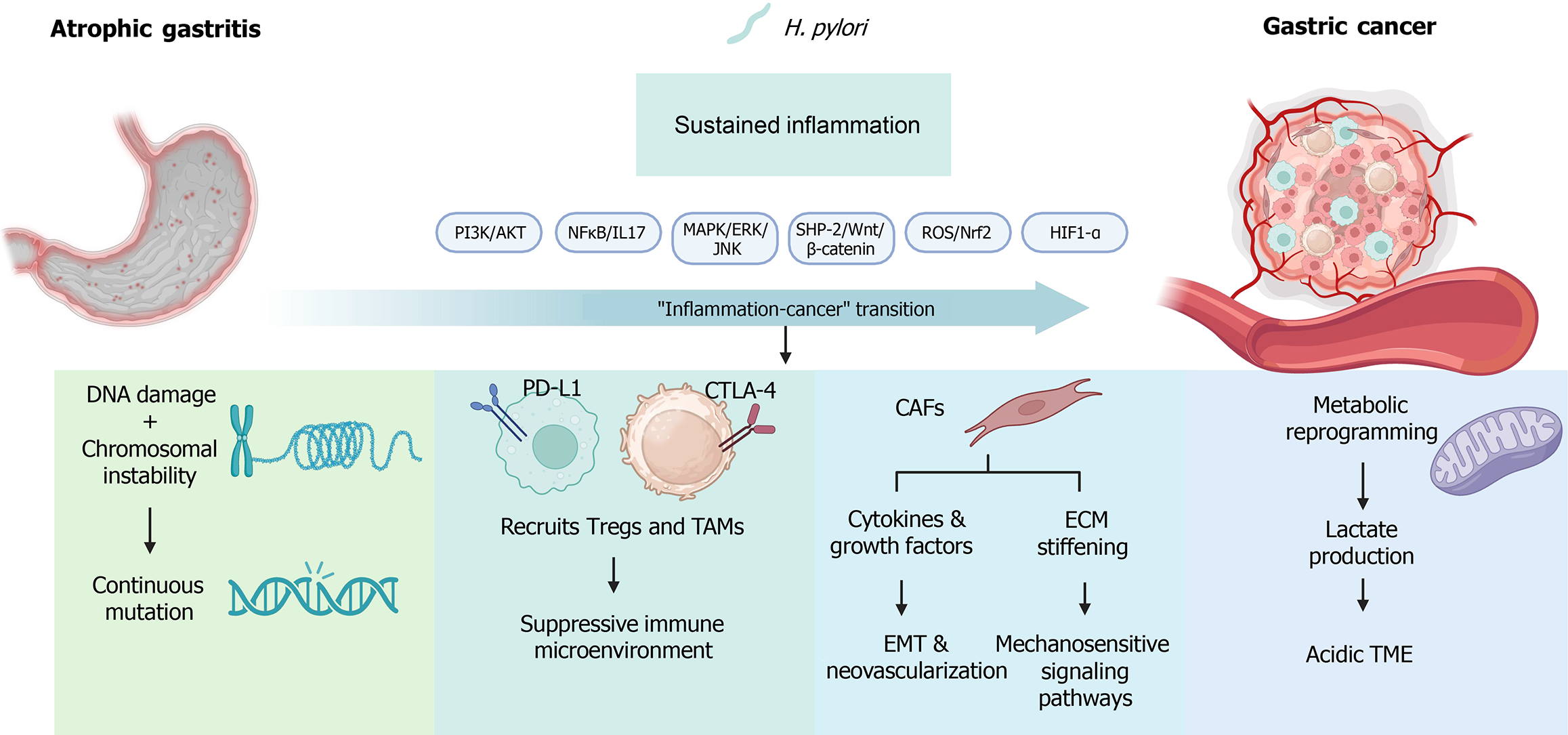
Figure 4 Molecular and cellular mechanisms driving “inflammation-cancer” transition in atrophic gastritis.
H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; P13K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; IL: Interleukin; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase; SHP-2: Src homology-2 domain-containing phosphatase 2; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2; HIF: Hypoxia inducible factor; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4; TAMs: Tumor-associated macrophages; CAF: Cancer-associated fibroblasts; ECM: Extracellular matrix; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; TME: Tumor microenvironment.
- Citation: Liu C, Wu CH, Jia YB, Qiu JX, Li XY, Ling JH. Gastric organoids: A promising model for studying “inflammation-cancer” transition in atrophic gastritis. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(11): 110453
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i11/110453.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i11.110453