©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Diabetes. Jan 15, 2026; 17(1): 112942
Published online Jan 15, 2026. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v17.i1.112942
Published online Jan 15, 2026. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v17.i1.112942
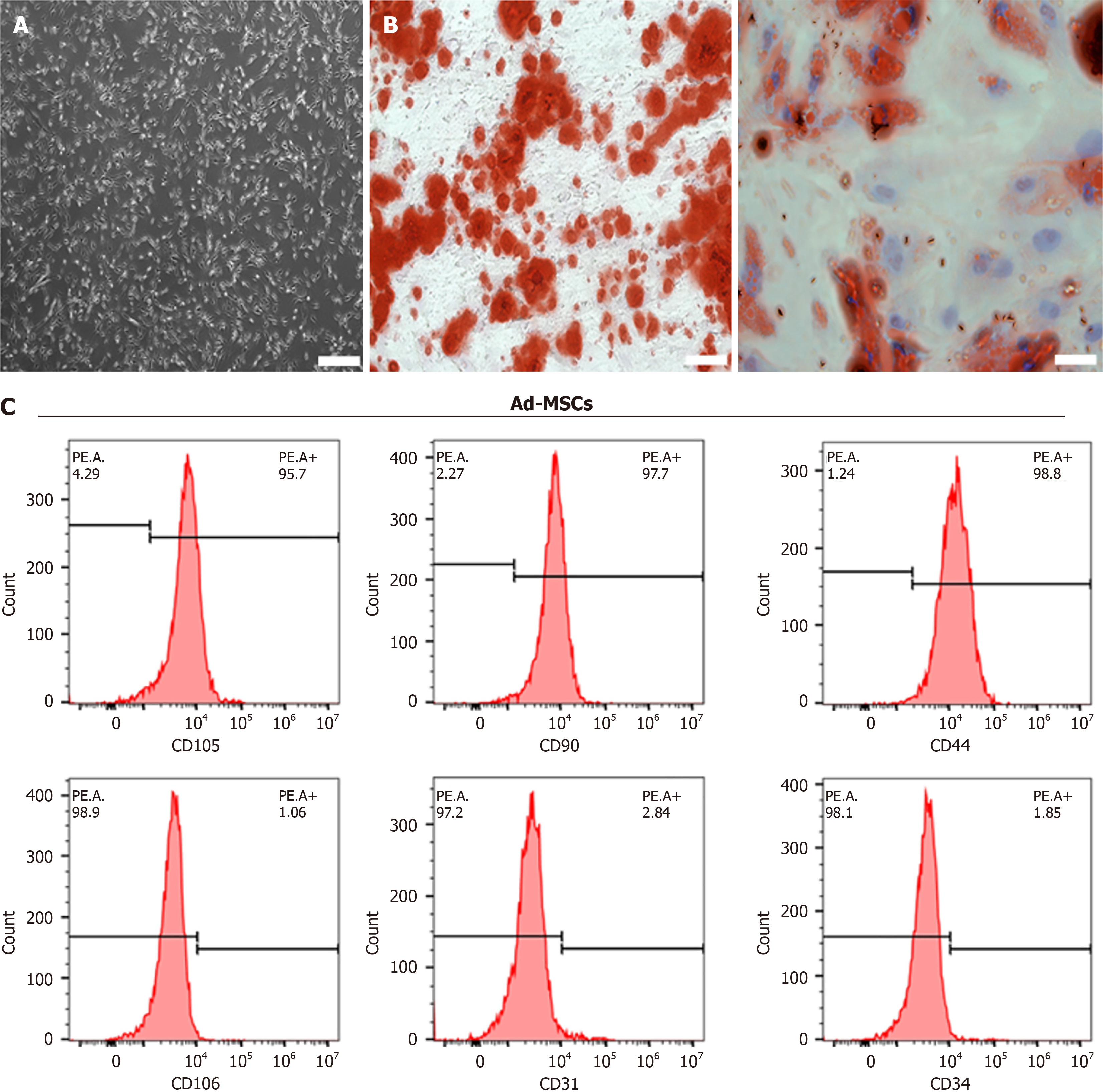
Figure 1 Characterization of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
A: Morphology of third-passage adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (Ad-MSCs). Scale bar = 200 μm; B: Osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation potential of Ad-MSCs. Scale bar = 100 μm; C: Flow cytometry analysis of surface markers on Ad-MSCs, including CD105, CD90, CD44, CD106, CD31, and CD34. Ad-MSCs: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
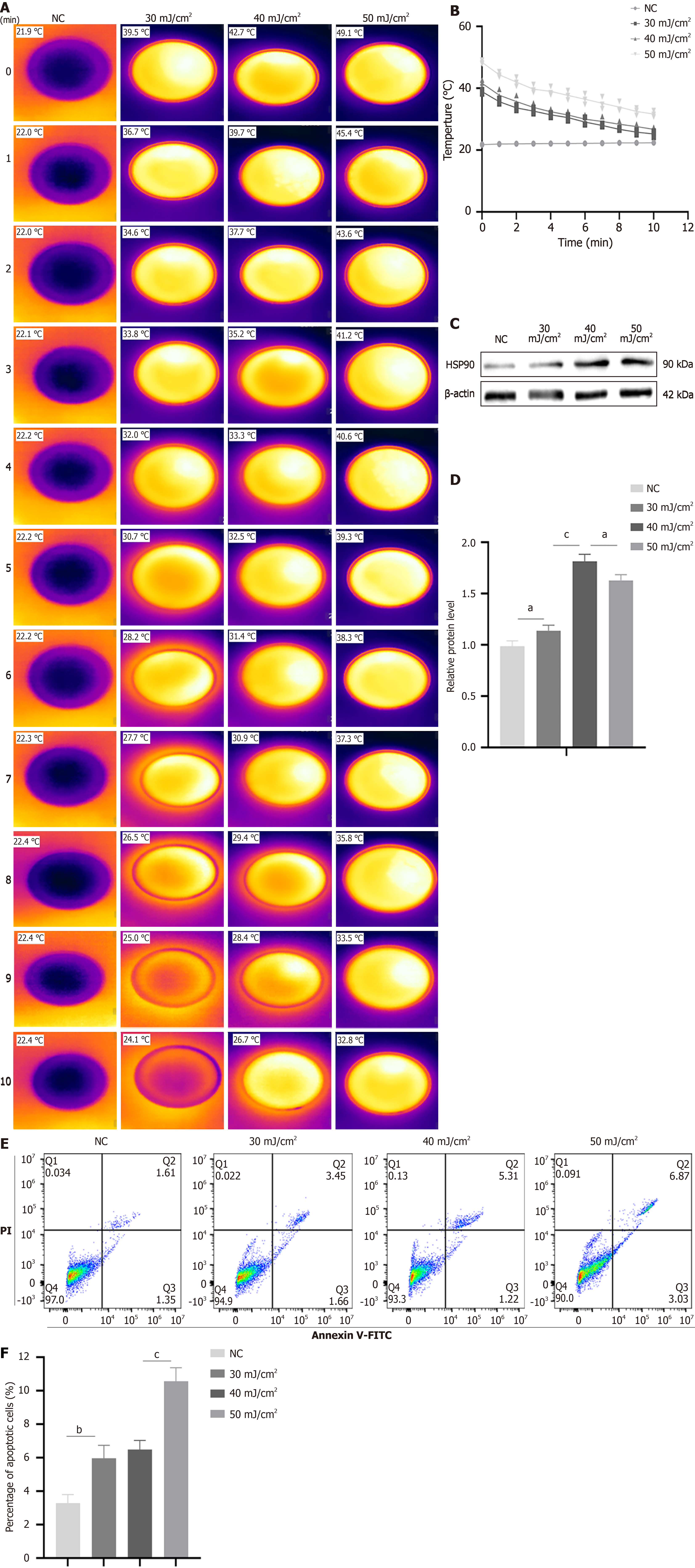
Figure 2 Low-energy fractional CO2 laser-induced heat stress enhances heat shock protein 90 expression in adipose-derived mese
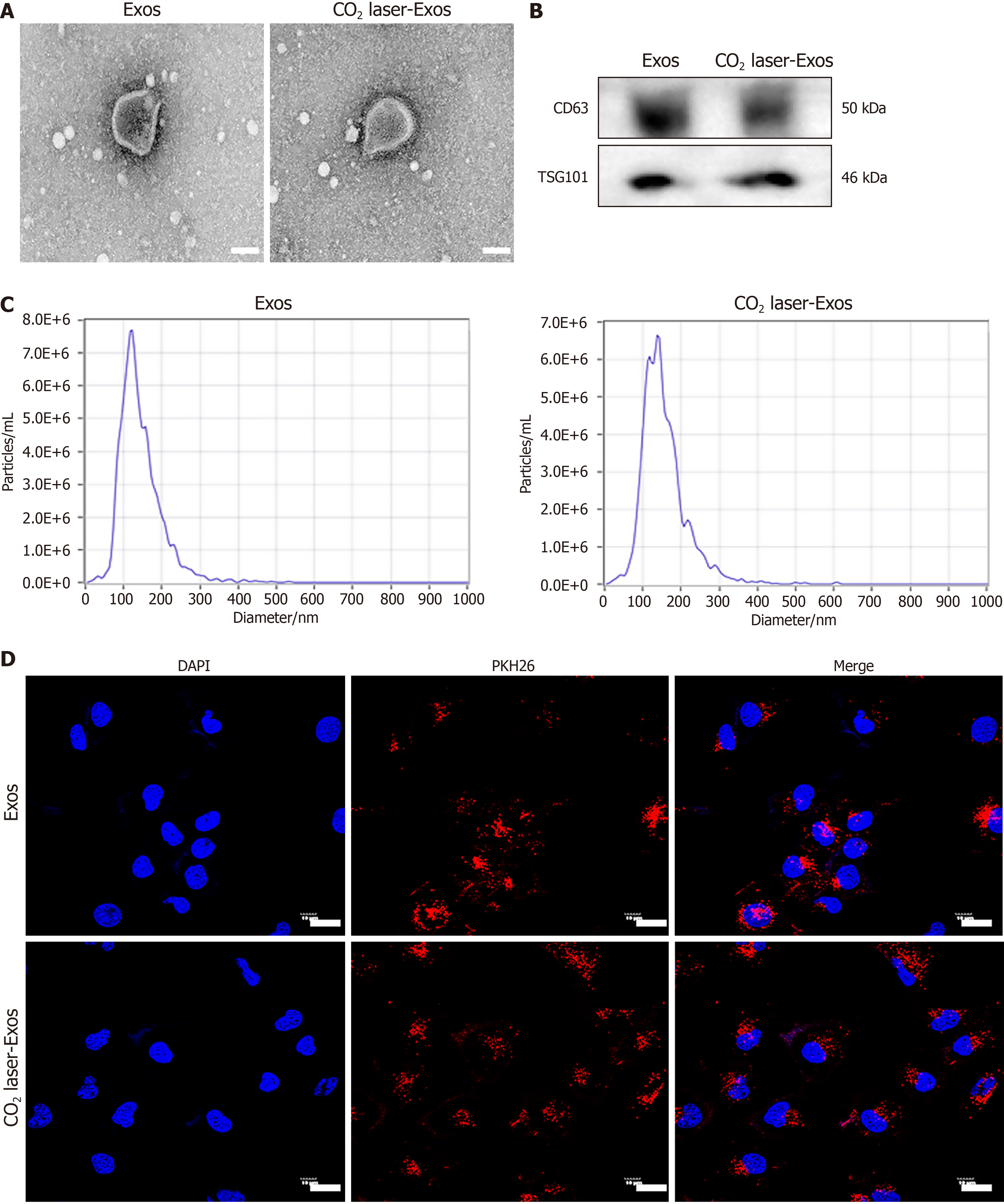
Figure 3 Characterization of exosomes.
A: Transmission electron microscopy images showing the morphology of exosomes (Exos) and CO2 laser-Exos. Scale bar = 100 nm; B: Western blot analysis of exosomal markers CD63 and tumor susceptibility gene 101 in Exos and CO2 laser-Exos; C: Nanoparticle tracking analysis of size distribution of Exos and CO2 laser-Exos; D: Confocal laser scanning microscopy showing the uptake of PKH26-labeled Exos and CO2 laser-Exos by human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Exos and nuclei were stained red and blue, respectively. Scale bar = 10 μm. Exos: Exosomes; CO2 laser-Exos: Exosomes derived from CO2 laser-preconditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells; TSG101: Tumor susceptibility gene 101.
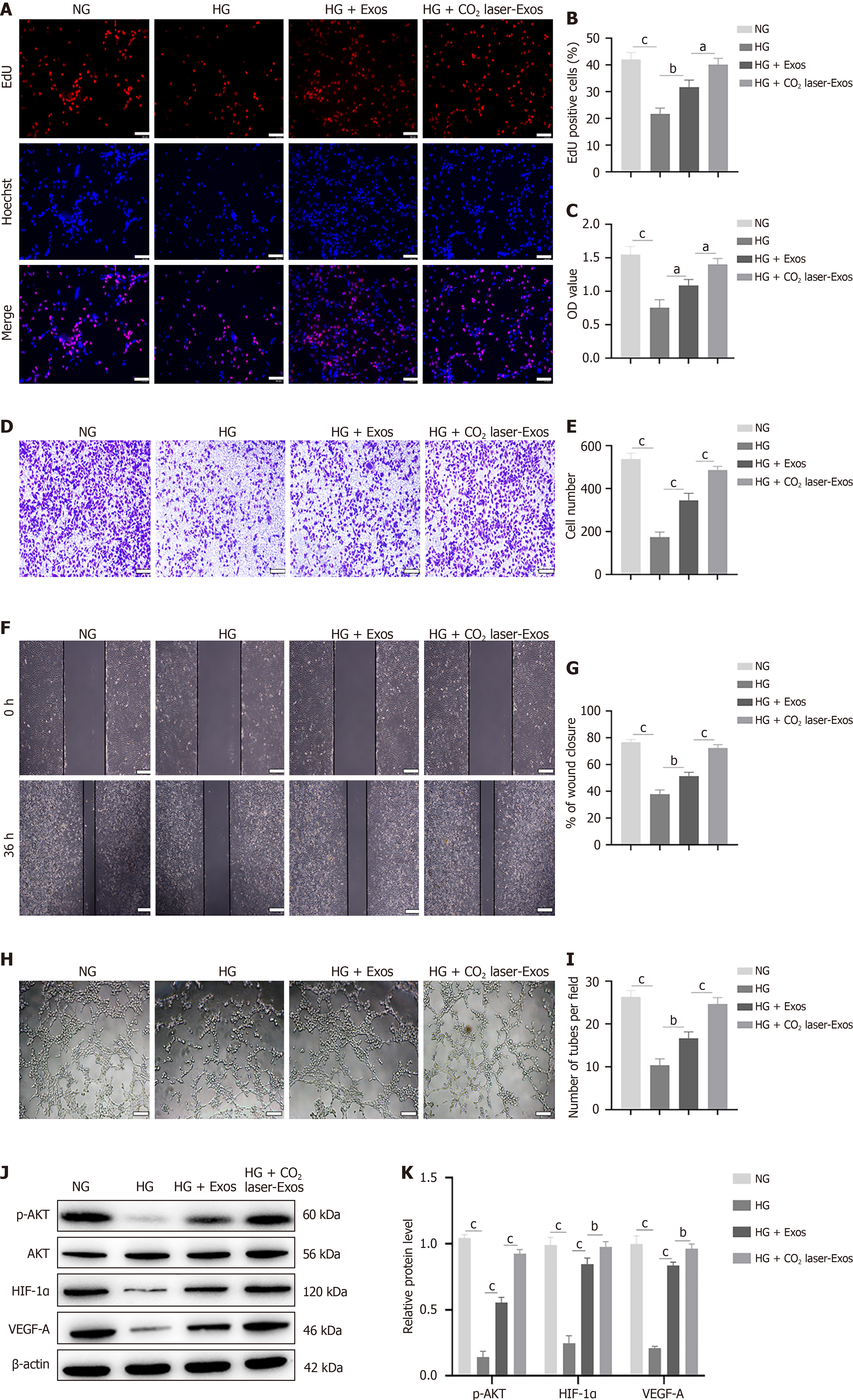
Figure 4 CO2 laser-exosomes promote angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). A and B: 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine incorporation assay to assess the proliferative capacity of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Scale bar = 100 μm; C: Cell Counting Kit-8 assay to evaluate the viability of HUVECs after treatment with high glucose and exosomes; D and E: Transwell migration assay to evaluate the migratory ability of HUVECs. Scale bar = 200 μm; F and G: In vitro wound healing assay to assess cell migration. Scale bar = 200 μm; H and I: Tube formation assay to evaluate the ability of HUVECs to form capillary-like structures. Scale bar = 200 μm; J and K: Western blot analysis of the expression levels of phosphorylated protein kinase B, protein kinase B, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, and vascular endothelial growth factor-A. NG: Normal glucose; HG: High glucose; Exos: Exosomes; CO2 laser-Exos: Exosomes derived from CO2 laser-preconditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells; EdU: 5-Ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine; AKT: Protein kinase B; p-AKT: Phosphorylated protein kinase B; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; VEGF-A: Vascular endothelial growth factor-A.
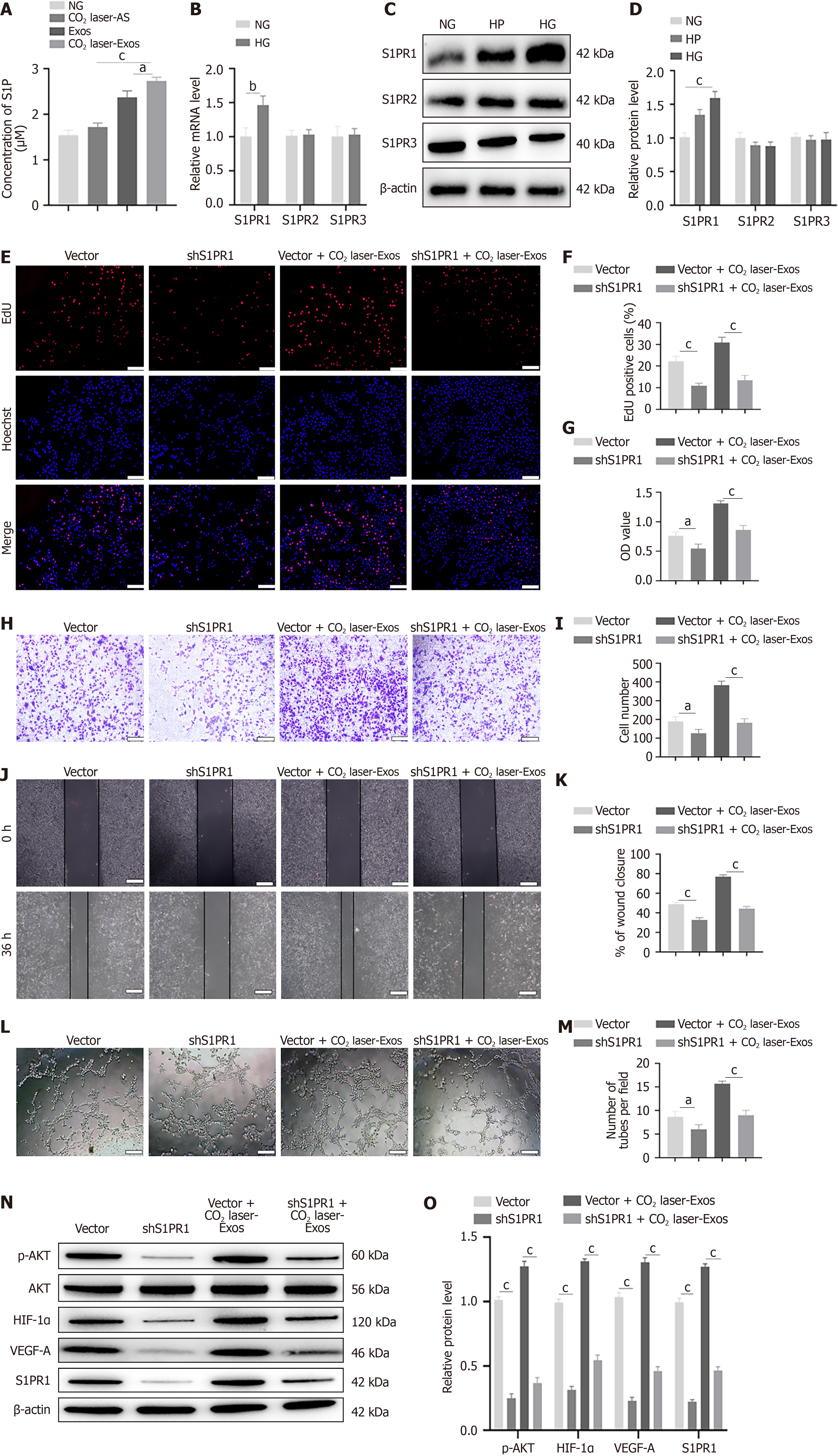
Figure 5 The sphingosine-1-phosphate/sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signaling axis mediates exosomes derived from CO2 laser-preconditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-induced angiogenesis.
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). A: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis of sphingosine-1-phosphate concentrations in activated supernatant from non-irradiated adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (Ad-MSCs), activated supernatant from laser-irradiated Ad-MSCs, exosomes, and exosomes derived from CO2 laser-preconditioned Ad-MSCs; B: Relative mRNA expression levels of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor (S1PR1)-3 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs); C and D: Western blot and quantitative analysis of the relative protein expression of S1PR1-3 in HUVECs; E and F: 5-Ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine incorporation assay to evaluate HUVEC proliferation. Scale bar = 100 μm; G: Cell Counting Kit-8 assay to assess HUVEC viability; H and I: Transwell migration assay to evaluate HUVEC motility. Scale bar = 200 μm; J and K: In vitro wound healing assay to assess migration. Scale bar = 200 μm; L and M: Tube formation assay to examine capillary-like network formation by HUVECs. Scale bar = 200 μm; N and O: Western blot analysis of the expression levels of phosphorylated protein kinase B, protein kinase B, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, vascular endothelial growth factor-A, and S1PR1. NC: Activated supernatant from non-irradiated adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells; NG: Normal glucose; HG: High glucose; HP: High permeability; CO2 laser-AS: Activated supernatant from laser-irradiated adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells; Exos: Exosomes; CO2 laser-Exos: Exosomes derived from CO2 laser-preconditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells; EdU: 5-Ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine; S1P: Sphingosine-1-phosphate; S1PR: Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor; shS1PR: Short hairpin RNA targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor; AKT: Protein kinase B; p-AKT: Phosphorylated protein kinase B; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; VEGF-A: Vascular endothelial growth factor-A.
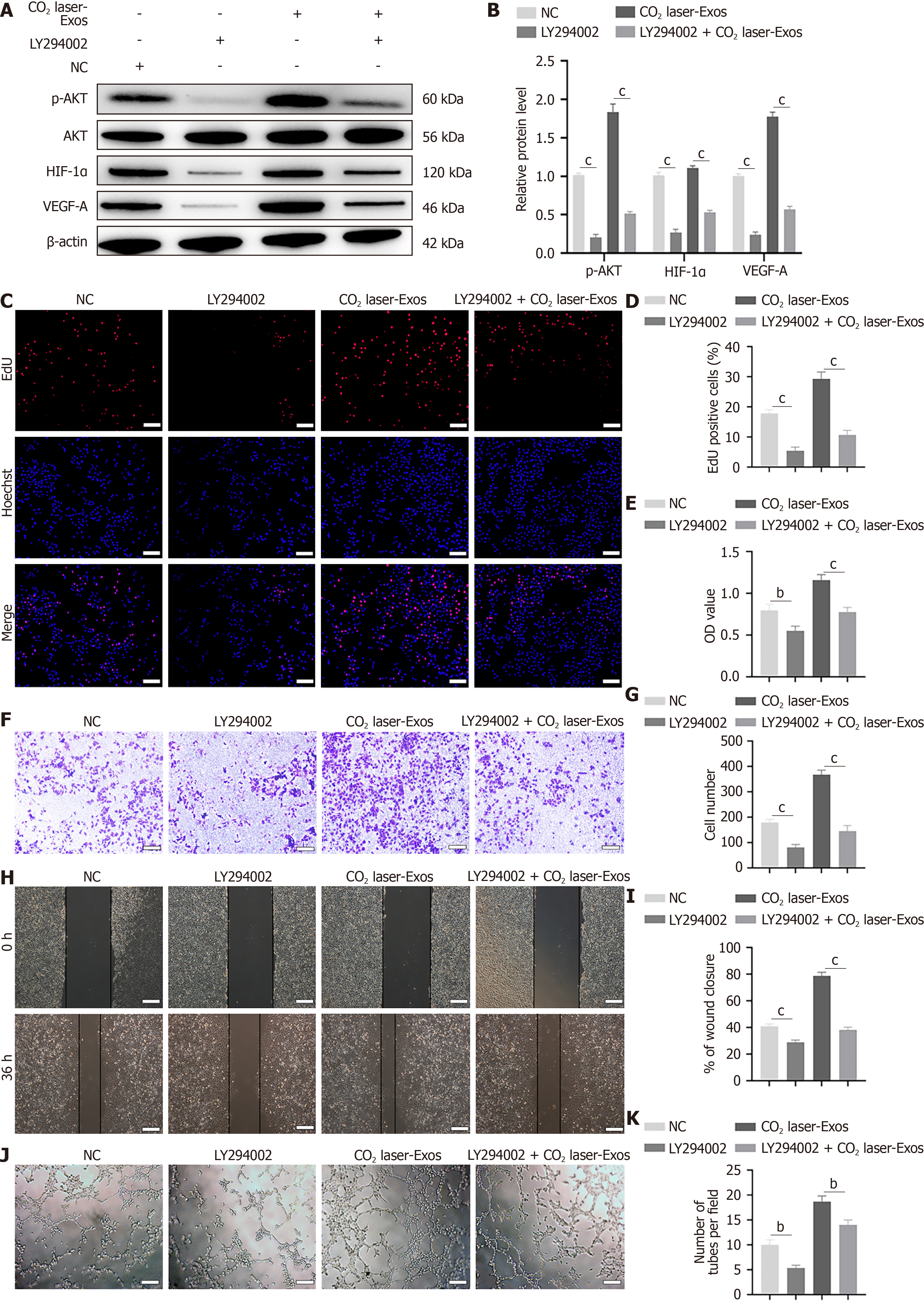
Figure 6 LY294002 suppresses exosomes derived from CO2 laser-preconditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells -induced an
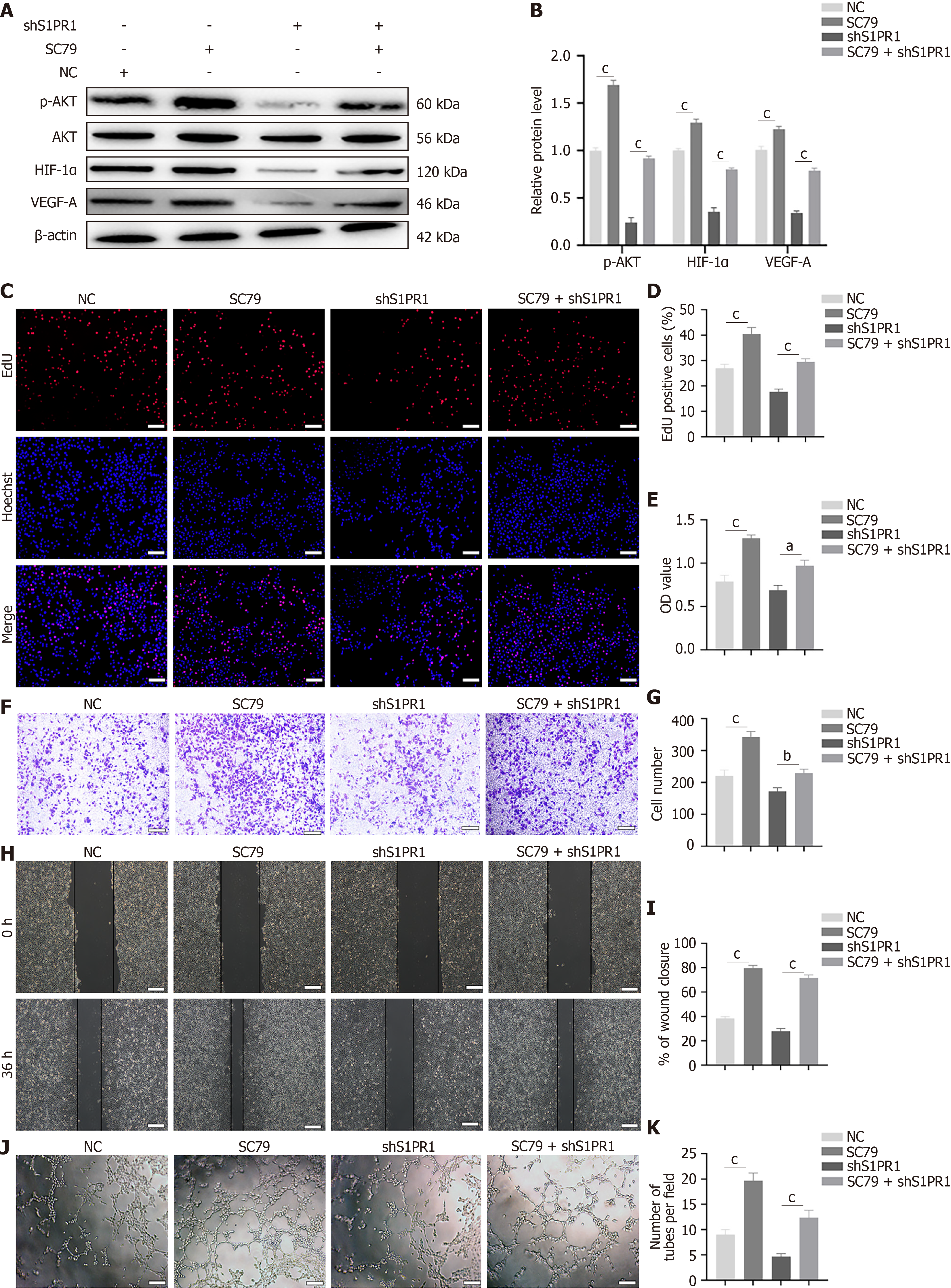
Figure 7 SC79 enhances exosomes derived from CO2 laser-preconditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-induced angio
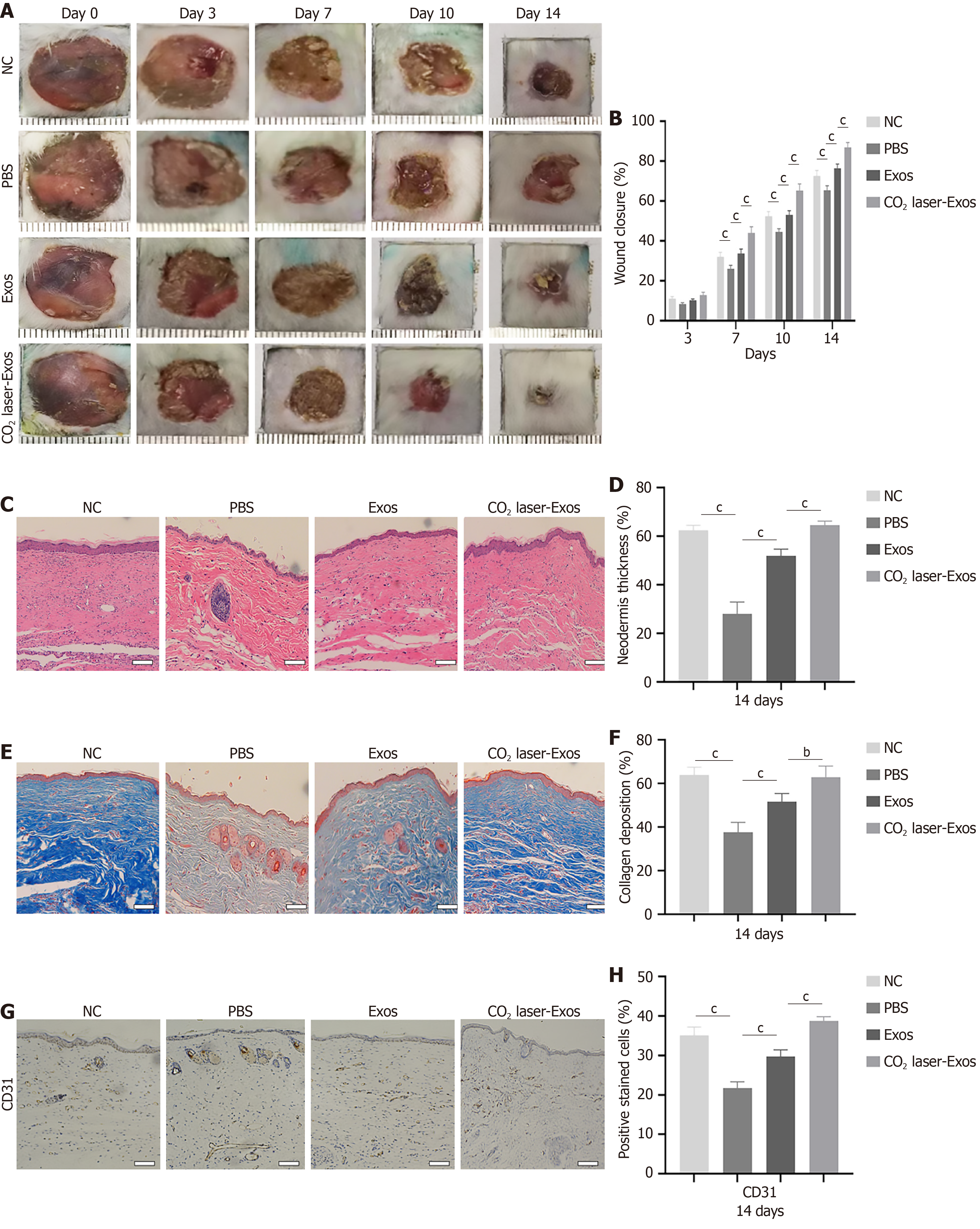
Figure 8 Exosomes derived from CO2 laser-preconditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerate angiogenesis in diabetic wounds.
bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). A and B: Representative images of full-thickness skin defects in non-diabetic mice and diabetic mice treated with phosphate-buffered saline, exosomes, or exosomes derived from CO2 laser-preconditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on 0 day, 3 days, 7 days, 10 days, and 14 days post-surgery; C and D: Quantification of hematoxylin and eosin staining and skin thickness on day 14. Scale bar = 100 μm; E and F: Quantification of Masson’s trichrome staining and collagen deposition on day 14. Scale bar = 100 μm; G and H: Representative immu
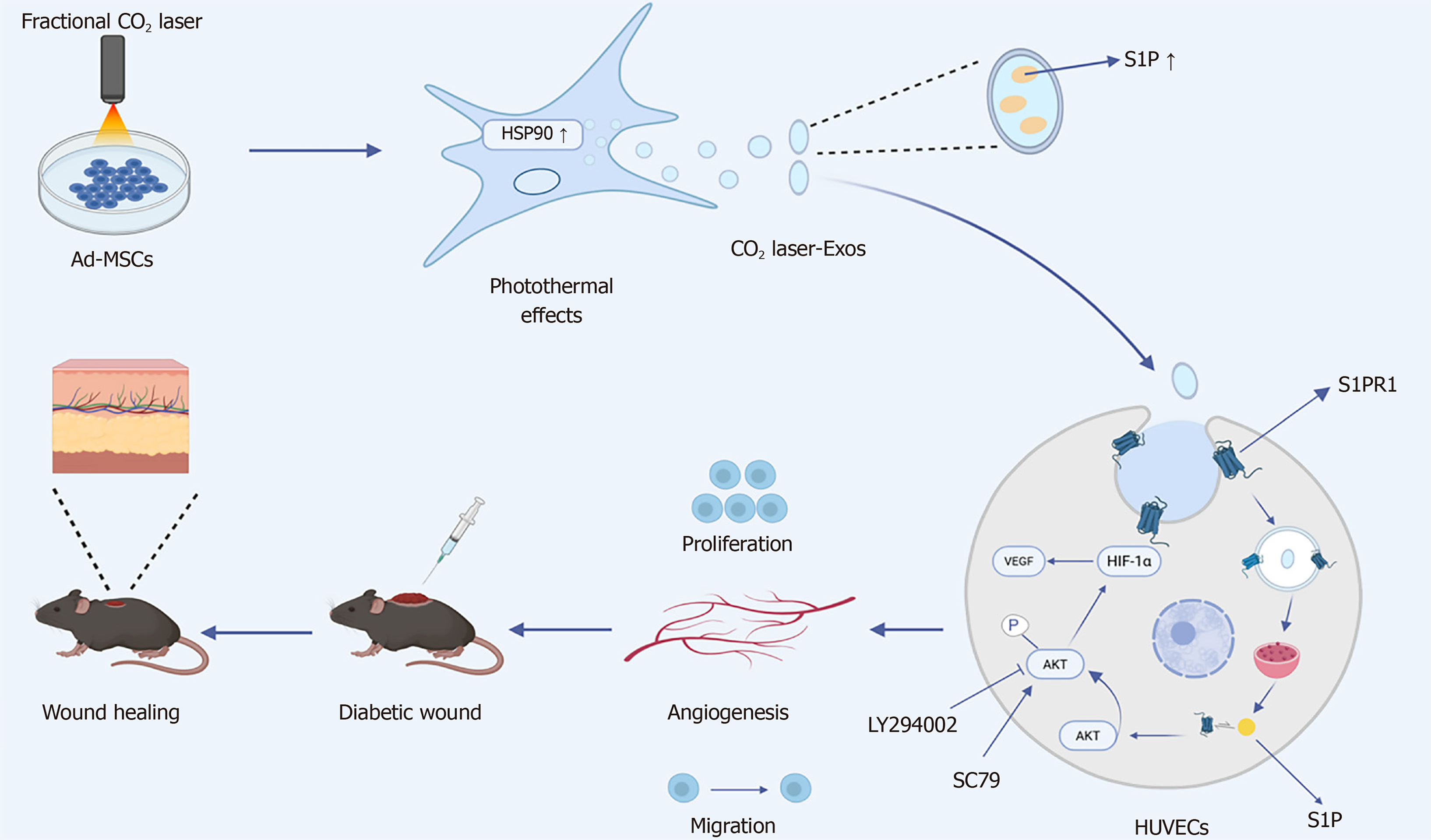
Figure 9 Schematic illustration showing that low-energy fractional CO2 laser enhances heat-shock protein 90 expression in adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells via photothermal effects, thereby improving the biological activity of their derived exosomes.
These exosomes derived from CO2 laser-preconditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis and accelerate diabetic wound healing by activating the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor/protein kinase B/hypoxia-inducible factor-1α signaling pathway. Ad-MSCs: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells; CO2 laser-Exos: Exosomes derived from CO2 laser-preconditioned adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells; HSP90: Heat-shock protein 90; AKT: Protein kinase B; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; VEGF-A: Vascular endothelial growth factor-A; S1P: Sphingosine-1-phosphate; S1PR: Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor; HUVECs: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
- Citation: Chen JY, Ji Z, Guo K, Wang HN, Zhu CC, Li T, Zhao XB, Wang YT, Li Q, Jin PS, Li XY. Fractional carbon dioxide laser-induced photothermal activation of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes accelerates diabetic wound healing by enhancing angiogenesis. World J Diabetes 2026; 17(1): 112942
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v17/i1/112942.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v17.i1.112942