©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Sep 15, 2025; 16(9): 110590
Published online Sep 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i9.110590
Published online Sep 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i9.110590
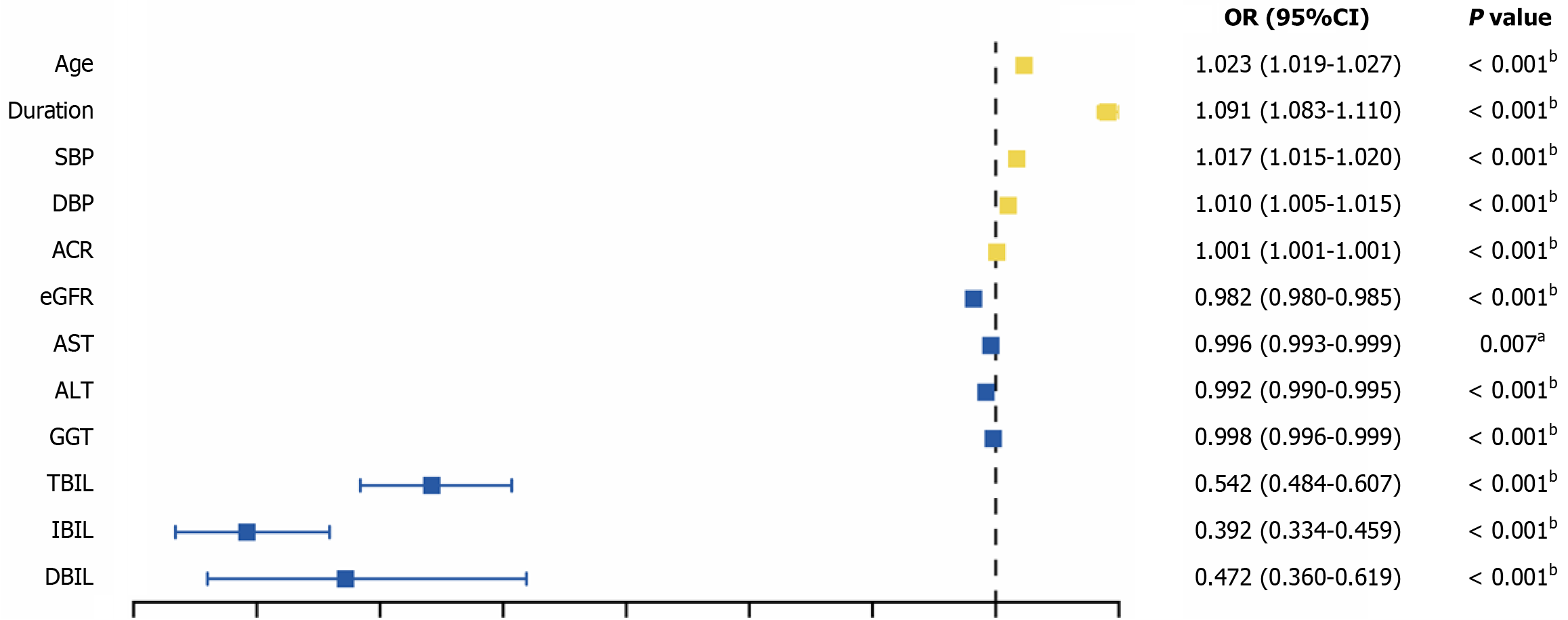
Figure 1 Univariate analysis of the associations between factors associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
Univariate logistic regression models were constructed to explore the correlations between type 2 diabetes mellitus factors and the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. aP < 0.01; bP < 0.001. Statistical significance was determined at a P value < 0.05. OR: Odds ratio; 95%CI: 95% confidence interval; SBP: Systolic blood pressure; DBP: Diastolic blood pressure; ACR: Albumin/creatinine ratio; eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; AST: Aspartate transaminase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; GGT: Gamma-glutamyl transferase; TBIL: Total bilirubin; IBIL: Indirect bilirubin; DBIL: Direct bilirubin.
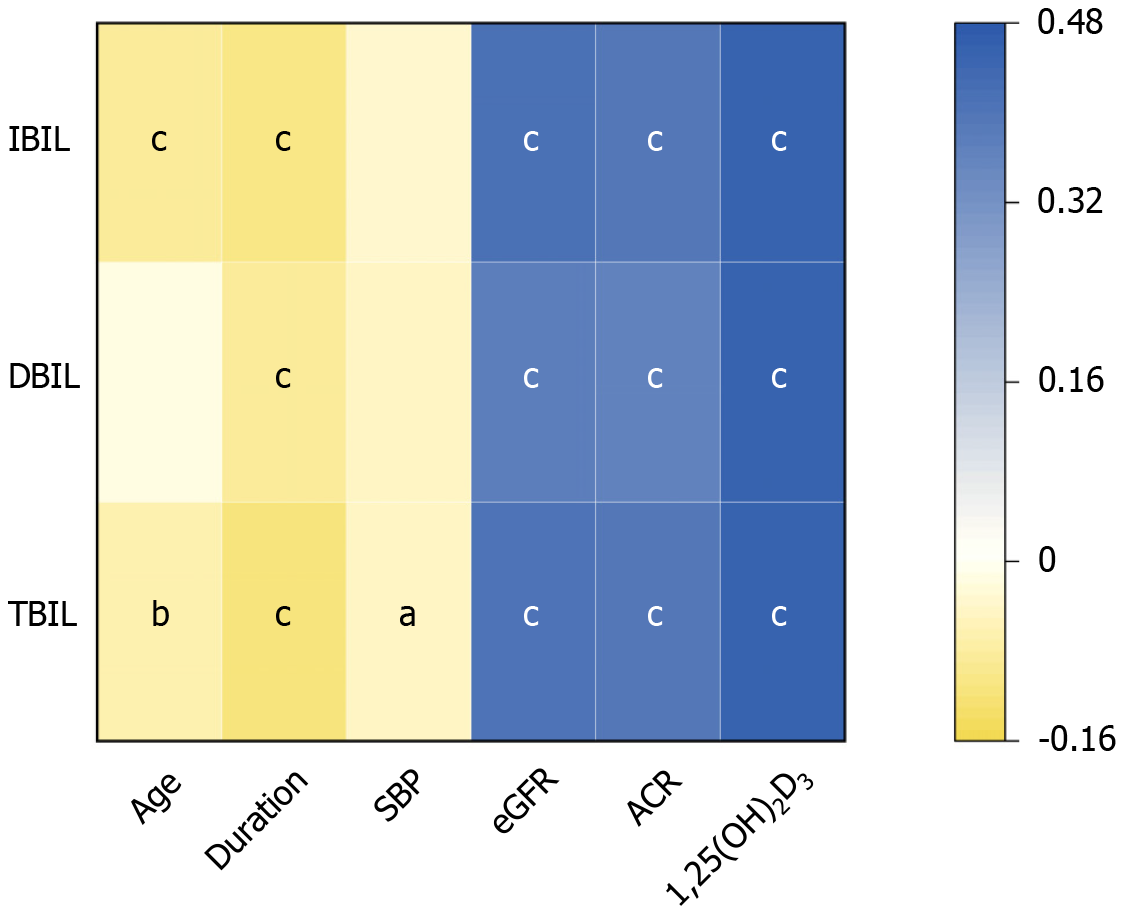
Figure 2 Correlations between bilirubin indices and other clinical characteristics.
Spearman’s correlation analysis was used to evaluate the relationships between bilirubin indices and other clinical features in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. Statistical significance was determined at a P value < 0.05. IBIL: Indirect bilirubin; DBIL: Direct bilirubin; TBIL: Total bilirubin; SBP: Systolic blood pressure; eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; ACR: Albumin/creatinine ratio.
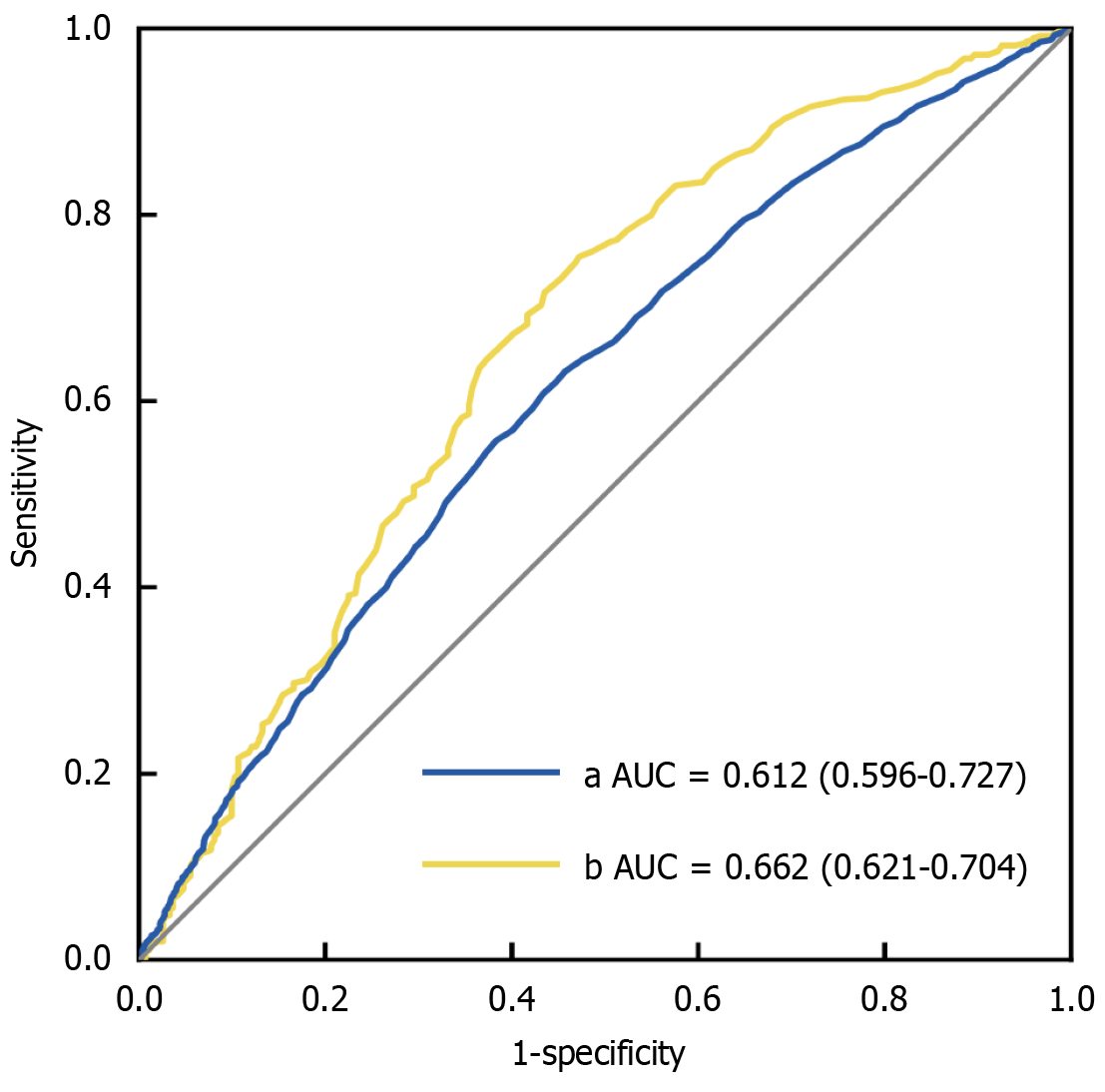
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic analysis of the association between indirect bilirubin and the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was carried out to determine the cutoff point of indirect bilirubin (IBIL) for predicting the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy (DR). Statistical significance was determined at a P value < 0.05. a: ROC analysis of IBIL for predicting the risk of developing DR in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM); b: ROC analysis of IBIL for predicting the risk of developing DR in male T2DM patients with elevated diastolic blood pressure. AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Lin XY, Zheng YX, Liu MM, Liang Q, Li M, Sui J, Qiang W, Guo H, Shi BY, He MQ. Indirect bilirubin is inversely associated with diabetic retinopathy risk and is a potential predictive biomarker. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(9): 110590
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i9/110590.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i9.110590