©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Diabetes. Jan 15, 2026; 17(1): 112027
Published online Jan 15, 2026. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v17.i1.112027
Published online Jan 15, 2026. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v17.i1.112027
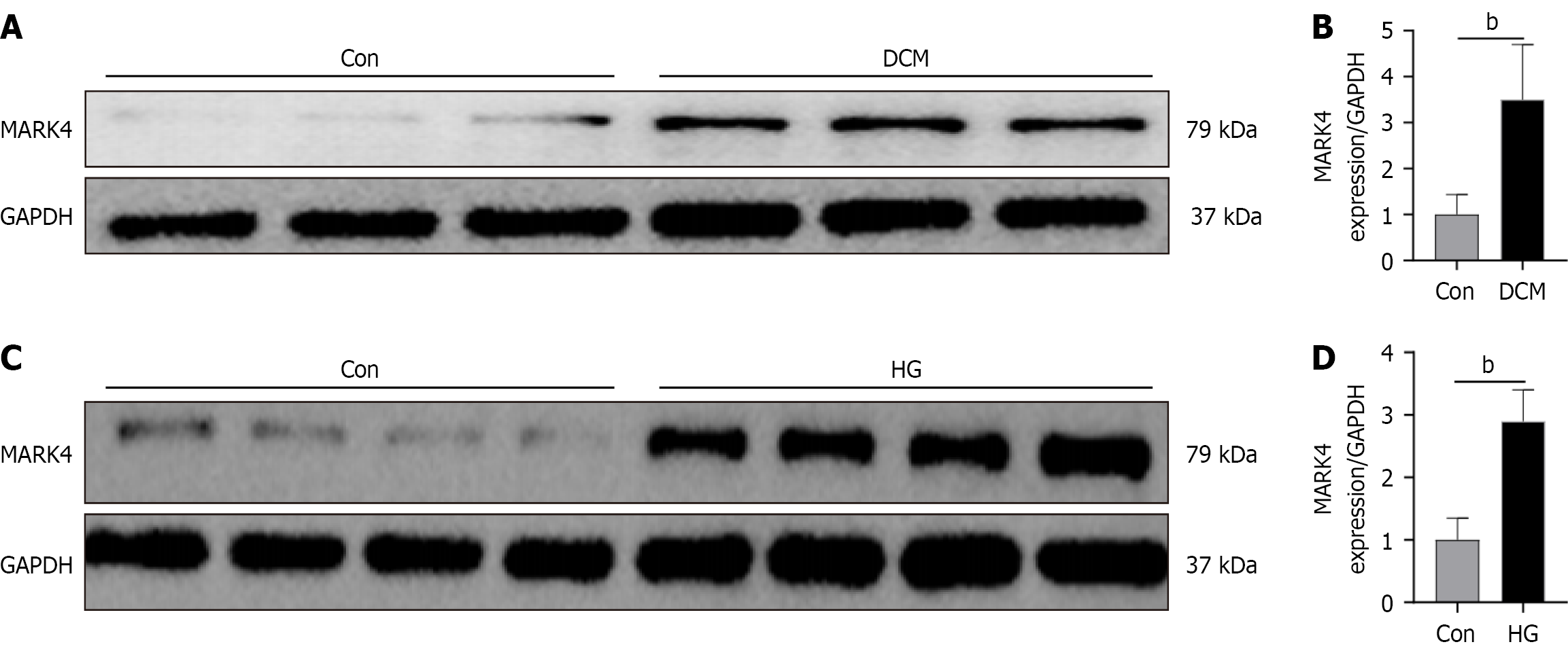
Figure 1 Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 was upregulated in diabetic cardiomyopathy models.
A and B: Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 protein levels in diabetic cardiomyopathy model mice; C and D: Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 protein levels in cardiomyocytes stimulated with 200 μM palmitic acid and 33.3 mmol/L glucose. Values are mean ± SD (n = 4). aP < 0.05, and bP < 0.01. Con: Control; DCM: Diabetic cardiomyopathy; MARK4: Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; HG: High glucose.
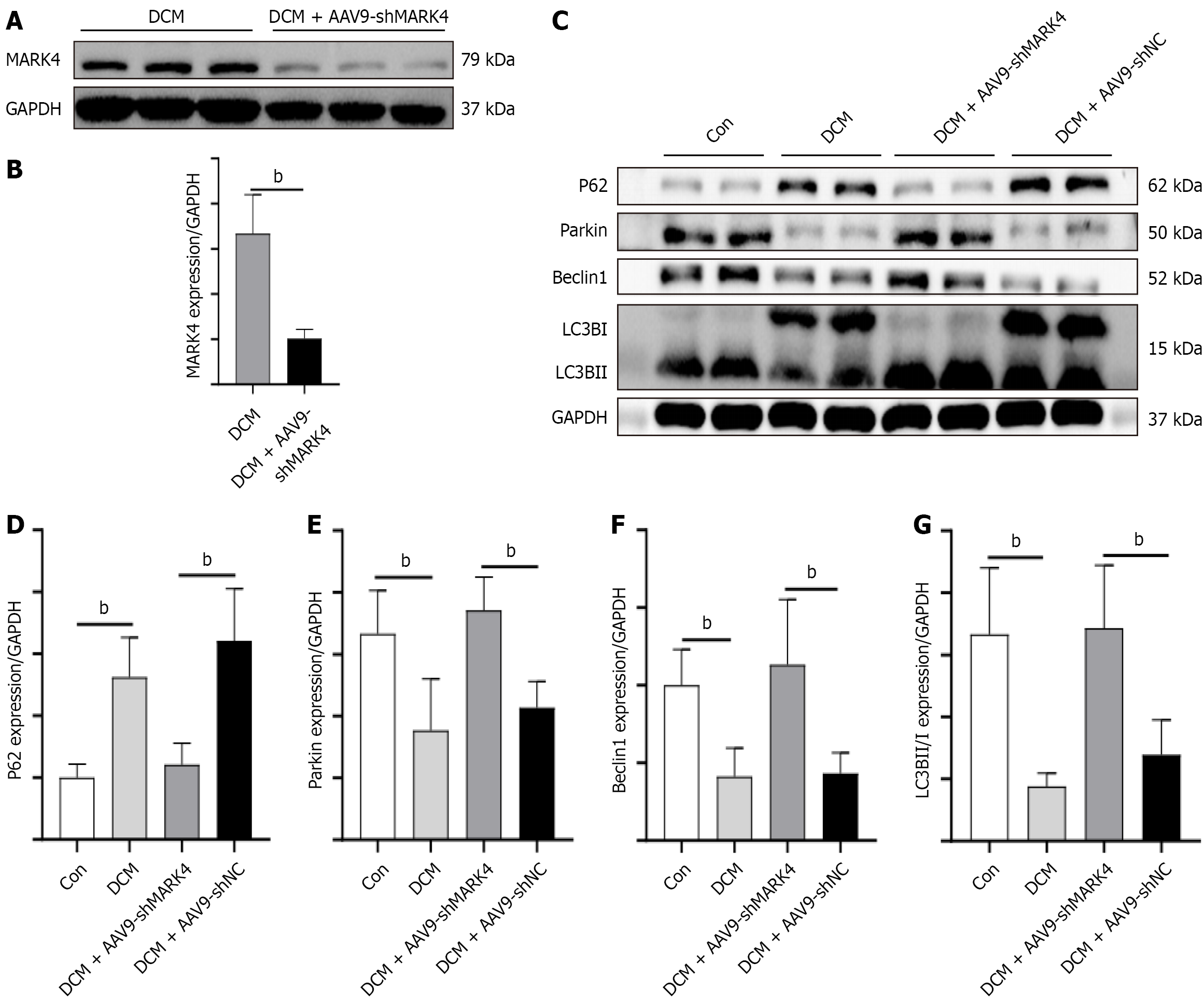
Figure 2 Effect of microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 knockdown on mitophagy in mice with diabetic cardiomyopathy.
A and B: Evaluation of microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 knockdown efficiency in diabetic cardiomyopathy model mice via western blotting quantification; C-G: Western blotting quantification of p62, Parkin, Beclin1, and microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3B. Values are mean ± SD (n = 4). aP < 0.05, and bP < 0.01. DCM: Diabetic cardiomyopathy; MARK4: Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; sh: Small hairpin; Con: Control; NC: Negative control; LC3B: Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3B; AAV9: Adeno-associated virus 9.
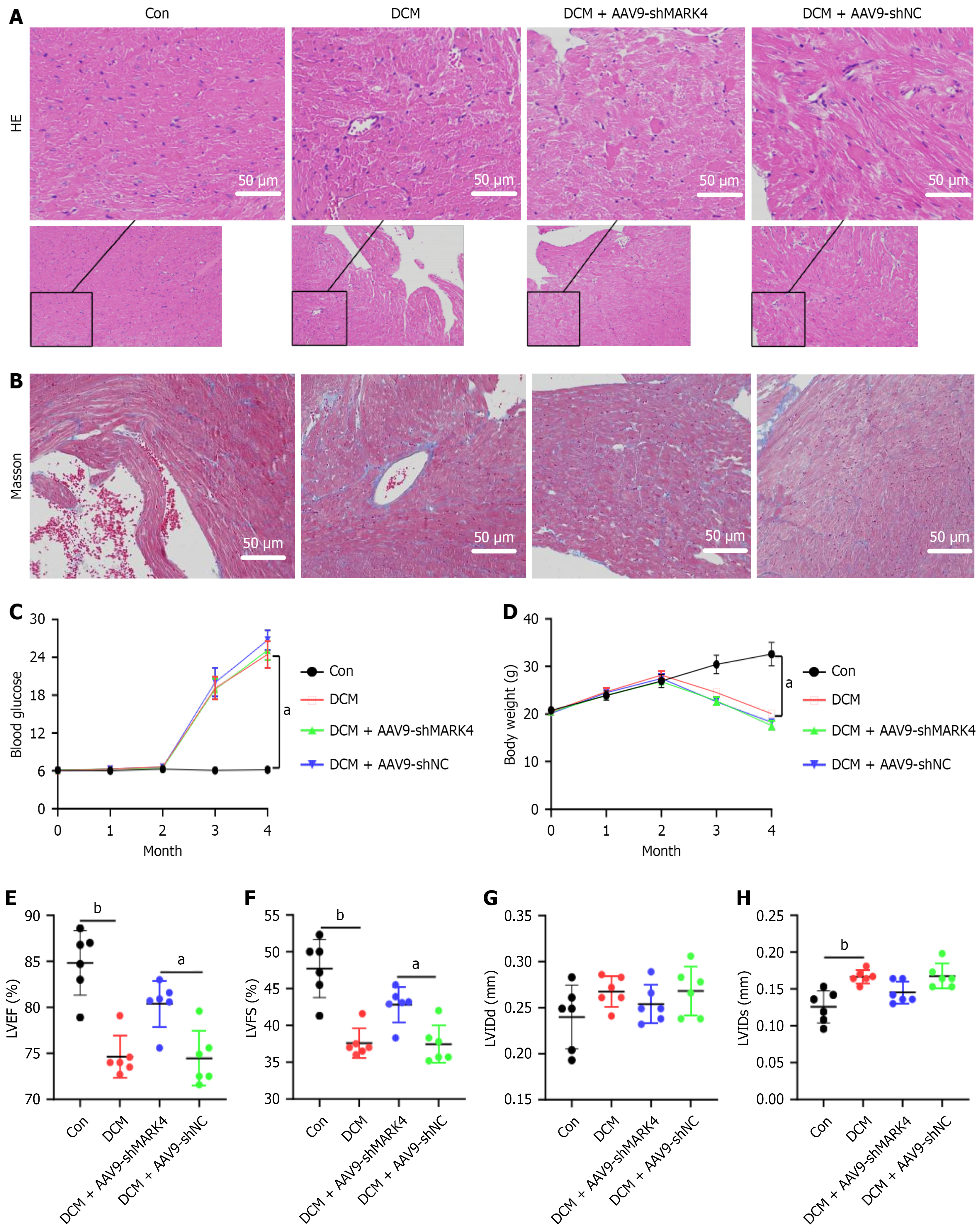
Figure 3 Impact of microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 knockdown on myocardial injury and fibrosis, blood glucose, body weight, and cardiac function and structure in diabetic cardiomyopathy model mice.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of left ventricular tissue (× 200); B: Masson’s staining of left ventricular tissue (× 200); C: Blood glucose levels; D: Body weights; E: The left ventricular ejection fractions; F: The left ventricular short axis shortening rates; G: Left ventricular end-diastolic diameters; H: Left ventricular end-systolic diameters. Values are mean ± SD (n = 4). aP < 0.05, and bP < 0.01. HE: Hematoxylin and eosin; Con: Control; DCM: Diabetic cardiomyopathy; MARK4: Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4; sh: Small hairpin; NC: Negative control; LVEF: Left ventricular ejection fractions; LVFS: Left ventricular shortening fraction; LVIDd: Left ventricular end-diastolic diameters; LVIDs: Left ventricular end-systolic diameter; AAV9: Adeno-associated virus 9.
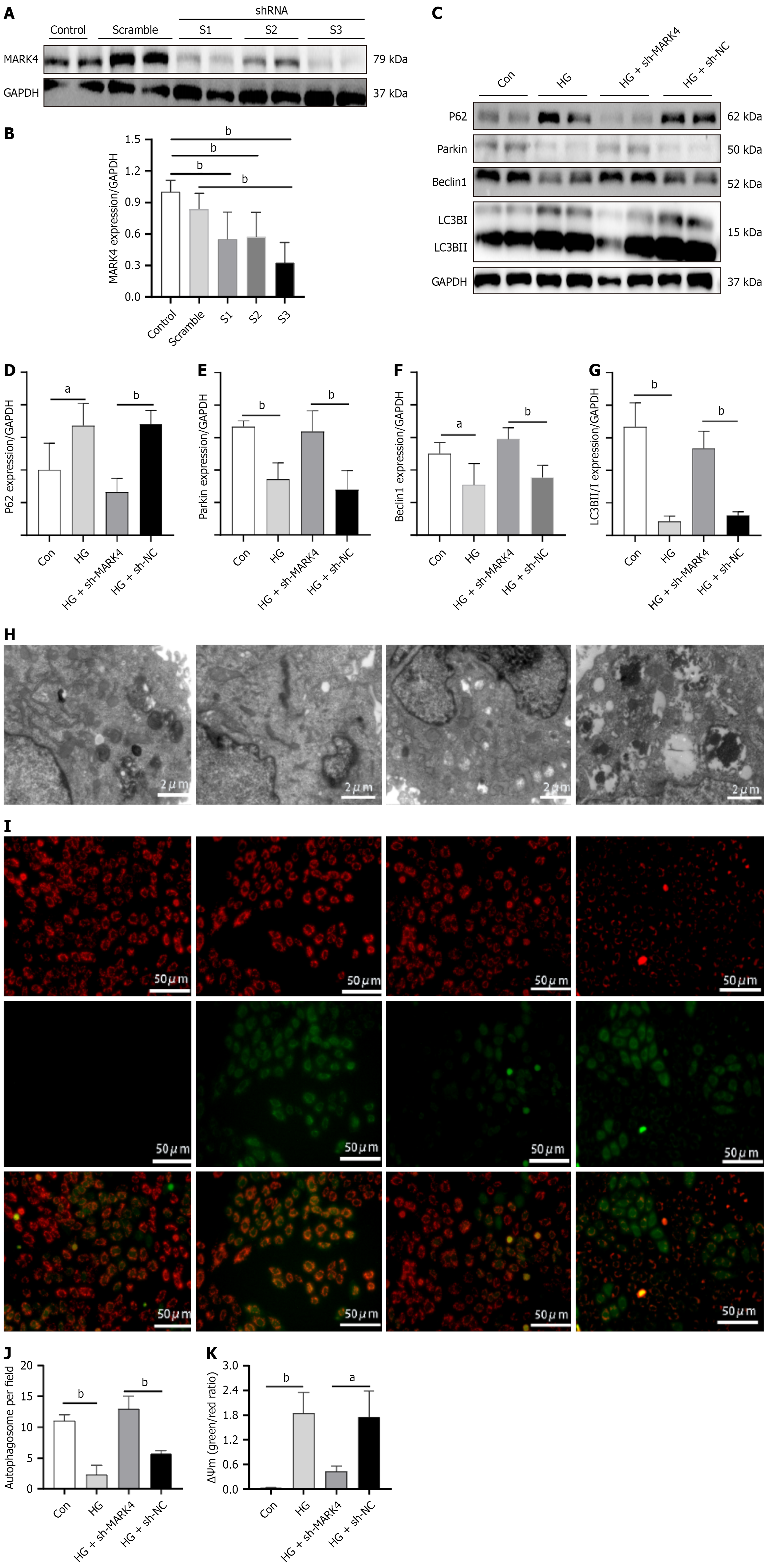
Figure 4 Effect of microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 knockdown on mitophagy and mitochondrial membrane potentials in car
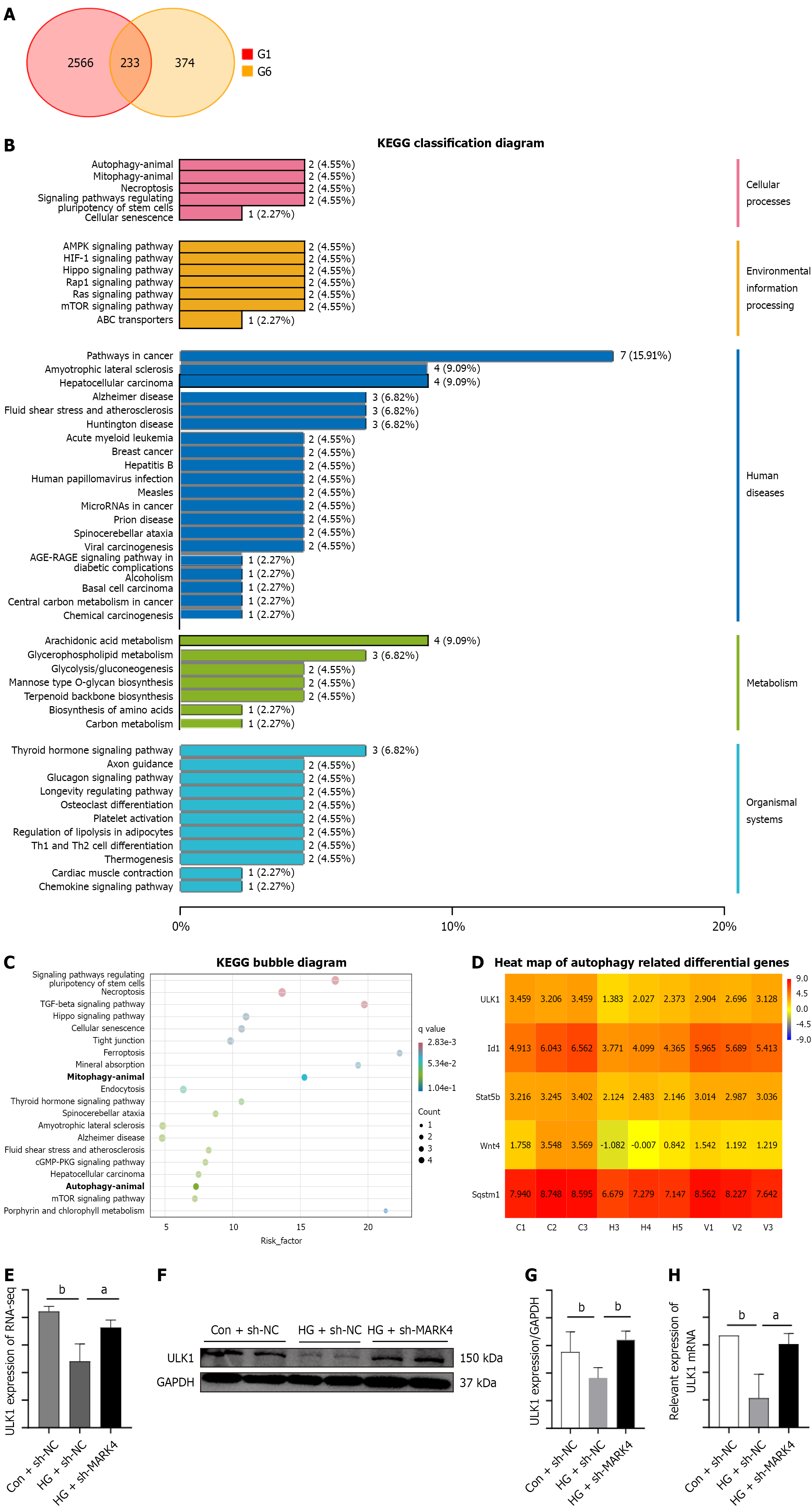
Figure 5 Transcriptomic results and verification of the effects of microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 knockdown.
A: Downregulated genes between the control + small hairpin (sh)-negative control (NC) and high glucose (HG) + sh-NC groups and upregulated genes between the HG + sh-NC and HG + sh-microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 groups are shown as a cross-Venn diagram; B: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes classification of differentially expressed genes; C: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes bubble diagram of the differentially expressed genes; D: Heatmap of differentially expressed genes; E: RNA-seq results of UNC-51-like kinase 1; F-H: Consistency of the western blotting, quantitative real-time PCR, and RNA-seq results. Values are shown as mean ± SD (n = 4). aP < 0.05, and bP < 0.01. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; ULK1: UNC-51-like kinase 1; Con: Control; NC: Negative control; sh: Small hairpin; MARK4: Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; HG: High glucose.
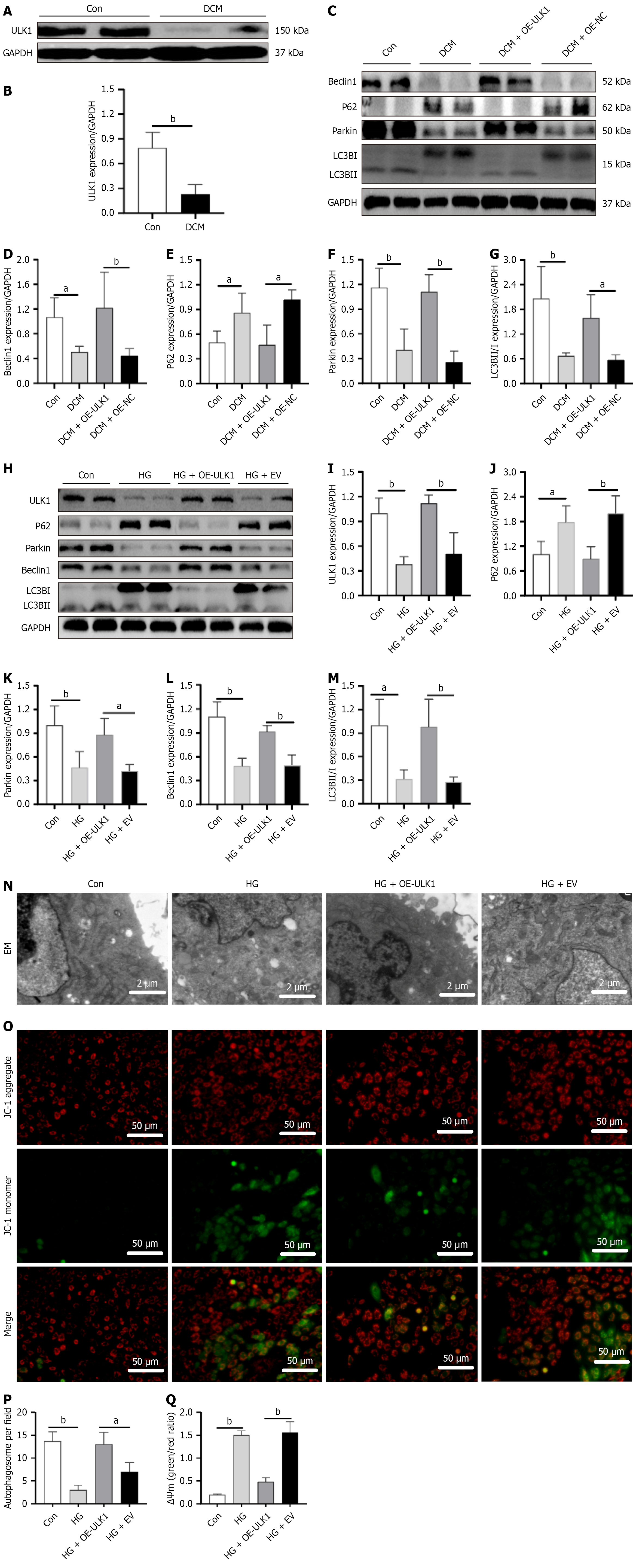
Figure 6 Impact of UNC-51-like kinase 1 upregulation on the mitophagy-associated proteins and the mitochondrial membrane potential in diabetic cardiomyopathy.
A and B: UNC-51-like kinase 1 protein levels in diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) mice; C-G: Western blotting quantification of Beclin1, p62, Parkin, and microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3B proteins in DCM mice; H-M: Western blotting quantification of mitophagy-associated proteins (UNC-51-like kinase 1, p62, Parkin, Beclin1, and microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3B) in DCM cell models; N: Electron micrographs of mitophagy (scale bar: 2 μm); O: Changes in the mitochondrial membrane potential (scale bar: 50 μm); P: Statistical analysis of mitophagy from electron micrographs; Q: Statistical analysis of the mitochondrial membrane potential. Values are mean ± SD (n = 4). aP < 0.05, and bP < 0.01. Con: Control; DCM: Diabetic cardiomyopathy; ULK1: UNC-51-like kinase 1; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; OE: Overexpress; NC: Negative control; LC3B: Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3B; HG: High glucose; EV: Empty vector; EM: Electron microscopy.
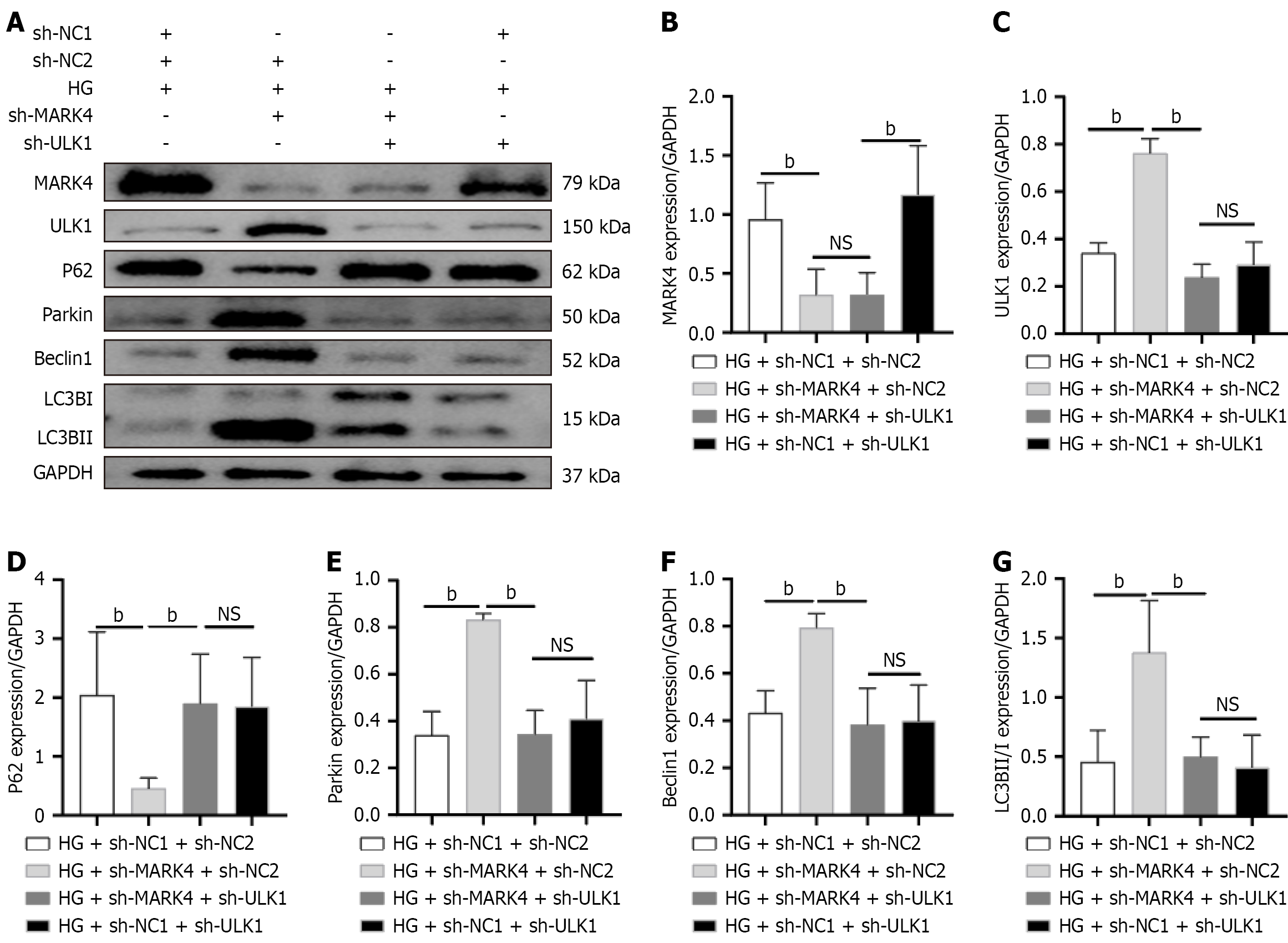
Figure 7 Impact of microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 knockdown on mitophagy was counteracted by UNC-51-like kinase 1 knock
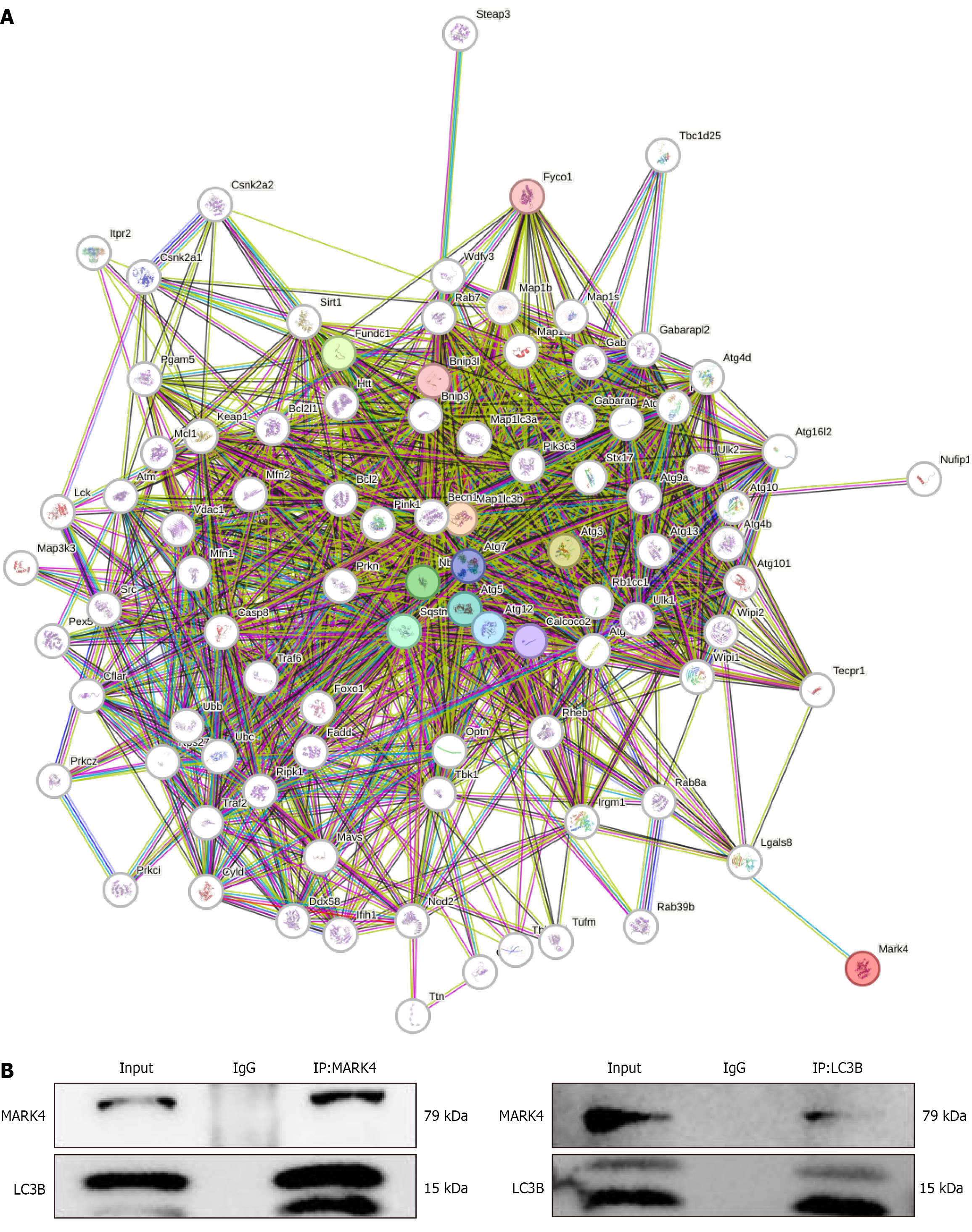
Figure 8 Interaction between microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 and microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3B.
A: Several proteins that interact with microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4; B: Co-immunoprecipitation verification of the interaction between microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 and microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3B in cardiomyocytes (n = 4). Results from triplicate experiments. MARK4: Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4; LC3B: Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3B; IP: Immunoprecipitation.
- Citation: Wu Y, Wang WY, Zhang JQ, Wang S, Zeng Z, Fu L, Li B. Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 exacerbates diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting UNC-51-like kinase 1-mediated mitochondrial autophagy. World J Diabetes 2026; 17(1): 112027
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v17/i1/112027.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v17.i1.112027