©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2025; 16(12): 110028
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i12.110028
Published online Dec 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i12.110028
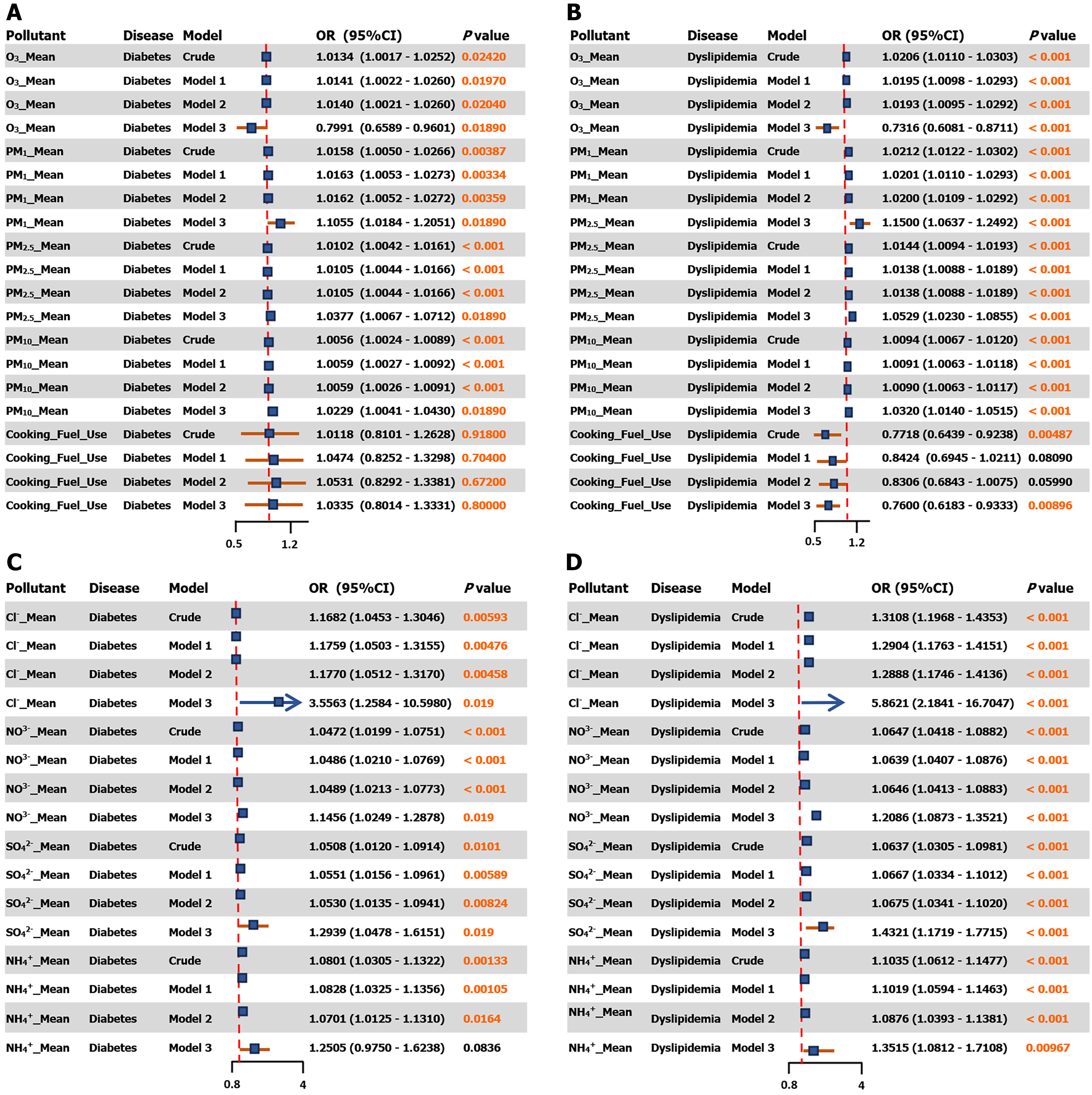
Figure 1 Associations of long-term air pollutant exposure with the risk of diabetes and dyslipidaemia, and of specific PM2.
5 components with the risk of diabetes and dyslipidaemia. A: Associations of long-term air pollutant exposure with the risk of diabetes; B: Associations of long-term air pollutant exposure with the risk of dyslipidaemia; C: Specific PM2.5 components with the risk of diabetes; D: Specific PM2.5 components with the risk of dyslipidaemia. Results are presented across sequentially adjusted models: Crude model (unadjusted); model 1 (adjusted for age, gender, residence, education, and marital status); model 2 (further adjusted for smoking and drinking status); model 3 (additionally adjusted for provincial distribution). Arrow indicates direction of effect. PM1: Parti
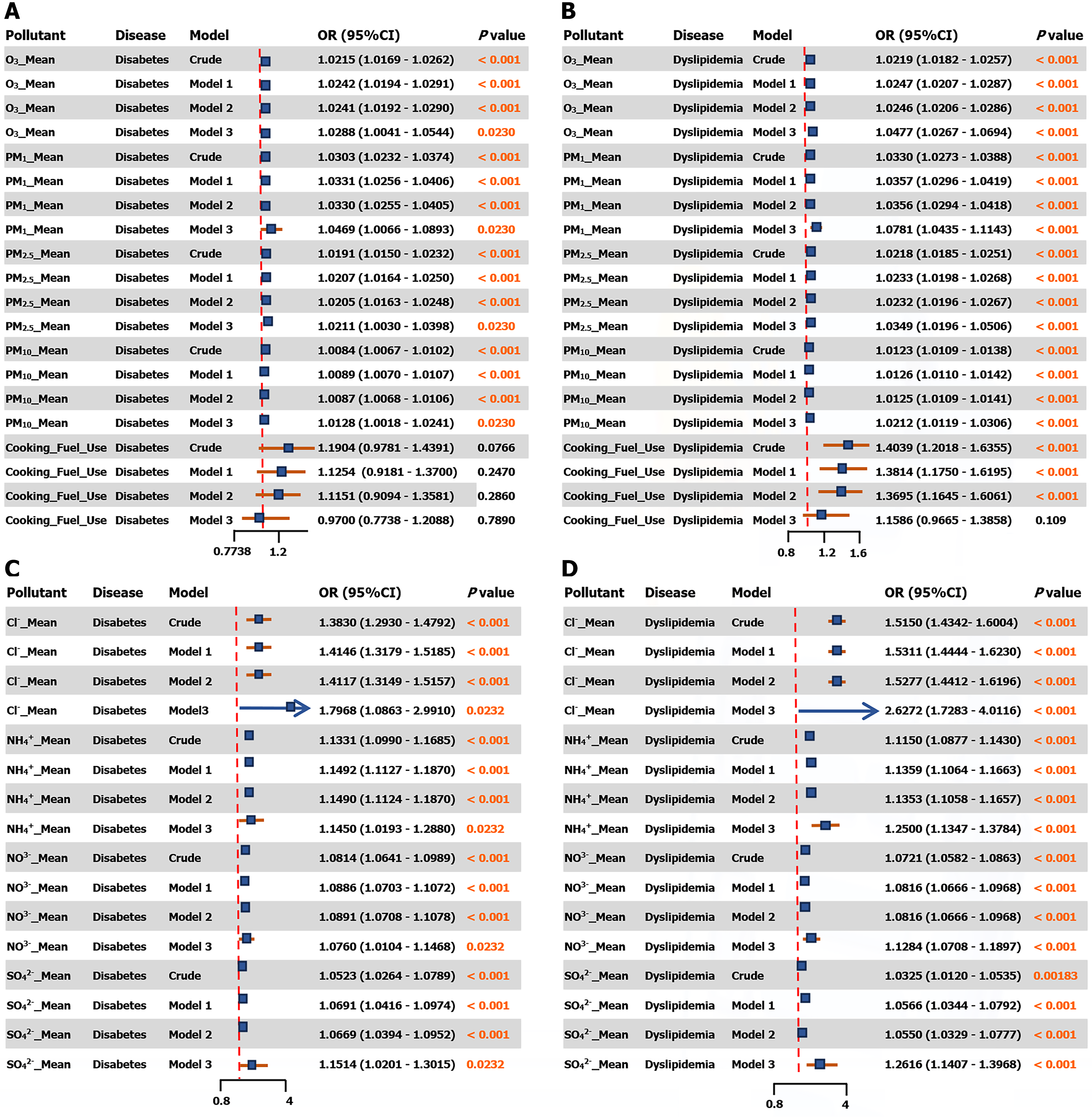
Figure 2 Associations between short-term air pollutant exposure and the risk of diabetes and dyslipidaemia, and between specific PM2.
5 components and the risk of diabetes and dyslipidaemia. A: Associations of short-term air pollutant exposure with the risk of diabetes; B: Associations of short-term air pollutant exposure with the risk of dyslipidaemia; C: Specific PM2.5 components with the risk of diabetes; D: Specific PM2.5 components with the risk of dyslipidaemia. Results are shown across sequentially adjusted models: The crude model (unadjusted); model 1 (adjusted for age, gender, residence, education, and marital status); model 2 (additionally adjusted for smoking and drinking status); and model 3 (further adjusted for provincial distribution). PM1: Particulate matter 1; PM2.5: Particulate matter 2.5; PM10: Particulate matter 10; O3: Ozone. SO42-: Sulfate ion; NO3-: Nitrate ion; Cl-: Chloride ion; NH4+: Ammonium ion.
- Citation: Zhou C, Cui GY, Tang YH, Zhang WY, Zou XL. Long-term and short-term exposure to outdoor air pollution and its association with glycolipid metabolic disorders. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(12): 110028
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i12/110028.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i12.110028