Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Cardiol. Sep 26, 2024; 16(9): 531-541
Published online Sep 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i9.531
Published online Sep 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i9.531
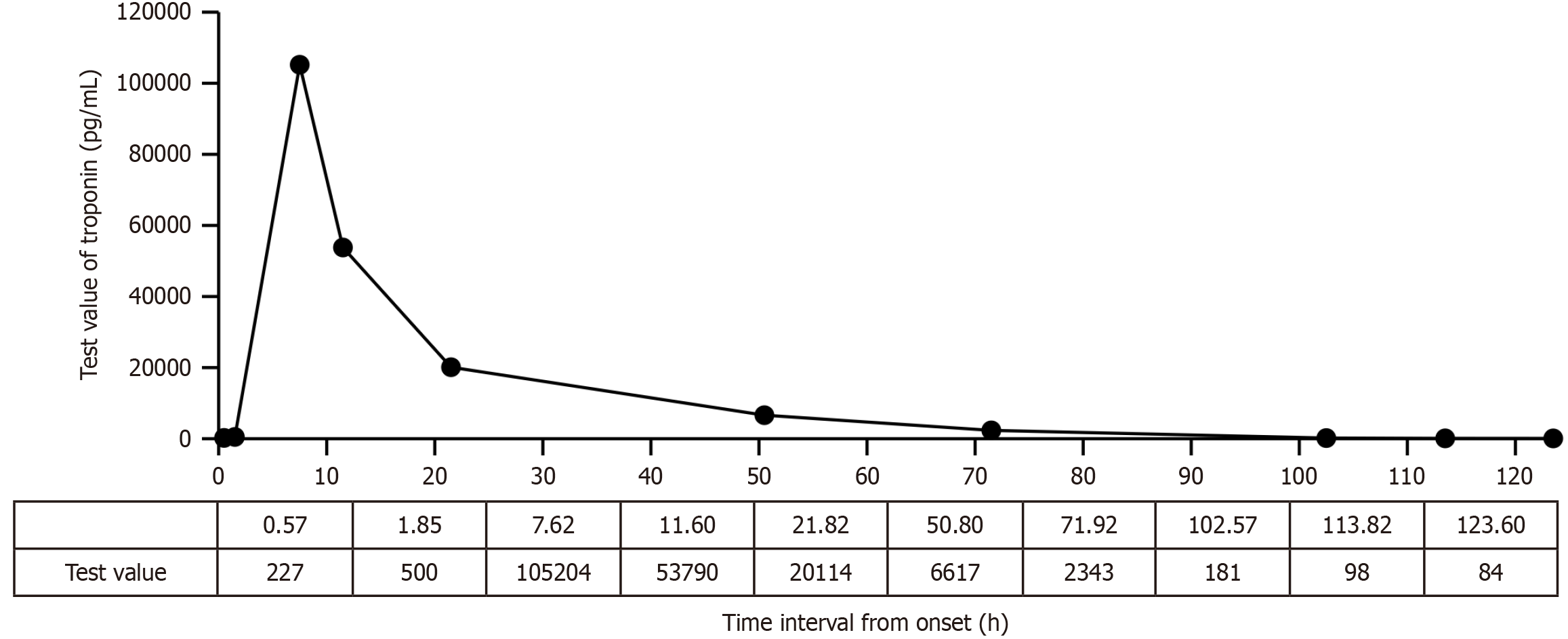
Figure 1 Dynamic trend of the troponin level.
The peak value appears at 7.62 hours after onset.
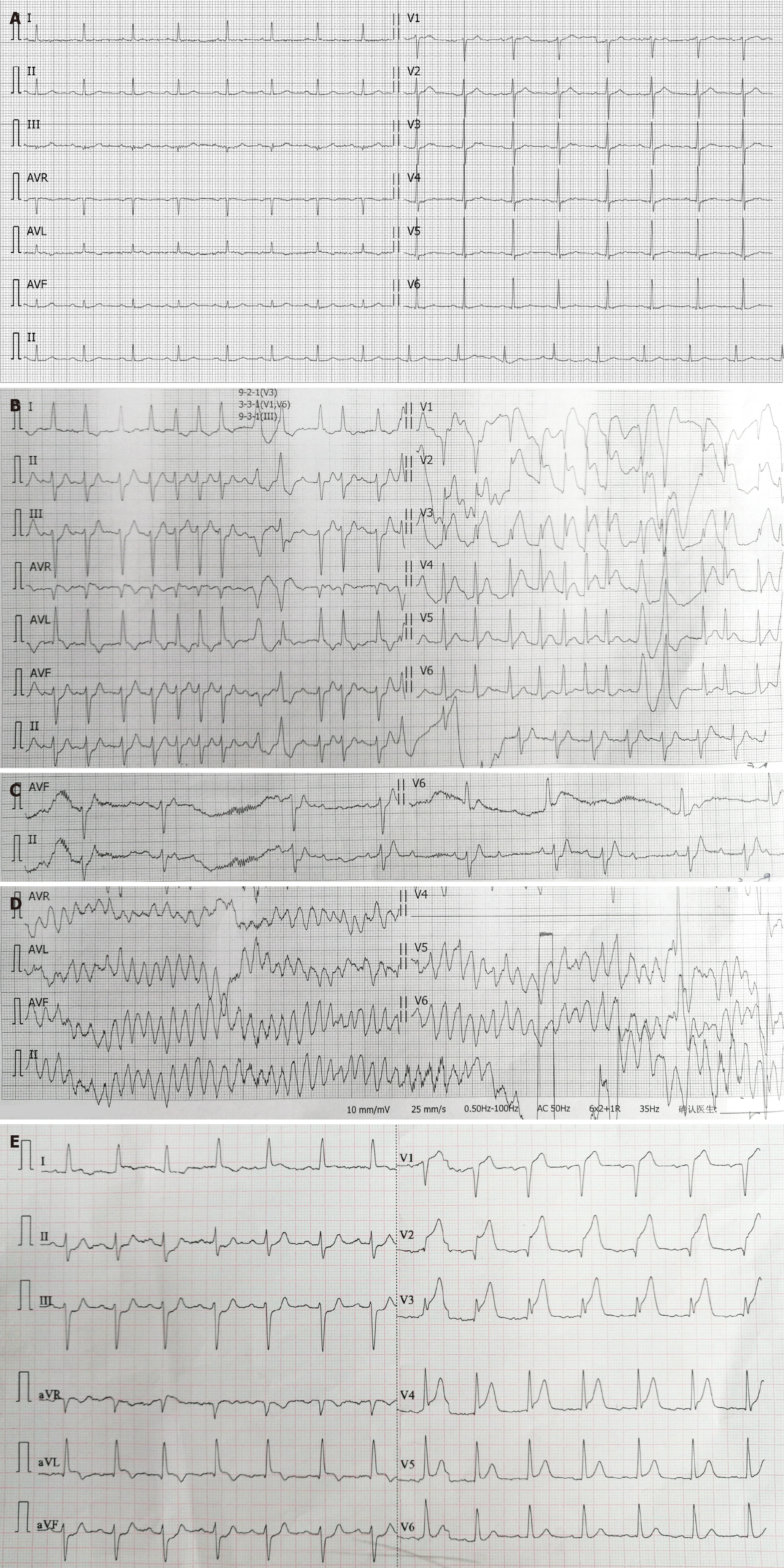
Figure 2 Transient evolution of electrocardiogram in hyperacute myocardial infarction.
A: Baseline electrocardiogram (ECG) on January 29, 2018; B and C: Initial emergency ECG at 11:38 on June 24, 2019, showing atrial fibrillation with ST-segment elevation or depression in some leads, ventricular premature beats, and spontaneous conversion of atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm with second-degree type I atrioventricular block within one minute; D and E: ECG during syncope at 11:40 on June 24, 2019, showing torsades de pointes ventricular tachycardia (TdP), with TdP lasting approximately ten seconds before spontaneous conversion to sinus rhythm with ST-segment elevation or depression in some leads.
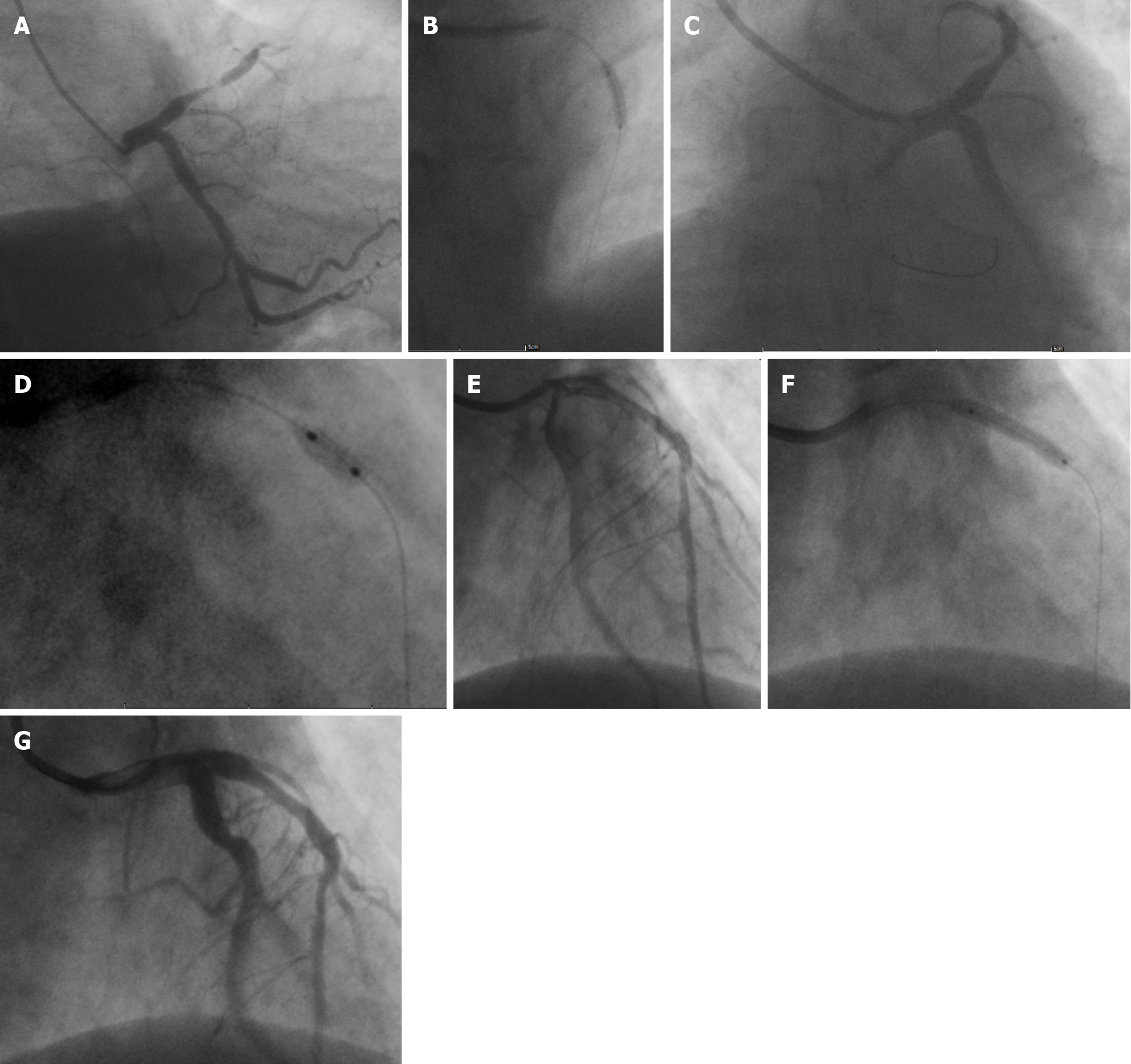
Figure 3 Procedure of target vessel operation.
A: Subtotal occlusion with thrombus formation in the proximal segment of the left anterior descending artery; B: Predilation using a TREK 2.5 mm × 15 mm balloon; C: Significant recoil at the stenotic site; D: Predilation using a Boston Scientific FlextomeTM Cutting Balloon 3.0 mm × 6 mm; E: Approximately 20% residual stenosis after predilation; F: Dilation using a paclitaxel drug-eluting balloon (QINGZHOU Bingo DEB3020); G: Approximately 40% residual stenosis.
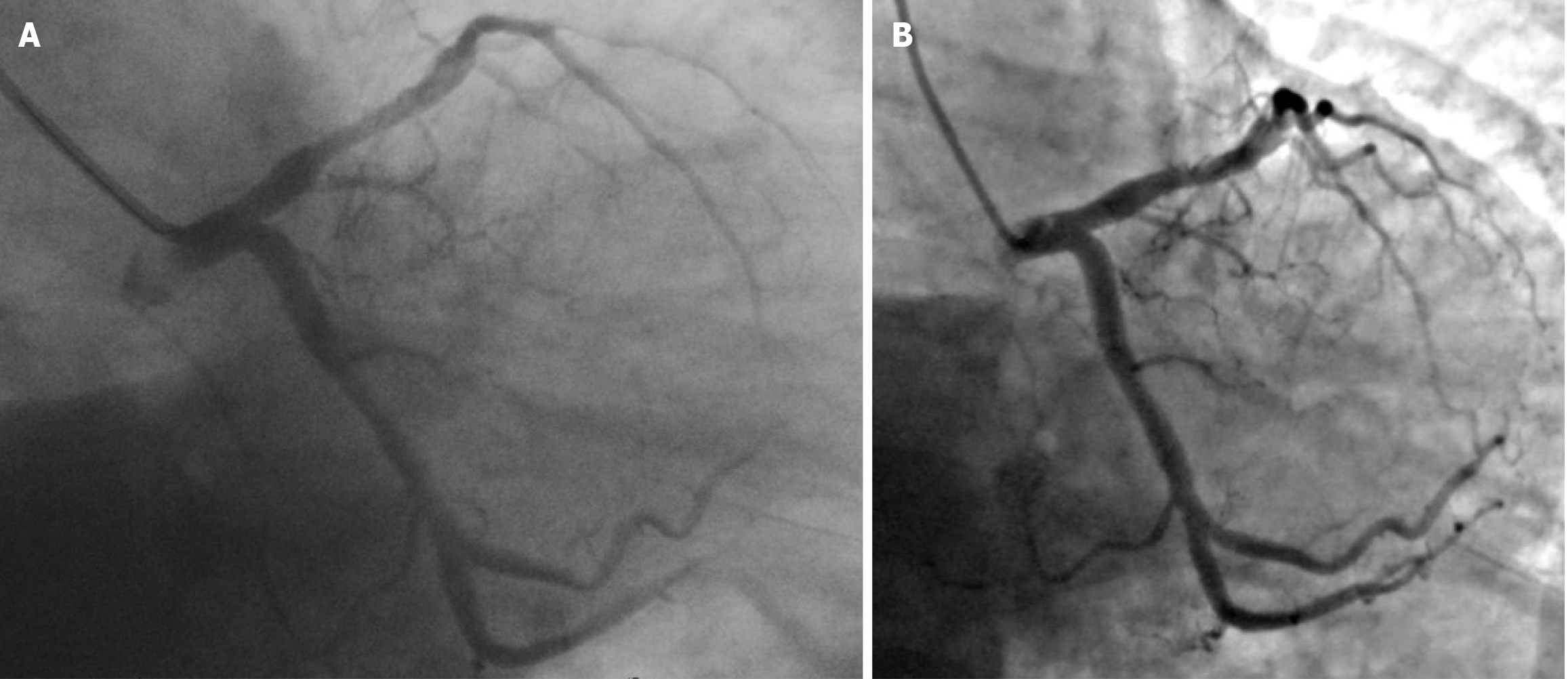
Figure 4 Comparison of the left coronary angiography images obtained in the same position.
A: On June 24, 2019, the residual stenosis in the proximal segment of the left anterior descending artery (LAD) after the primary percutaneous coronary intervention was approximately 40%, and the net lumen gain at the site of the most substantial stenosis was approximately 2.3 mm (RAO 30.0°, CAU 30.0°); B: On June 19, 2023, approximately 25% residual stenosis was observed in the proximal LAD, and the net lumen gain at the site of the most substantial stenosis was approximately 3.0 mm (RAO 30.4°, CAU 29.9°).
- Citation: She LQ, Gao DK, Hong L, Tian Y, Wang HZ, Huang S. Intracoronary thrombolysis combined with drug balloon angioplasty in a young ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patient: A case report. World J Cardiol 2024; 16(9): 531-541
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v16/i9/531.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v16.i9.531