©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. Dec 5, 2025; 16(4): 109304
Published online Dec 5, 2025. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v16.i4.109304
Published online Dec 5, 2025. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v16.i4.109304
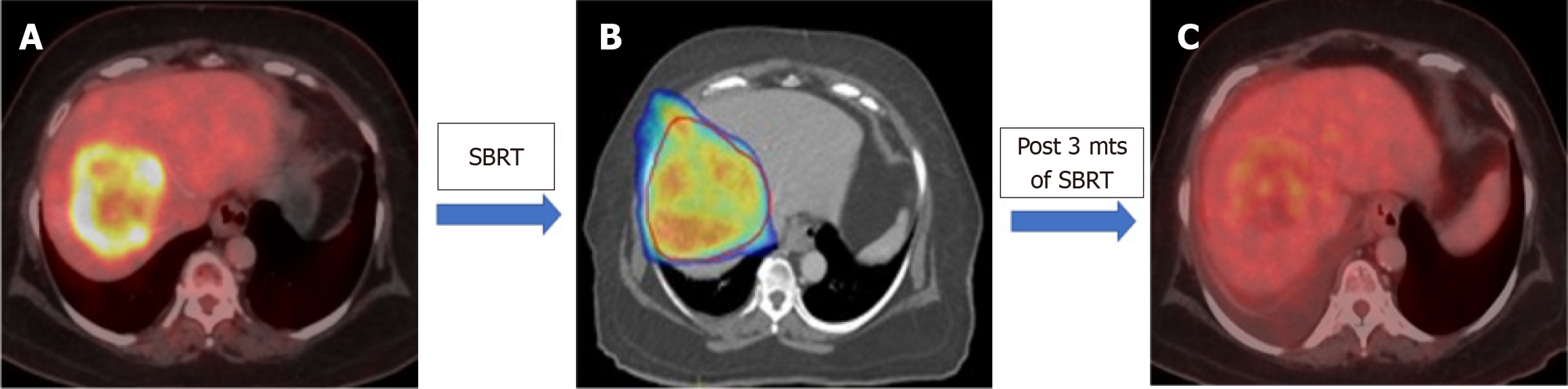
Figure 1 Post stereotactic body radiation therapy response in a case of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
A: Pre-stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) positron emission tomography/computed tomography: Metabolically active ill-defined hypodense lesions with heterogeneous peripheral arterial enhancement and central necrotic changes involving segments VIII and V suggestive of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; B: Stereotactic body radiation therapy colorwash; C: Positron emission tomography/computed tomography (post SBRT and three cycles of Gemcitabine /cisplatin base chemotherapy): There is significant interval reduction in metabolic activity of the primary lesion along with mild interval reduction in size of the lesion with appearance of central necrotic changes. SBRT: Stereotactic body radiation therapy.
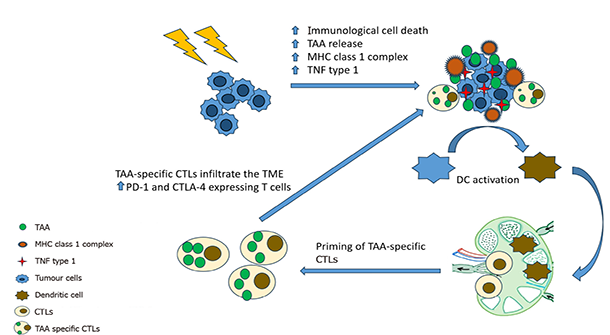
Figure 2 Immunomodulatory effects of stereotactic body radiation therapy.
TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; DC: Dendritic cells; TAA: Tumor-associated antigen; PD-1: Programmed cell death-1 receptor; CTLs: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes.
- Citation: Sharma D, Meena BL. Evolving role of radiation therapy in advanced/metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther 2025; 16(4): 109304
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5349/full/v16/i4/109304.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4292/wjgpt.v16.i4.109304