©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2026; 17(2): 112475
Published online Feb 15, 2026. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v17.i2.112475
Published online Feb 15, 2026. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v17.i2.112475
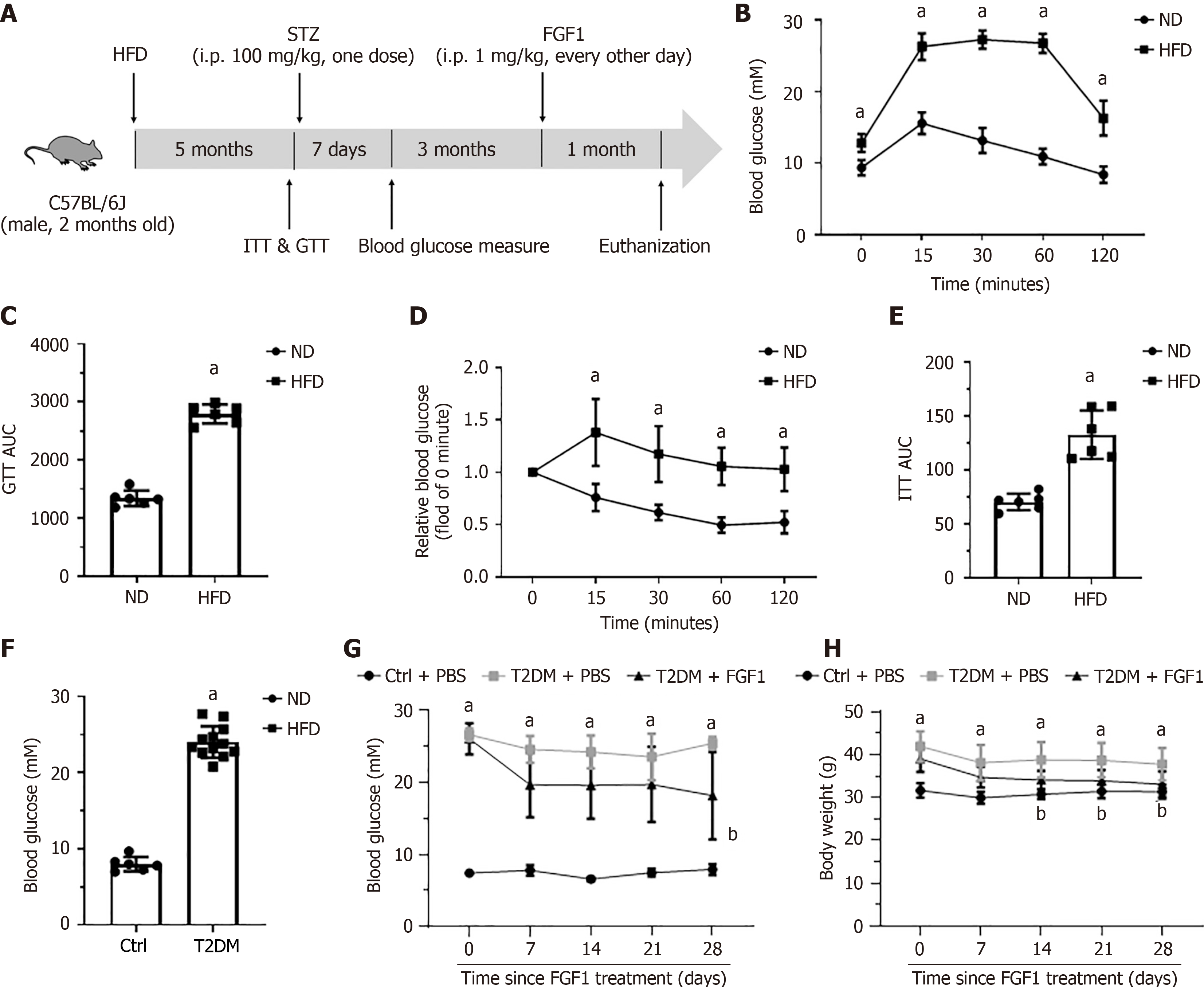
Figure 1 Induction of a type 2 diabetes mellitus mouse model and experimental design for fibroblast growth factor 1 intervention.
A: Schematic illustration of the experimental timeline, including high-fat diet feeding, streptozotocin injection, and fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1) administration; B: Glucose tolerance test; C: Area under the curve analysis of glucose tolerance test; D: Insulin tolerance test; E: Area under the curve analysis of insulin tolerance test; F: Non-fasting blood glucose levels measured 7 days after streptozotocin injection; G: Body weight monitoring during FGF1 treatment period; H: Time-course measurements of blood glucose levels during FGF1 treatment. Data were presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 vs control group; bP < 0.05 vs type 2 diabetes mellitus + phosphate buffered saline group. AUC: Area under the curve; Ctrl: Control; FGF1: Fibroblast growth factor 1; GTT: Glucose tolerance test; HFD: High-fat diet; ITT: Insulin tolerance test; ND: Normal diet; STZ: Streptozotocin; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
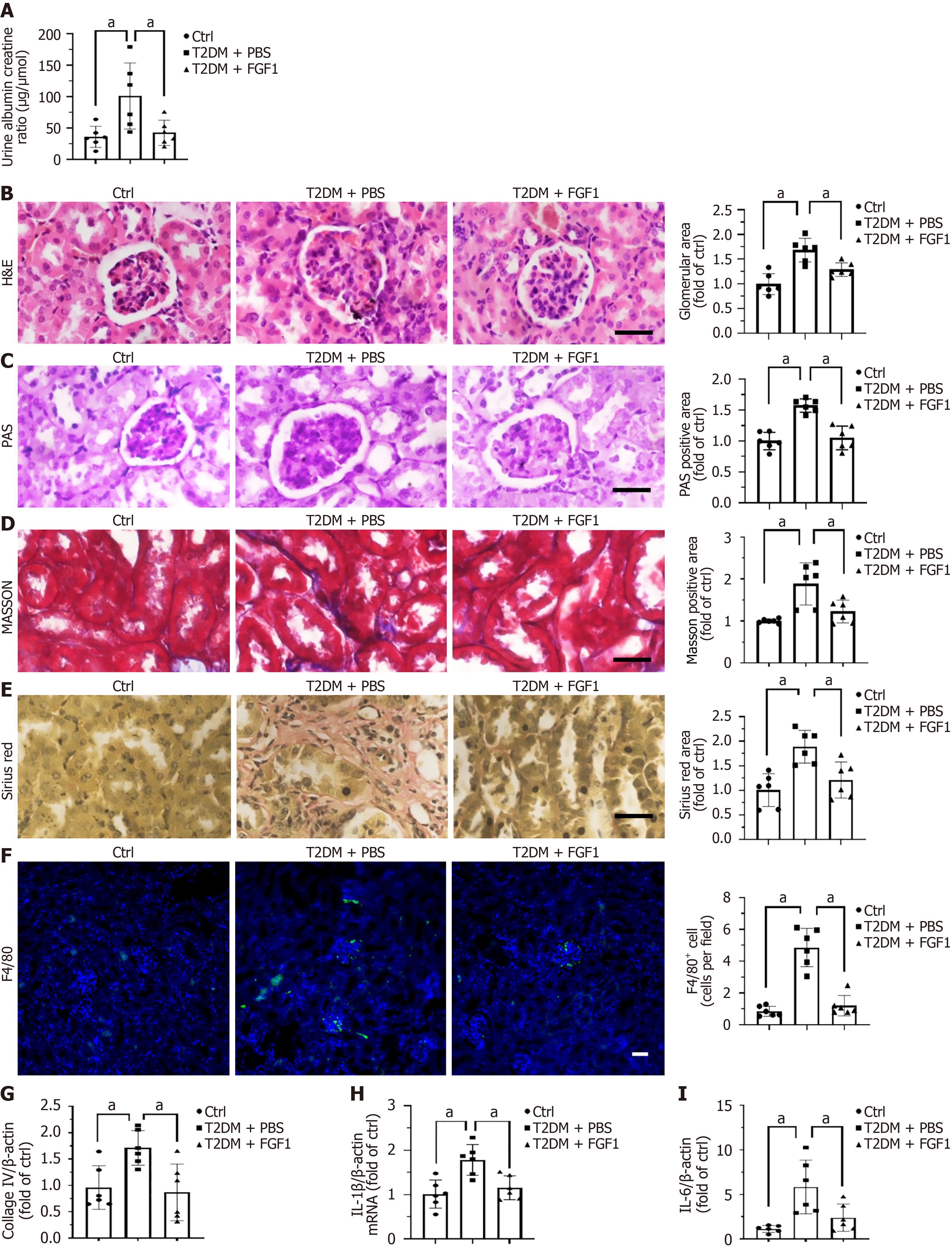
Figure 2 Fibroblast growth factor 1 ameliorates diabetes-induced renal dysfunction and histopathological alterations.
A: Urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio for assessing renal function; B: Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin staining of kidney tissue and quantification of glomerular sizes based on hematoxylin and eosin staining; C: Periodic acid-Schiff staining and quantification of Periodic acid-Schiff positive staining area; D: Masson trichrome staining and quantification of Masson positive staining area; E: Sirius Red staining and quantification of Sirius Red positive staining area; F: F4/80 immunofluorescence staining and quantification of F4/80 positive macrophage; G-I: The mRNA expression levels of collagen IV, interleukin-1β, and interleukin-6 analyzed by RT-qPCR. Data were presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. n = 6 mice per group. Bar = 200 μm. Ctrl: Control; FGF1: Fibroblast growth factor 1; HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; IL: Interleukin; PAS: Periodic acid-Schiff; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
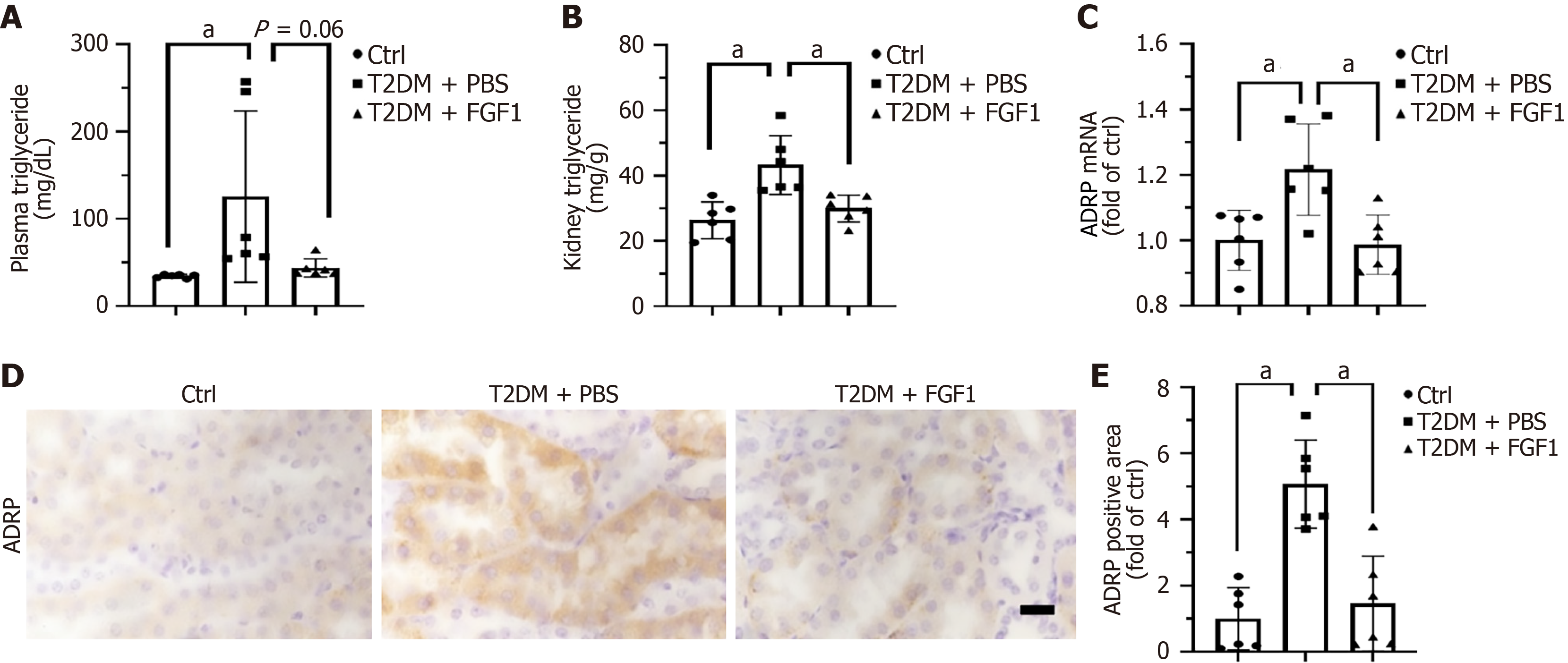
Figure 3 Fibroblast growth factor 1 attenuates lipid accumulation in the kidneys of type 2 diabetes mellitus mice.
A: Plasma triglyceride levels; B: Triglyceride content in kidney tissue; C: Adipose differentiation related protein (ADRP) mRNA expression analyzed by RT-qPCR; D: ADRP expression in the kidney assessed by immunohistochemistry; E: Quantification of ADRP immunostaining. Data were presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. Bar = 100 μm. ADPR: Adipose differentiation related protein; Ctrl: Control; FGF1: Fibroblast growth factor 1; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
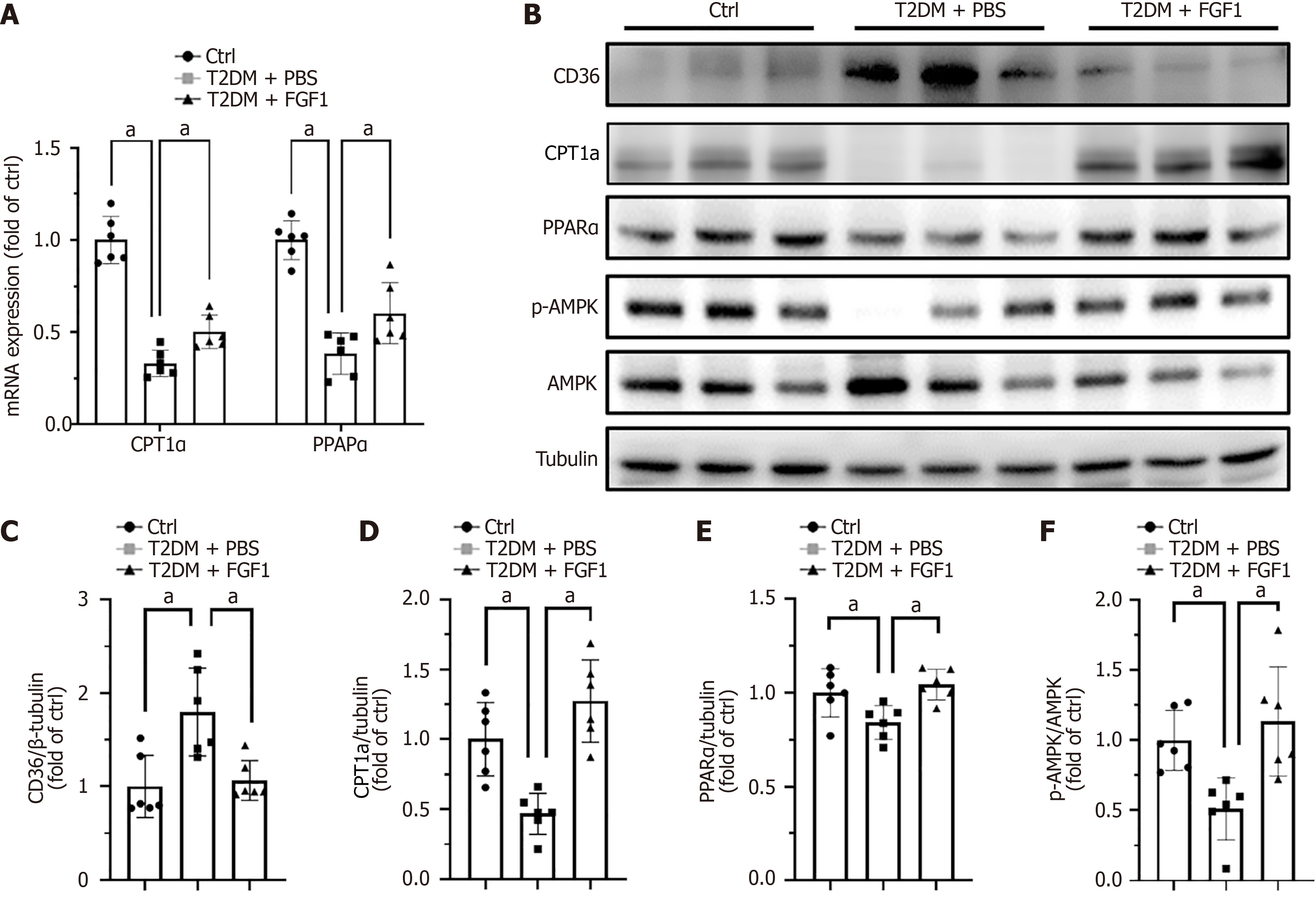
Figure 4 Fibroblast growth factor 1 regulates the expression of genes involved in fatty acid metabolism in diabetic nephropathy.
A: The mRNA expression levels of carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A (CPT1a) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) detected by RT-qPCR; B: Western blot analysis of cluster of differentiation 36, CPT1a, PPARα, and P-AMP-activated protein kinase in diabetic nephropathy; C-F: Quantification of protein expression levels of cluster of differentiation 36, CPT1a, PPARα, and AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation. Data were presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; CD36: Cluster of differentiation 36; CPT1a: Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A; Ctrl: Control; FGF1: Fibroblast growth factor 1; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
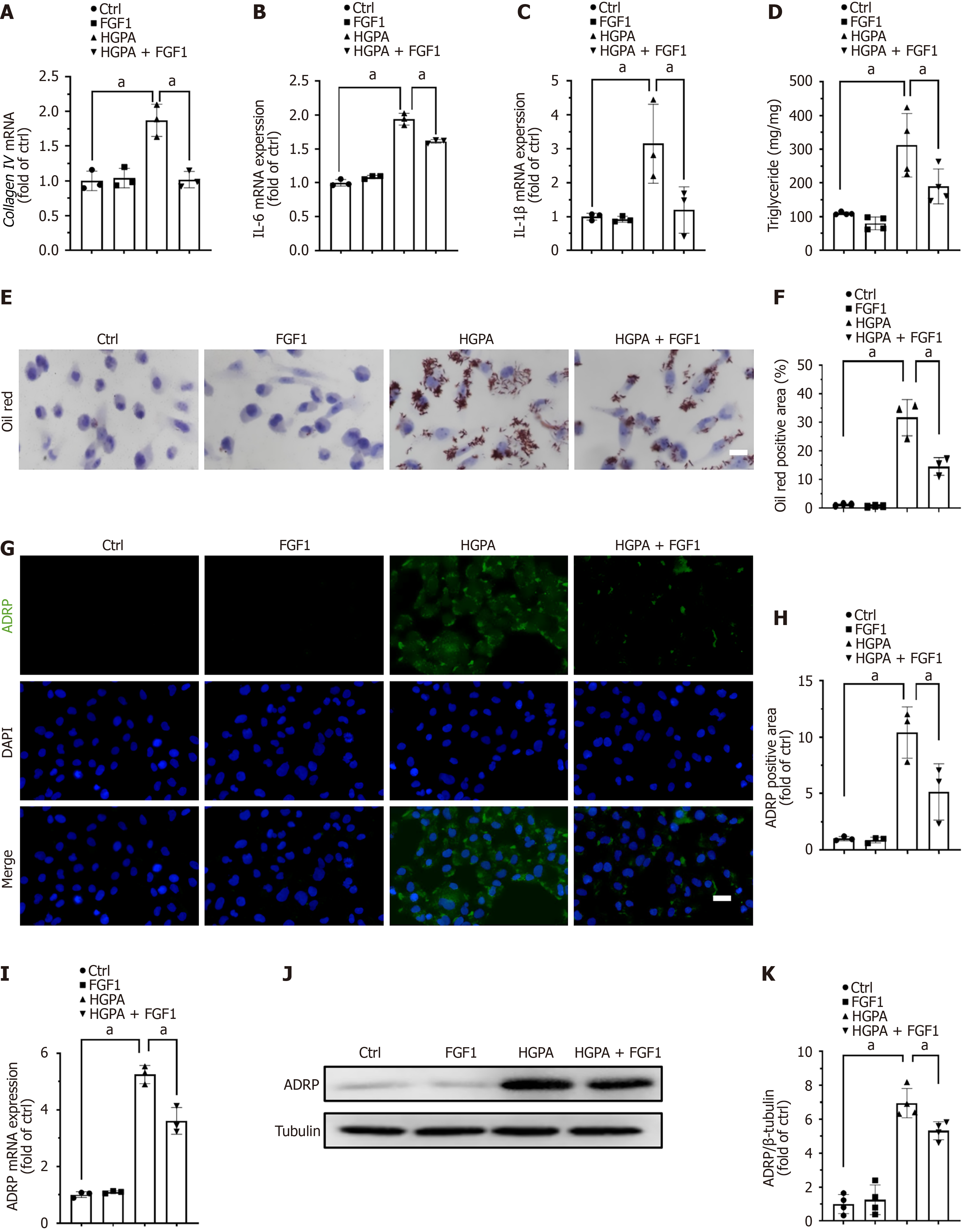
Figure 5 Fibroblast growth factor 1 attenuates fibrosis, inflammation, and lipid accumulation in high glucose and palmitate acid-treated human kidney-2 cells.
A-C: The mRNA expression of collagen IV, interleukin-1β, and interleukin-6 was analyzed by RT-qPCR; D: Triglyceride content measured to assess lipid accumulation in high glucose and palmitate acid-treated human kidney-2 cells with or without fibroblast growth factor 1; E: Representative images of Oil Red O staining; F: Quantification of Oil Red O staining; G: Adipose differentiation related protein (ADRP) expression detected by immunofluorescence; H: Quantification of ADRP immunofluorescence; I: The mRNA expression of ADRP was analyzed by RT-qPCR; J: ADRP protein expression levels detected by Western blot; K: Densitometric analysis of Western blot using ImageQuant. Three to four independent experiments were performed for each analysis. Data were presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. Bar = 20 μm. ADRP: Adipose differentiation related protein; Ctrl: Control; FGF1: Fibroblast growth factor 1; IL: Interleukin; HGPA: High glucose and palmitic acid.
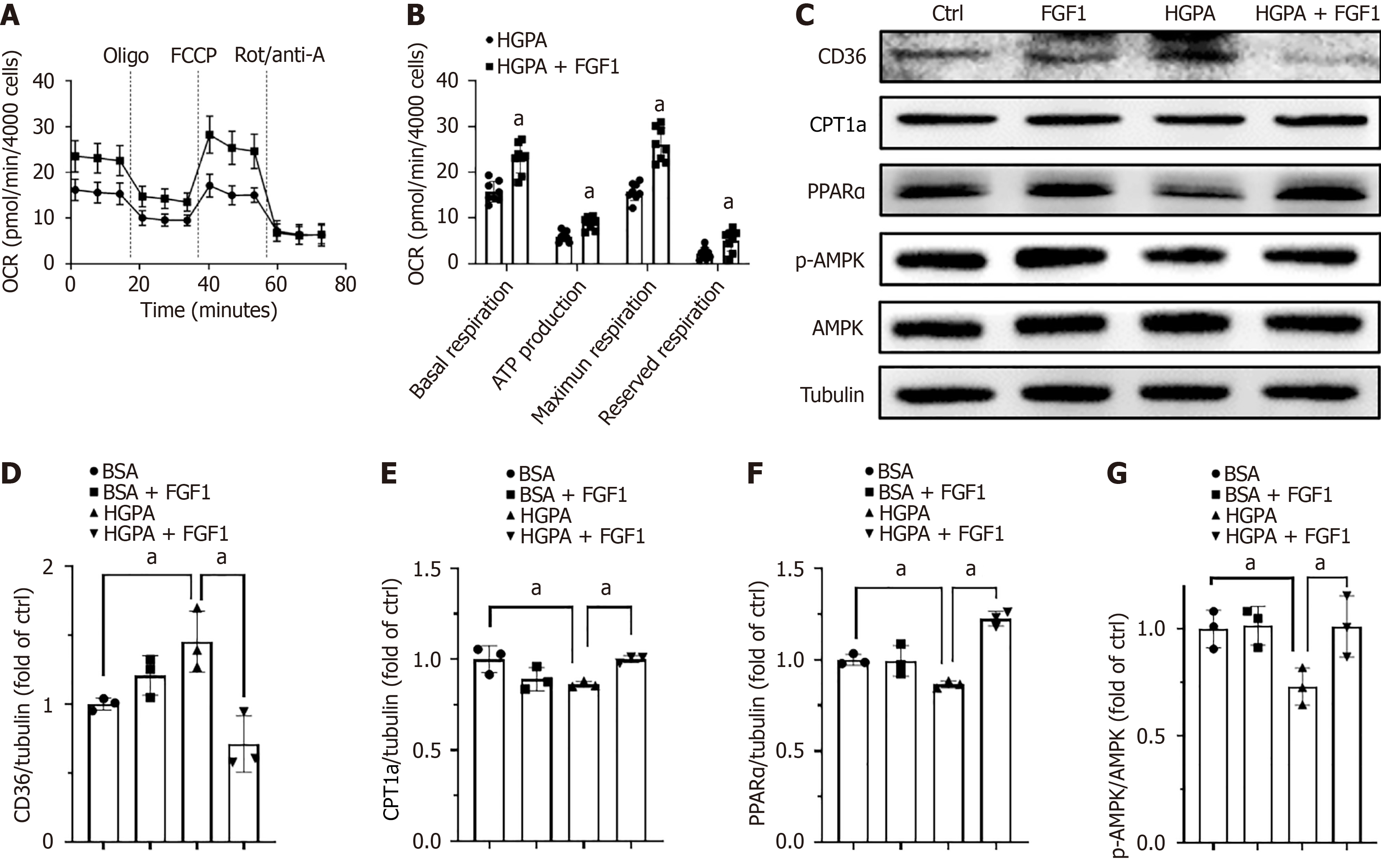
Figure 6 Fibroblast growth factor 1 regulates fatty acid metabolism gene expression in high glucose and palmitate acid-treated human kidney-2 cells.
A: Oxygen consumption rate of high glucose and palmitate acid-treated human kidney-2 cells with or without fibroblast growth factor 1 measured using the Seahorse XF Analyzer; B: Quantification of oxygen consumption rate; C: Protein expression levels of cluster of differentiation 36, carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha, and P-AMP-activated protein kinase assessed by Western blot; D-G: Quantification of protein expression levels of cluster of differentiation 36, carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha, and AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation. Three or eight independent experiments were conducted for each analysis. aP < 0.05. AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; BSA: Bovine serum albumin; CD36: Cluster of differentiation 36; CPT1a: Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A; Ctrl: Control; FCCP: Carbonyl cyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone; FGF1: Fibroblast growth factor 1; HGPA: High glucose and palmitic acid; OCR: Oxygen consumption rate; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha.
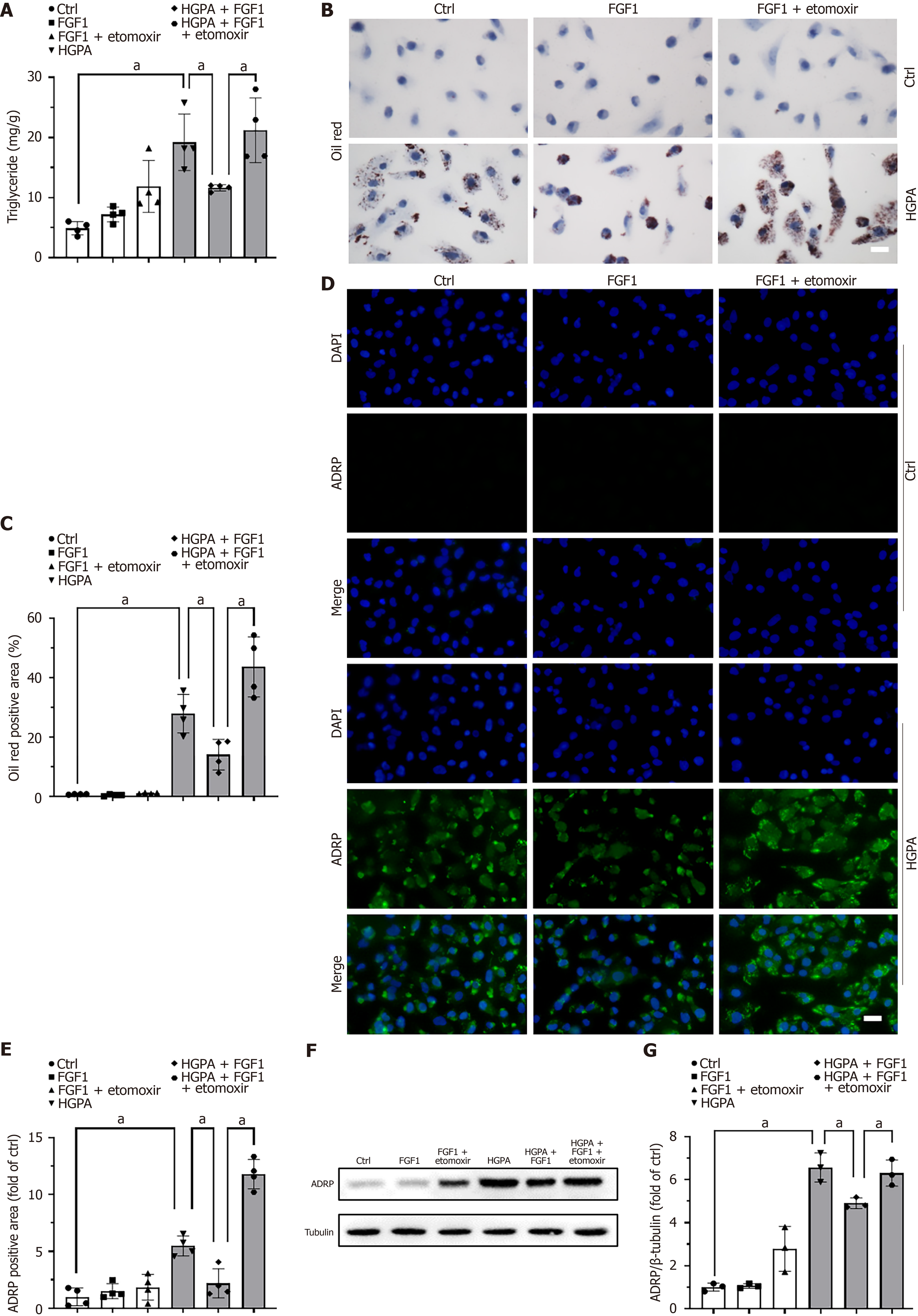
Figure 7 Fibroblast growth factor 1 reduces lipid accumulation in high glucose and palmitate acid-treated human kidney-2 cells by enhancing fatty acid beta-oxidation.
A: Triglyceride content measured to assess lipid accumulation in high glucose and palmitate acid-treated human kidney-2 cells with or without fibroblast growth factor 1 and etomoxir treatment; B: Lipid deposition visualized by Oil Red O staining; C: Quantification of Oil Red O staining; D: Adipose differentiation related protein (ADRP) expression evaluated by immunofluorescence; E: Quantification of ADRP immunofluorescence; F: ADRP protein expression detected by Western blot; G: Quantification of Western blot results. Three to four independent experiments were performed for each analysis. Data were presented as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05. ADPR: Adipose differentiation related protein; Ctrl: Control; Etomoxir: A high selective inhibitor of carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A; FGF1: Fibroblast growth factor 1; HGPA: High glucose and palmitic acid.
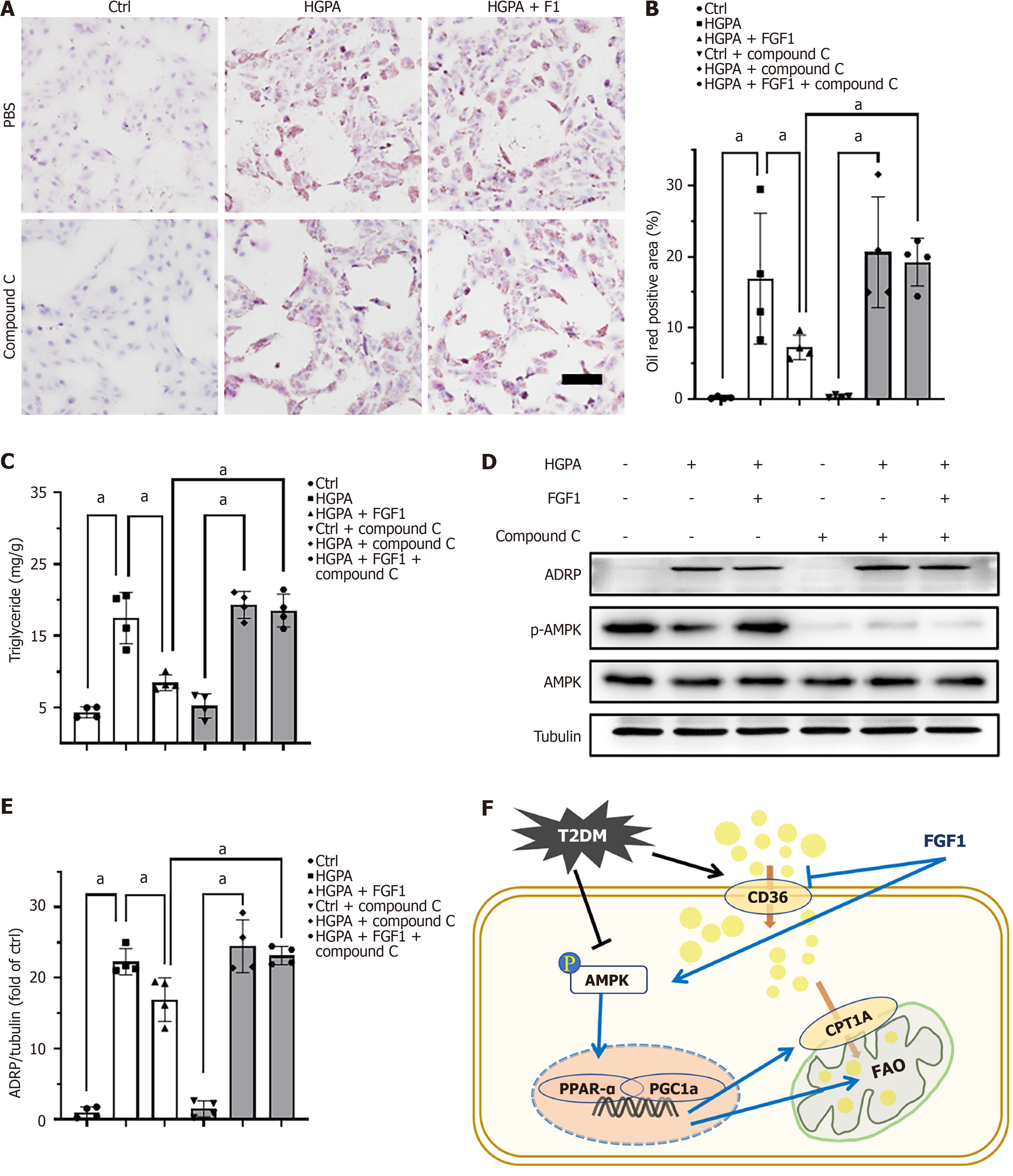
Figure 8 Fibroblast growth factor 1 reduces lipid accumulation by activating the AMP-activated protein kinase pathway.
A: Lipid accumulation assessed by Oil Red O staining in high glucose and palmitate acid-treated human kidney-2 cells with or without fibroblast growth factor 1 and compound C treatment; B: Quantification of Oil Red O staining; C: Triglyceride content measured to quantify lipid accumulation; D: AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation and adipose differentiation related protein expression detected by Western blot; E: Quantification of adipose differentiation related protein Western blot; F: Schematic illustration of the protective effects of fibroblast growth factor 1 in diabetic nephropathy and high glucose and palmitate acid-treated human kidney-2 cells. Three to four independent experiments were performed for each analysis. aP < 0.05. ADPR: Adipose differentiation related protein; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; CPT1a: Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A; Ctrl: Control; FGF1: Fibroblast growth factor 1; FAO: Fatty acid beta-oxidation; HGPA: High glucose and palmitic acid; PGC1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma co-activator-1 alpha; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Citation: Li YJ, Ge HY, Zhang GG, Chen HY, Xi YJ, Wang K, Huang YL, Zhang C, Fan X, Yan XQ. Fibroblast growth factor 1 alleviates diabetic nephropathy by reducing renal lipid accumulation in diabetic kidney. World J Diabetes 2026; 17(2): 112475
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v17/i2/112475.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v17.i2.112475