©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Cardiol. Feb 26, 2026; 18(2): 111861
Published online Feb 26, 2026. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v18.i2.111861
Published online Feb 26, 2026. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v18.i2.111861
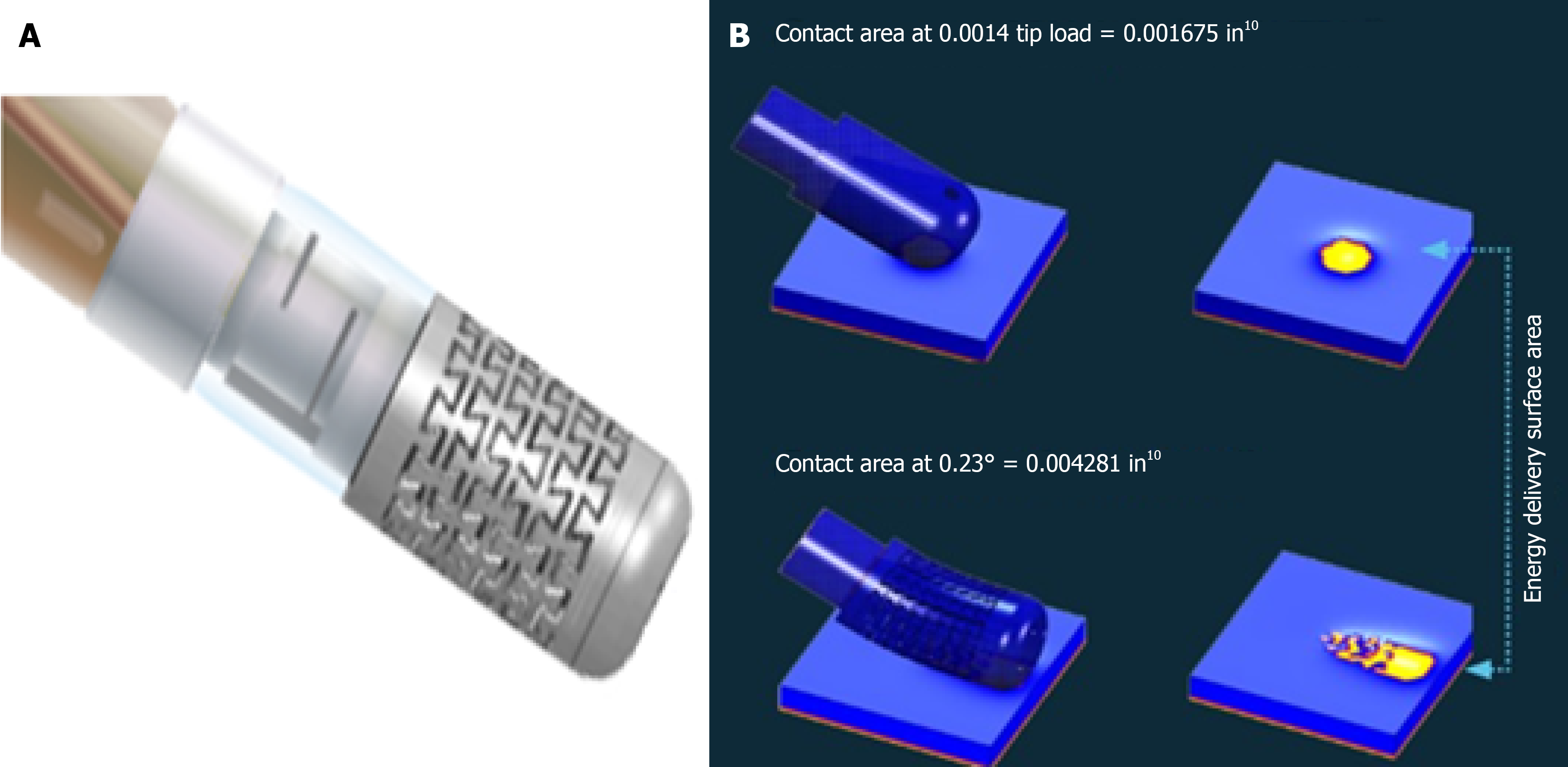
Figure 1 TactiFlex™ Sensor Enabled™ Catheter.
In the left panel, the flexible porous tip electrode is shown, in the right panel difference in energy delivery between a conventional catheter (on the top) and a flexible porous tip (on the bottom) (Supplementary material).
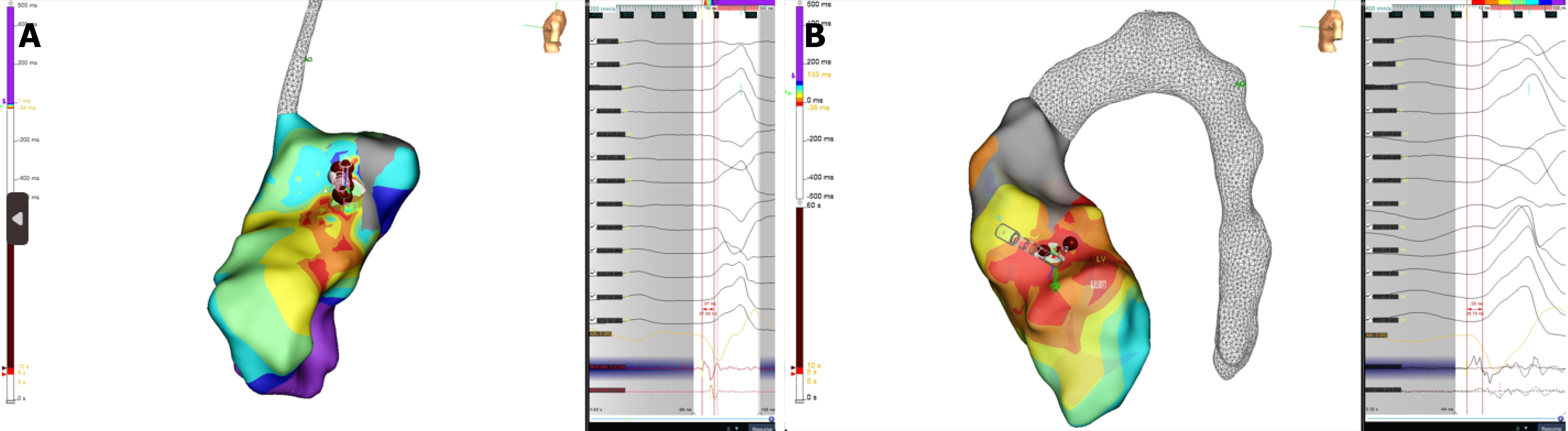
Figure 2 Electrocardiogram/electrogram signals.
A: Left ventricular activation map and electrocardiogram/electrogram signals. Best signals recorded (-27 milliseconds) in mitroaortic continuity, 6 lesions (max 35 W, 60 seconds, medium impedance drop 14.3 ohms) were performed without disappearance of arrhythmias; B: Left ventricular activation map and electrocardiogram/electrogram signals. Best signals (-25 milliseconds) recorded in mitroaortic continuity, 4 lesions (max 35 W, 60 seconds, medium impedance drop 11.4 ohms) were performed without disappearance of arrhythmias (Supplementary material).
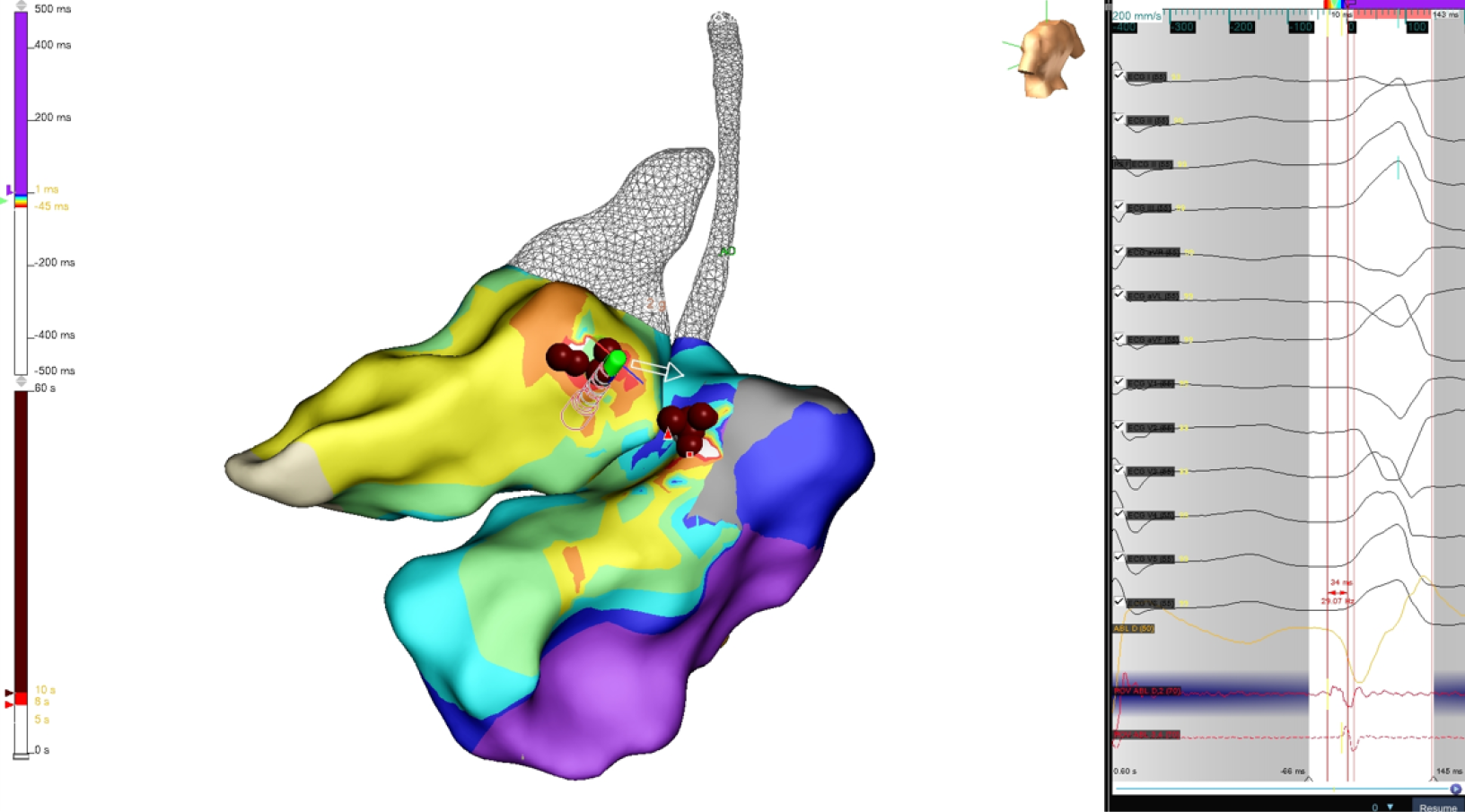
Figure 3 Left ventricular/right ventricular activation map and electrocardiogram/electrogram signals.
Best signals recorded (-34 milliseconds) in mitroaortic continuity, 5 lesions (max 35 W, 60 seconds, medium impedance drop 10.2 ohms) were performed without disappearance of arrhythmias. An anatomical approach was performed with the other 4 lesions in the posteroseptal right ventricular outflow tract. The arrow indicates catheter direction during mapping (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Palamà Z, Tricarico G, Scarà A, Robles AG, De Masi De Luca G, Nesti M, Romano S, Sciarra L. Late left ventricular summit premature ventricular contractions elimination with new TactiFlex irrigation technology. World J Cardiol 2026; 18(2): 111861
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v18/i2/111861.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v18.i2.111861