©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Nov 28, 2025; 17(11): 113012
Published online Nov 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i11.113012
Published online Nov 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i11.113012
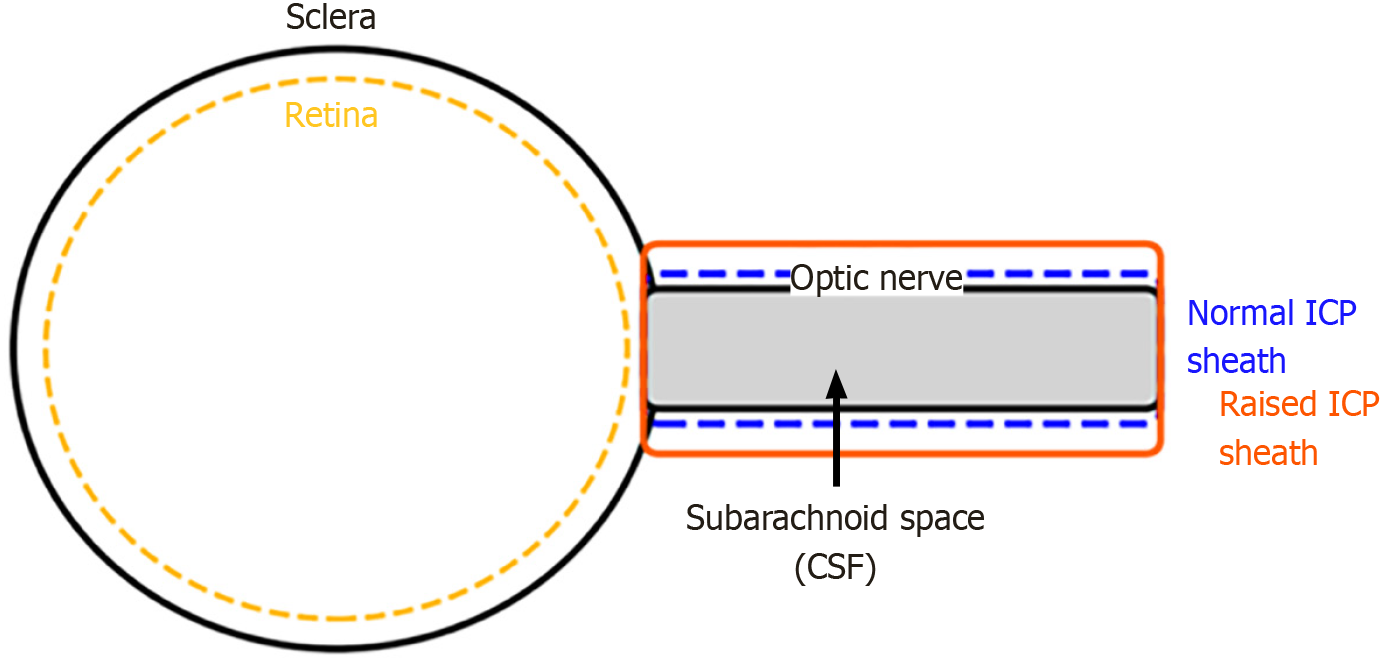
Figure 1 Anatomical relationship of the optic nerve sheath to the intracranial subarachnoid space, illustrating sheath expansion in raised intracranial pressure.
ICP: Intracranial pressure; CSF: Cerebrospinal fluid.
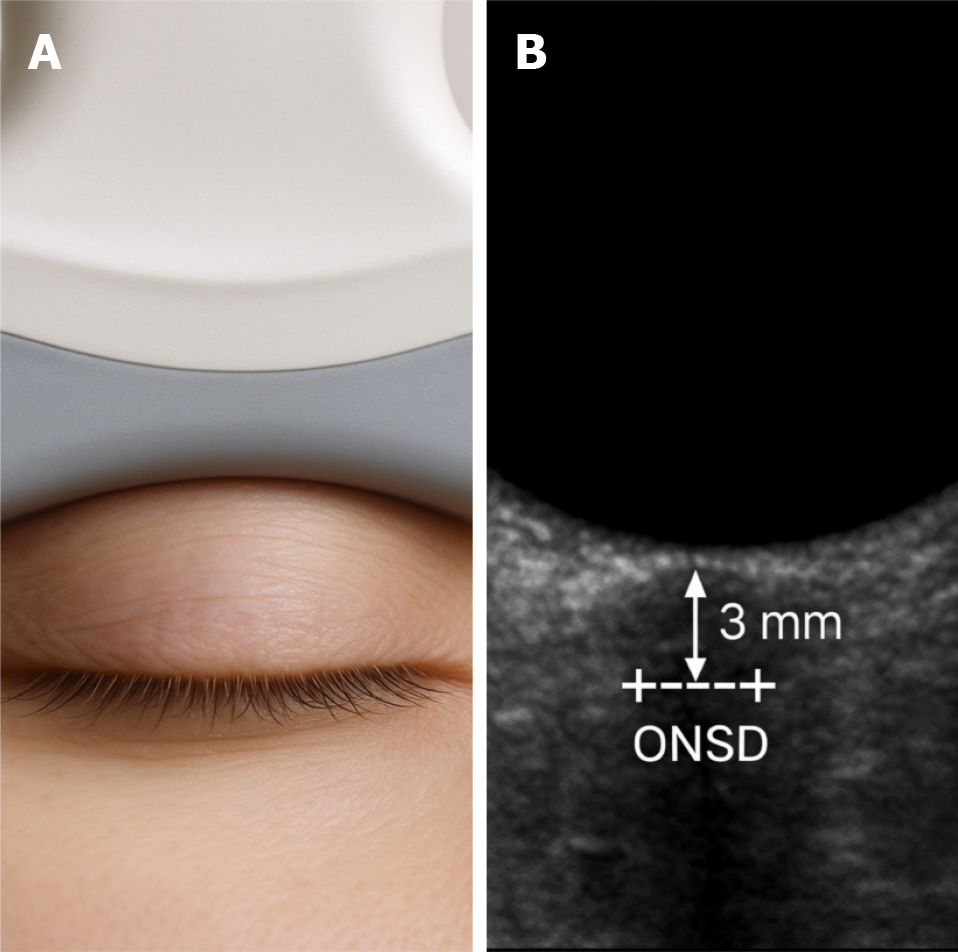
Figure 2 Ultrasonographic technique for measuring optic nerve sheath diameter using point-of-care ultrasound.
A: Proper ultrasound probe placement over the closed eyelid for optic nerve sheath diameter measurement; B: Sonographic image of the optic nerve sheath diameter with calipers placed 3 mm posterior to the retina. ONSD: Optic nerve sheath diameter.
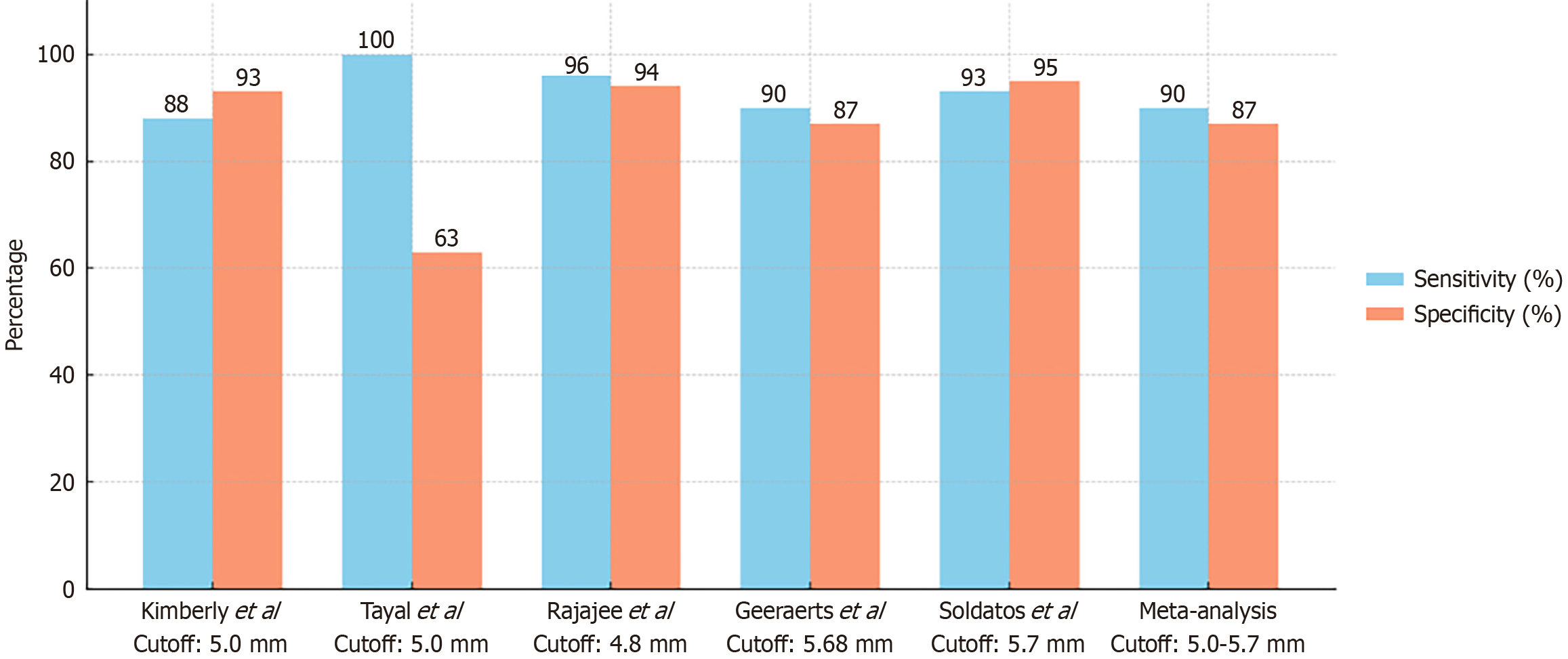
Figure 3
Diagnostic accuracy of point-of-care ultrasound–measured optic nerve sheath diameter for detecting raised intracranial pressure, showing sensitivity, specificity, and cut-off values from key studies.
- Citation: Tlaiss Y, Tarchichi A, Atallah K, Al Mashtoub E, Zalzali I, Chokor Z, Fassih I, Harb N, Kassas J, Hamze H. Point-of-care ultrasonography for detecting raised intracranial pressure through optic nerve sheath diameter in non-traumatic headache patients. World J Radiol 2025; 17(11): 113012
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i11/113012.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i11.113012