©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Diabetes. Jan 15, 2026; 17(1): 115685
Published online Jan 15, 2026. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v17.i1.115685
Published online Jan 15, 2026. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v17.i1.115685
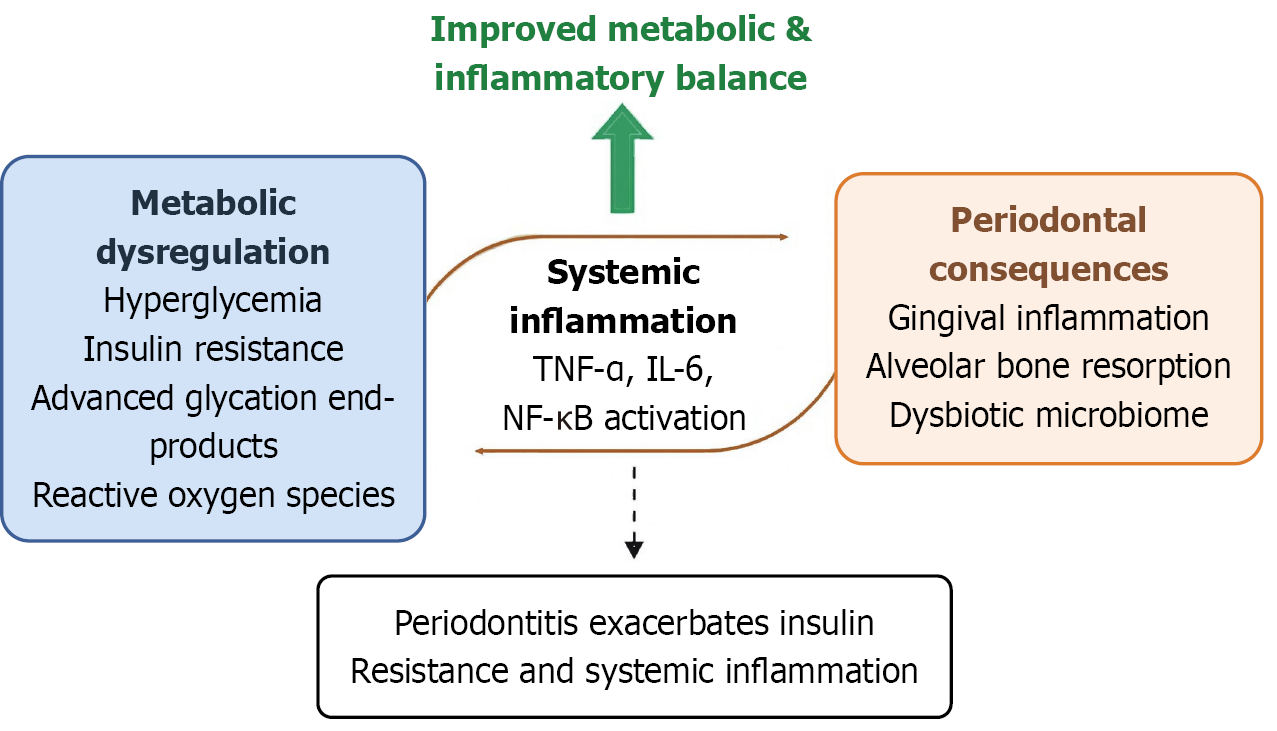
Figure 1 Proposed mechanisms linking metabolic-inflammatory imbalance and periodontal complications in type 2 diabetes.
Chronic hyperglycaemia, insulin resistance, and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes promote systemic inflammation via increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6) and activation of nuclear factor kappa B signaling. These processes impair host-microbiome homeostasis, leading to gingival inflammation, alveolar bone resorption, and dysbiotic microbial changes. Conversely, periodontitis aggravates systemic inflammation and insulin resistance, forming a bidirectional pathogenic loop. Improved metabolic and inflammatory balance may disrupt this cycle and protect oral health. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-6: Interleukin-6; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B.
- Citation: Tang HW, Zhang N. Improving metabolic and inflammatory balance prevents periodontal complications in diabetes. World J Diabetes 2026; 17(1): 115685
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v17/i1/115685.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v17.i1.115685