©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Oct 27, 2025; 17(10): 111943
Published online Oct 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i10.111943
Published online Oct 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i10.111943
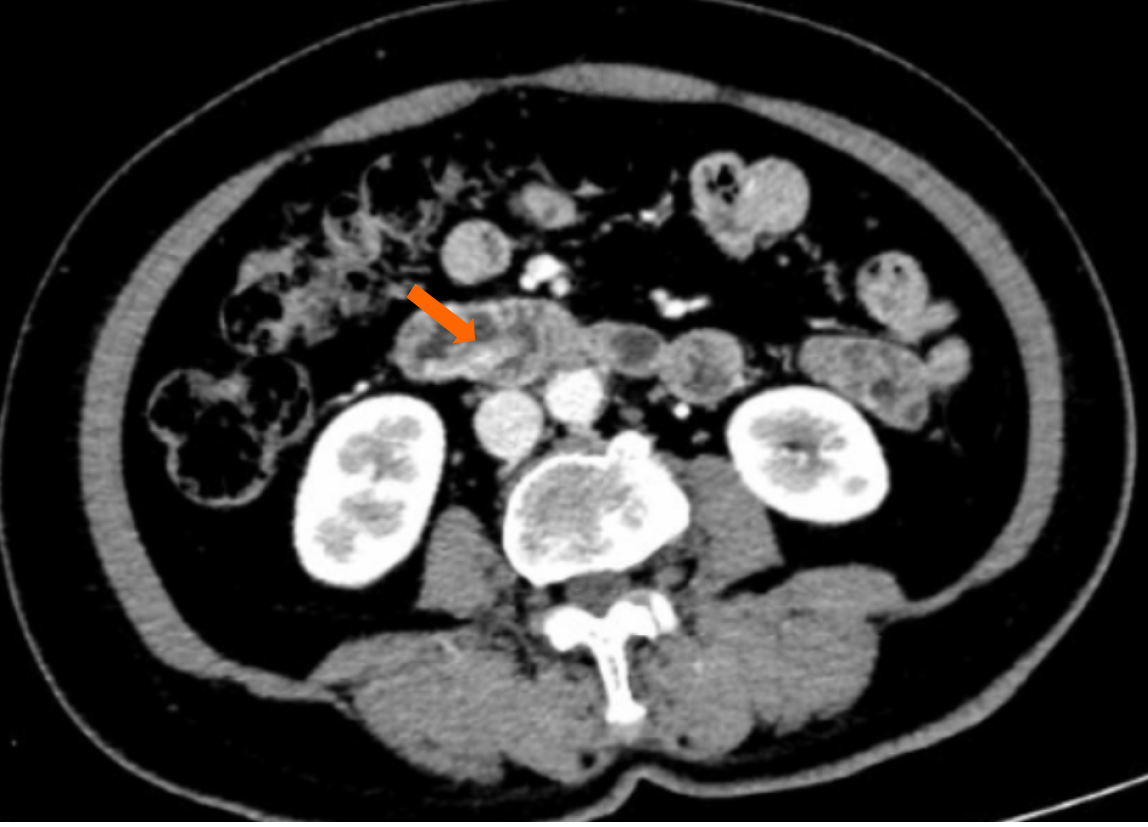
Figure 1
Computed tomography revealed a strip-like soft tissue density lesion in the descending duodenum (arrows).
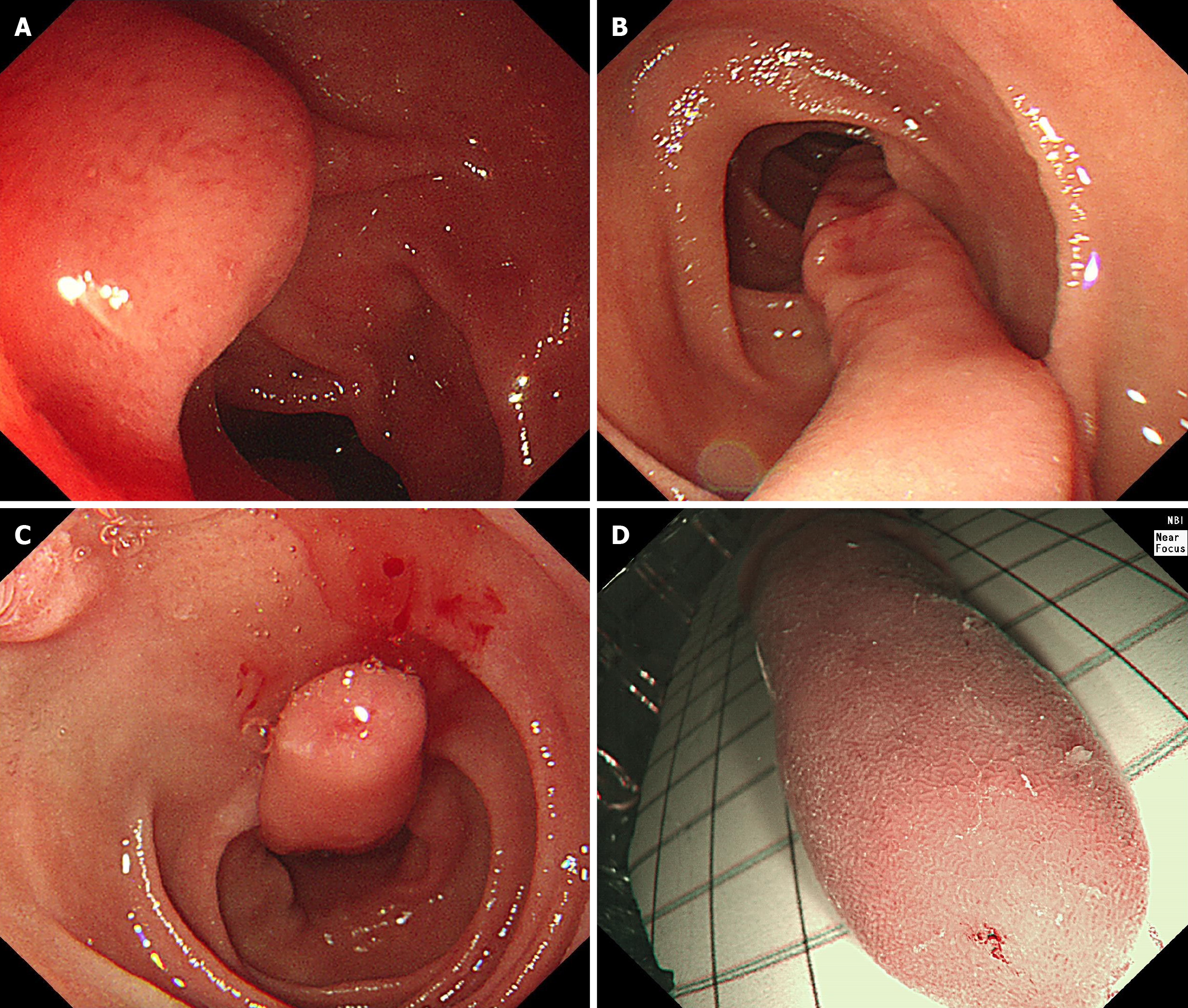
Figure 2 Endoscopic views of the polyps.
A: Gastroduodenoscopy performed 15 months earlier showing a 1.5-cm mucosal elevation in the second portion of the duodenum; B and C: Gastroduodenoscopy revealed a 10-cm slender, elongated, pedunculated, “worm-like mass with a smooth surface in D2; D: Endoscopic view under narrow band imaging.
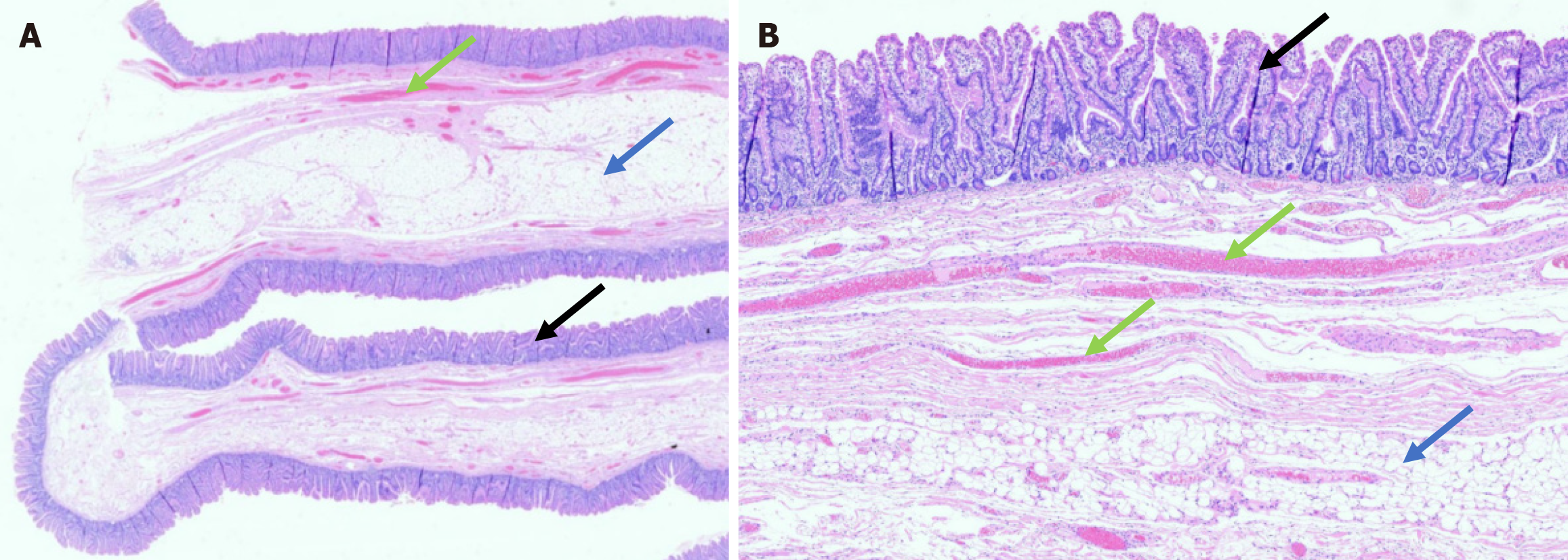
Figure 3 Histological section (hematoxylin and eosin staining).
A: Low-power view demonstrating the overall architecture of the polyp; B: Higher magnification highlighting architecturally normal small intestinal mucosa (black arrows) overlying a core of submucosa containing abundant adipose tissue (blue arrows) with submucosal vessels (green arrows). No significant inflammation is seen.
- Citation: Yang Y, Zhong DF. Unusually rapid growth of a duodenal muco-submucosal elongated polyp: A case report. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(10): 111943
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i10/111943.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i10.111943