©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2023; 14(6): 795-807
Published online Jun 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i6.795
Published online Jun 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i6.795
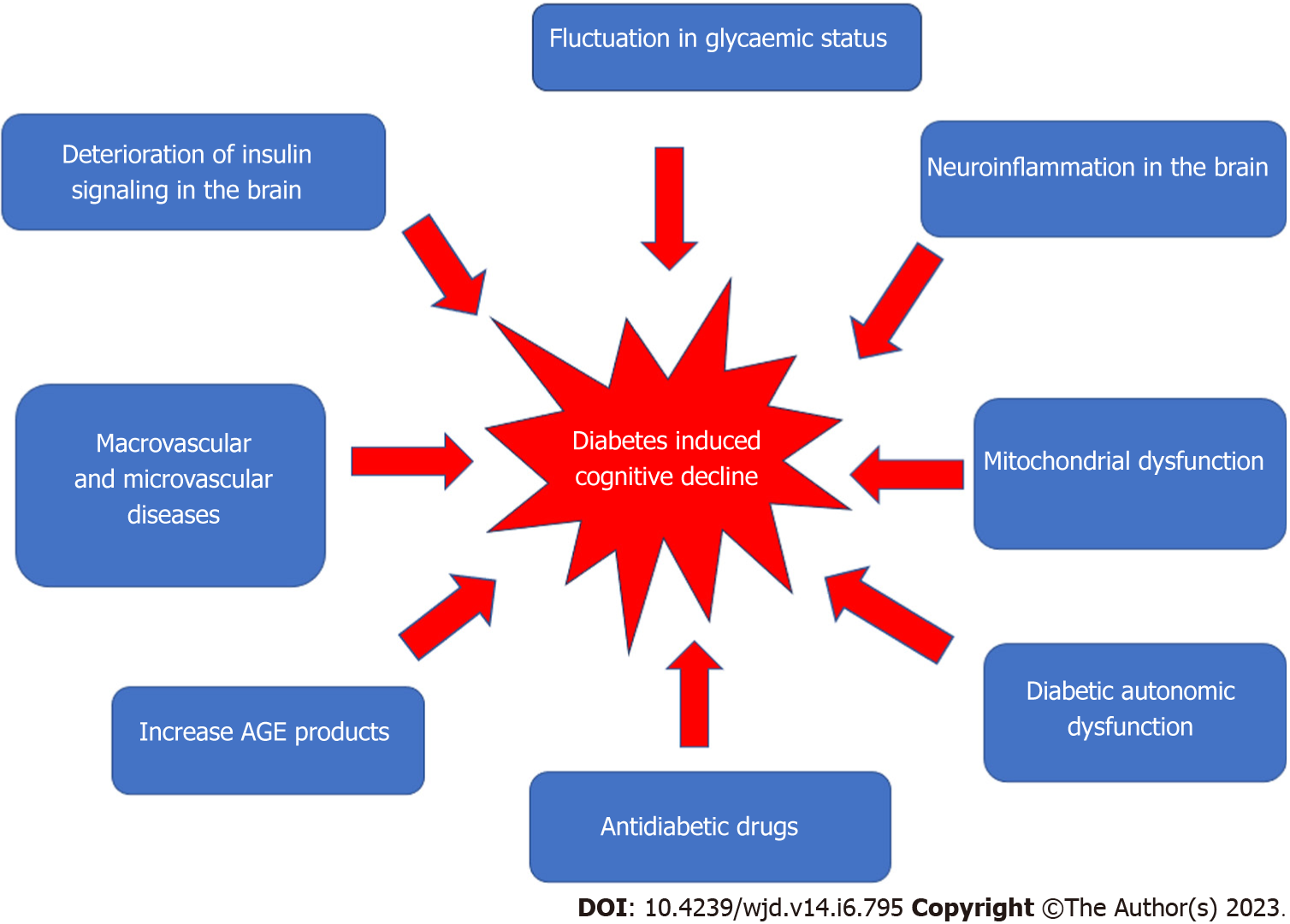
Figure 1 Multifactorial pathophysiology of diabetes-induced cognitive decline.
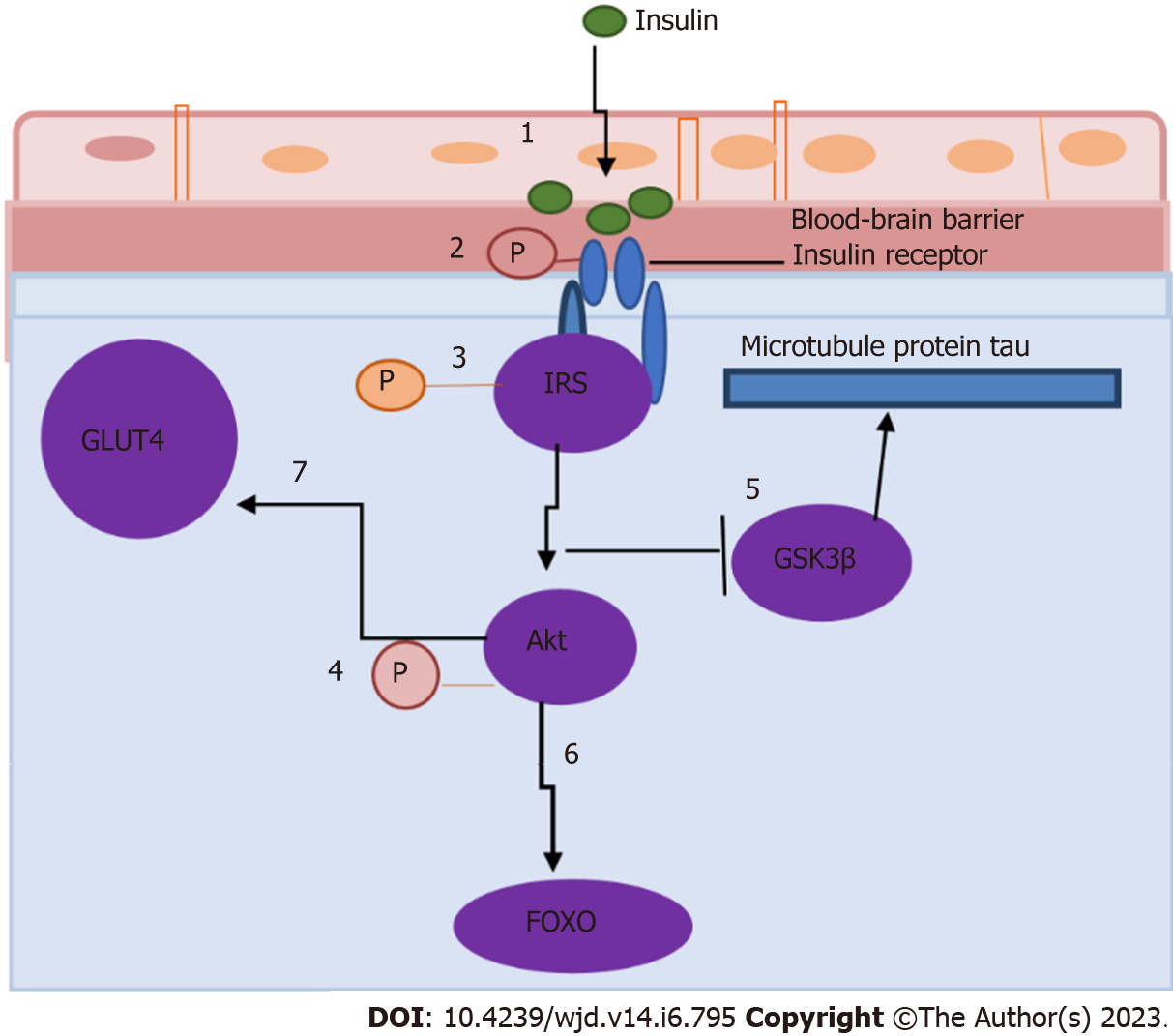
Figure 2 Insulin receptor signaling in the hippocampus (adapted from Biessels and Reagan[40], 2015).
Cerebral insulin resistance causes downregulation of insulin transporters at the blood-brain barrier, limiting the amount of insulin that can enter the brain (step 1), decreasing the expression and/or activity of insulin receptors (step 2), modulating the phosphorylation state of insulin receptor substrates (step 3), phosphorylation of Akt (step 4), affecting several downstream components in the insulin signaling cascade (including glycogen synthase kinase 3β) (step 5), regulating the phosphorylation state of the microtubule protein tau and forkhead box O family of transcription factors (step 6), and impairing the trafficking of GLUT4 to the plasma membrane of the brain (step 7). GSK3β: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β; FOXO: Forkhead box O.
- Citation: Ab-Hamid N, Omar N, Ismail CAN, Long I. Diabetes and cognitive decline: Challenges and future direction. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(6): 795-807
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i6/795.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i6.795