©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2025; 17(12): 114398
Published online Dec 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i12.114398
Published online Dec 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i12.114398
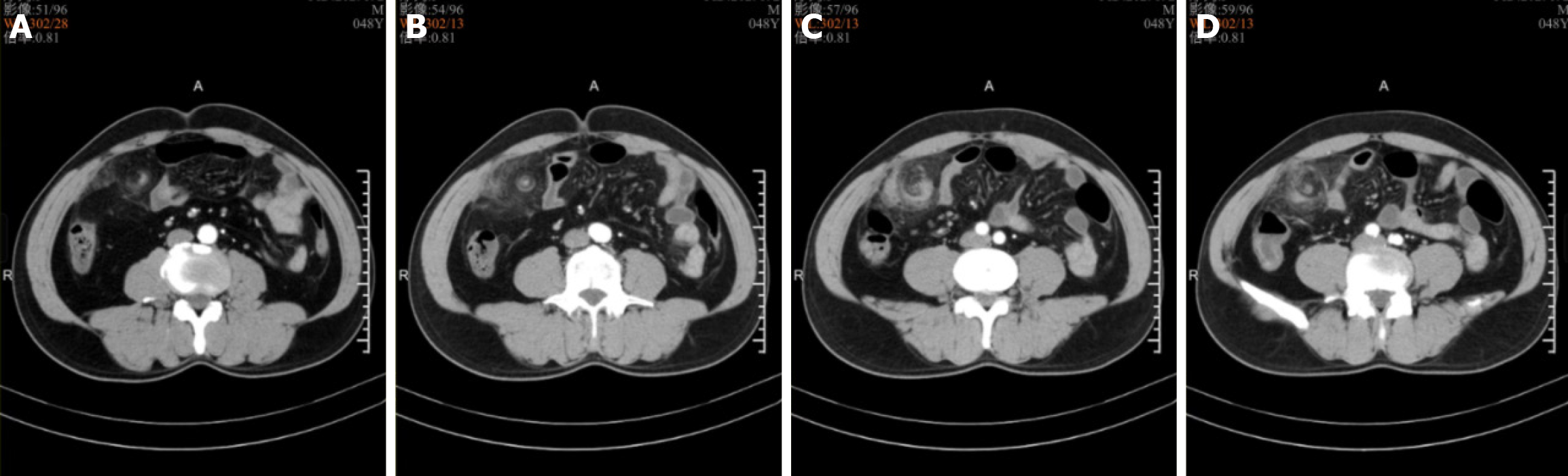
Figure 1 Contrast-enhanced computed tomography.
A-D: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography revealed thickening of the omentum in the right abdomen, with the omentum twisting spirally along its axis and having blurred edges.
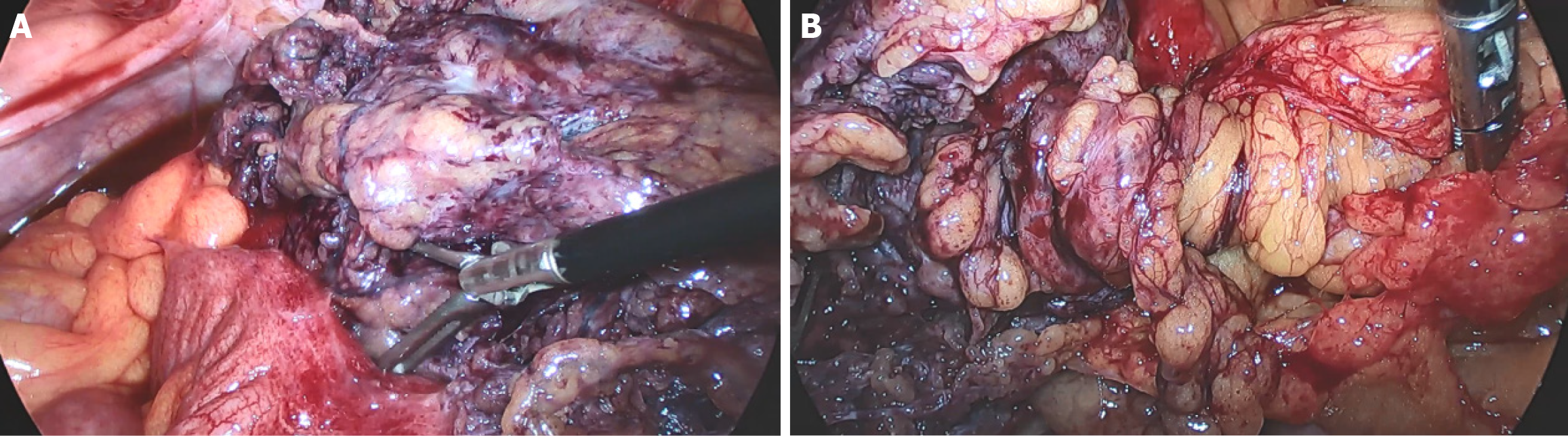
Figure 2 Laparoscopic surgery view.
A and B: Laparoscopy revealed 50 mL of dark-red bloody ascites in the pelvis and twisting of the right omentum along its longitudinal axis, with a 10 cm × 8 cm purple-black necrosis at the distal end.
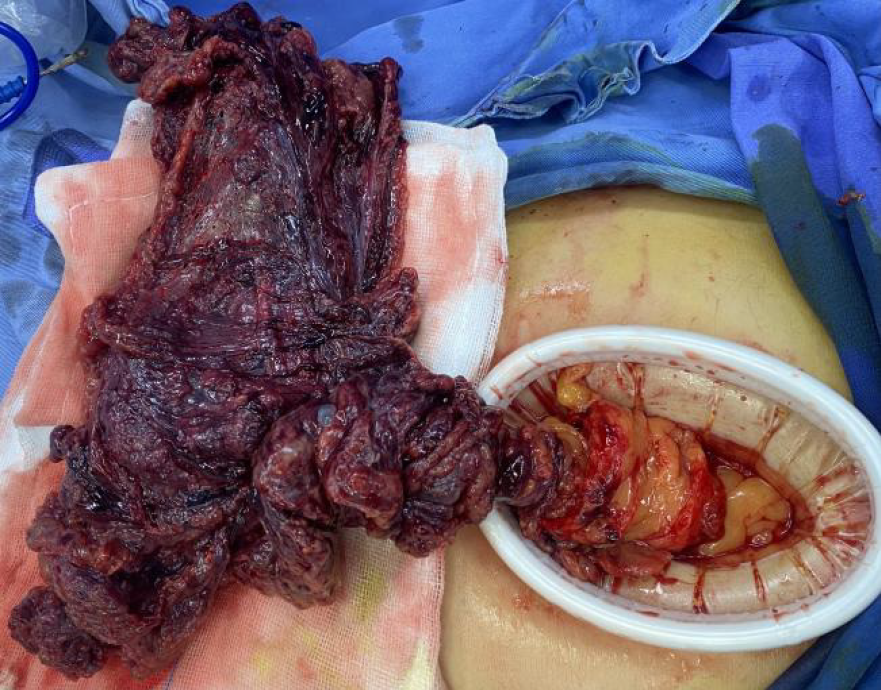
Figure 3 Open surgical view.
The right-sided omentum was found to be twisted clockwise by 1980 degrees.
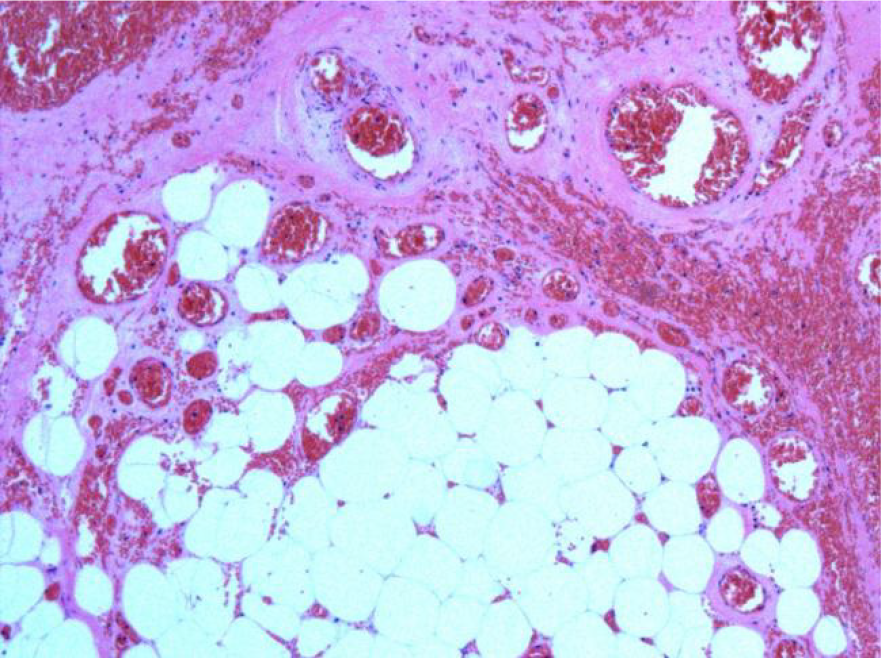
Figure 4 Postoperative pathology.
Histopathological examination revealed omental hemorrhage, degeneration, and necrosis (hematoxylin and eosin, × 50).
- Citation: Li YL, Fan JX, Yang Y, Yao MQ, Jiang YP. Omental torsion diagnosed by abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography: A case report. World J Radiol 2025; 17(12): 114398
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i12/114398.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i12.114398