©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Feb 15, 2026; 18(2): 113959
Published online Feb 15, 2026. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v18.i2.113959
Published online Feb 15, 2026. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v18.i2.113959
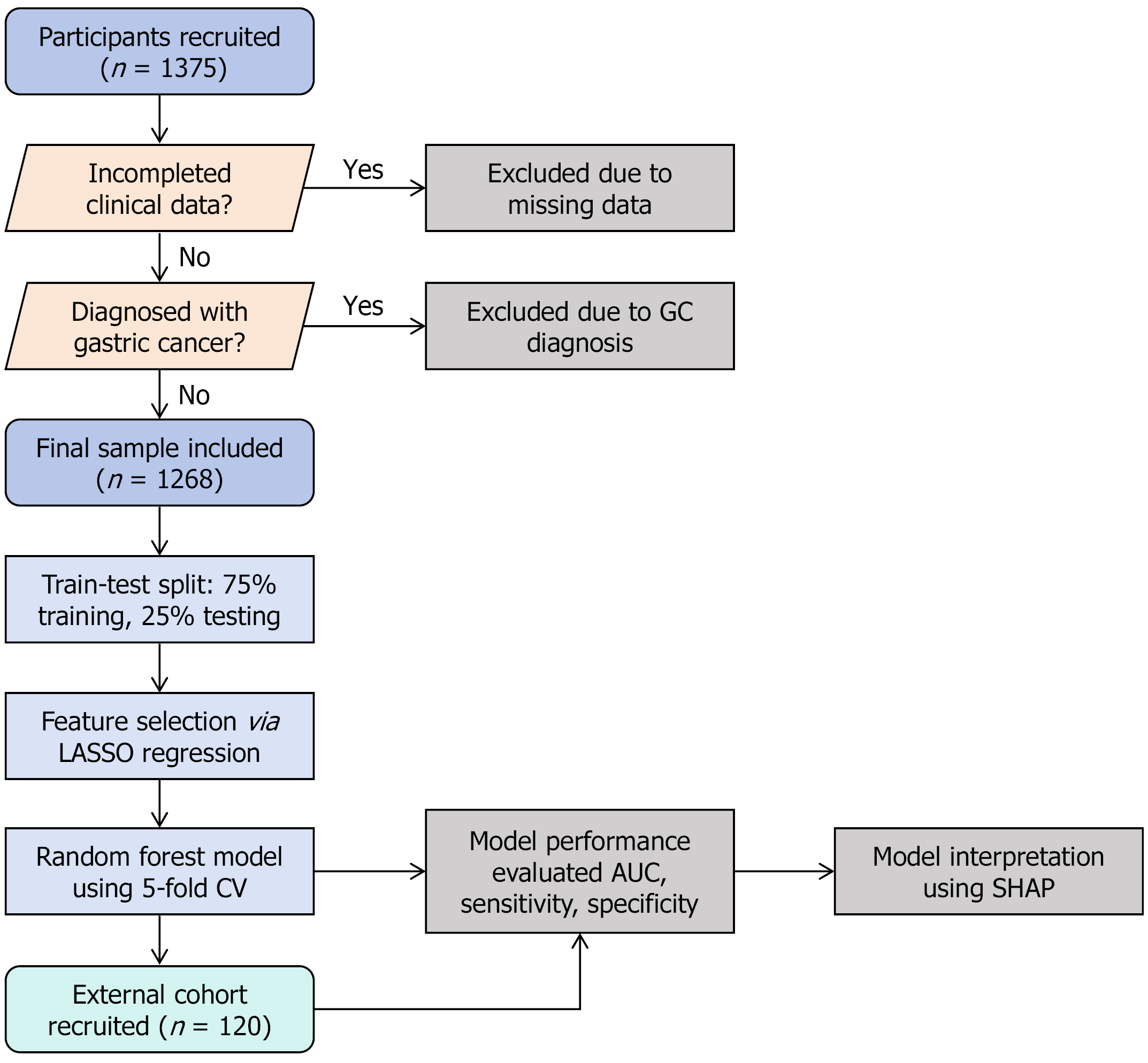
Figure 1 Study flowchart.
A total of 1375 subjects were initially recruited from a gastric cancer screening program. After participants were excluded because of missing clinical data or a diagnosis of gastric cancer, 1268 subjects were included in the final analysis. The dataset was split into a training set (75%) and a testing set (25%). Feature selection was performed using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression, followed by the construction of a random forest model using 5-fold cross-validation. The model's performance was evaluated, and its predictions were interpreted using SHapley Additive exPlanation. Finally, the model was validated on an independent external cohort of 120 subjects. GC: Gastric cancer; LASSO: Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; CV: Cross-validation; AUC: Area under the curve; SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanation.
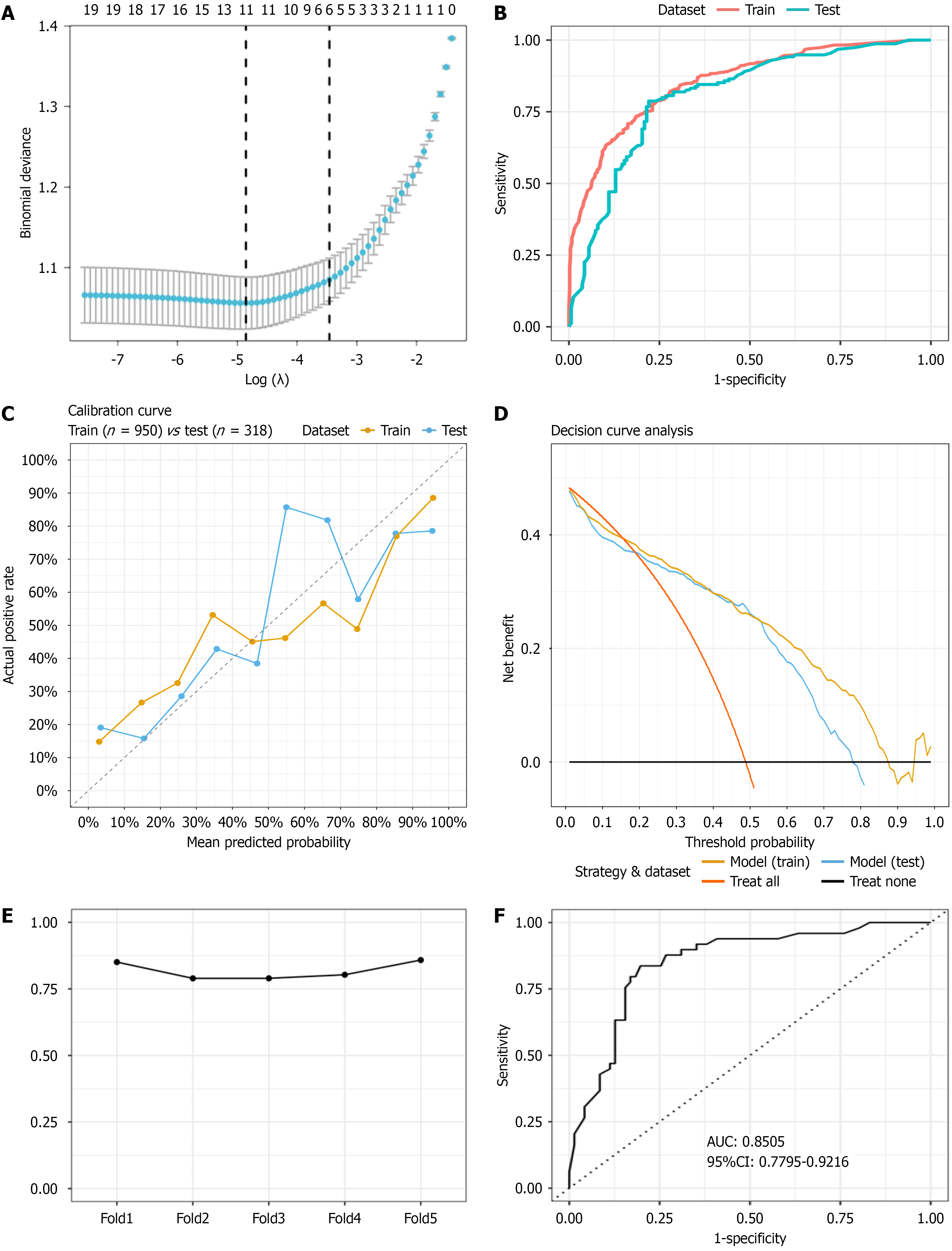
Figure 2 Development and validation of the prediction model for chronic atrophic gastritis.
A: Feature selection was performed using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression. The dashed line on the left (λ.min) represents the optimal solution with the minimum lambda value, whereas the line on the right (λ.1se) corresponds to the simplest model within one standard error of λ.min; B: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for the training and testing sets; C: Calibration curves for both the training and testing sets; D: Decision curve analysis for the model; E: Results of the 5-fold cross-validation, showing the area under the curve (AUC) for each fold; F: ROC curve for the external validation set, with an AUC of 0.8505. AUC: Area under the curve.
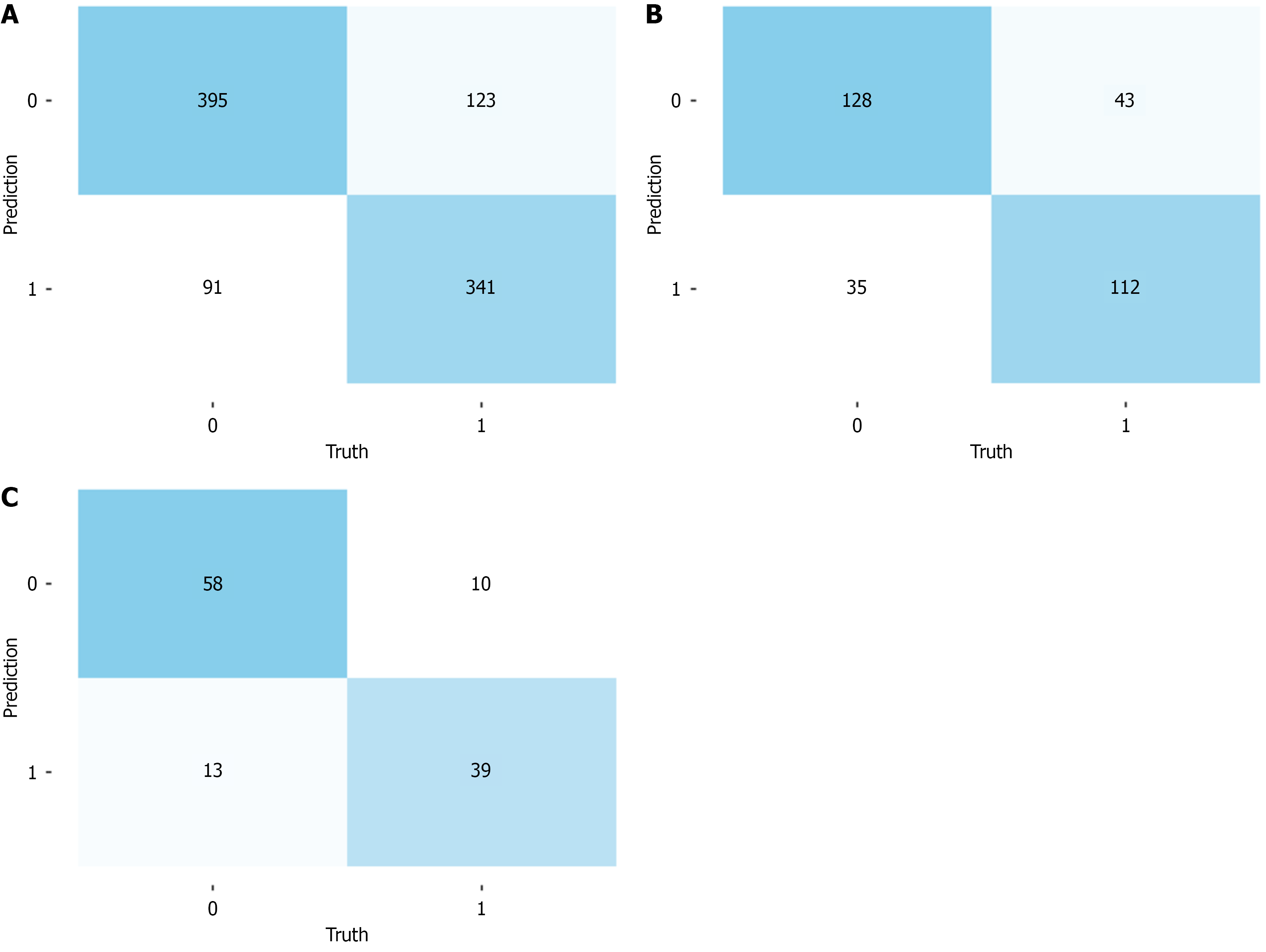
Figure 3 Confusion matrices of the model for training set, testing set, and external validation set.
A: Confusion matrix for the training set; B: Confusion matrix for the testing set; C: Confusion matrix for the external validation set.
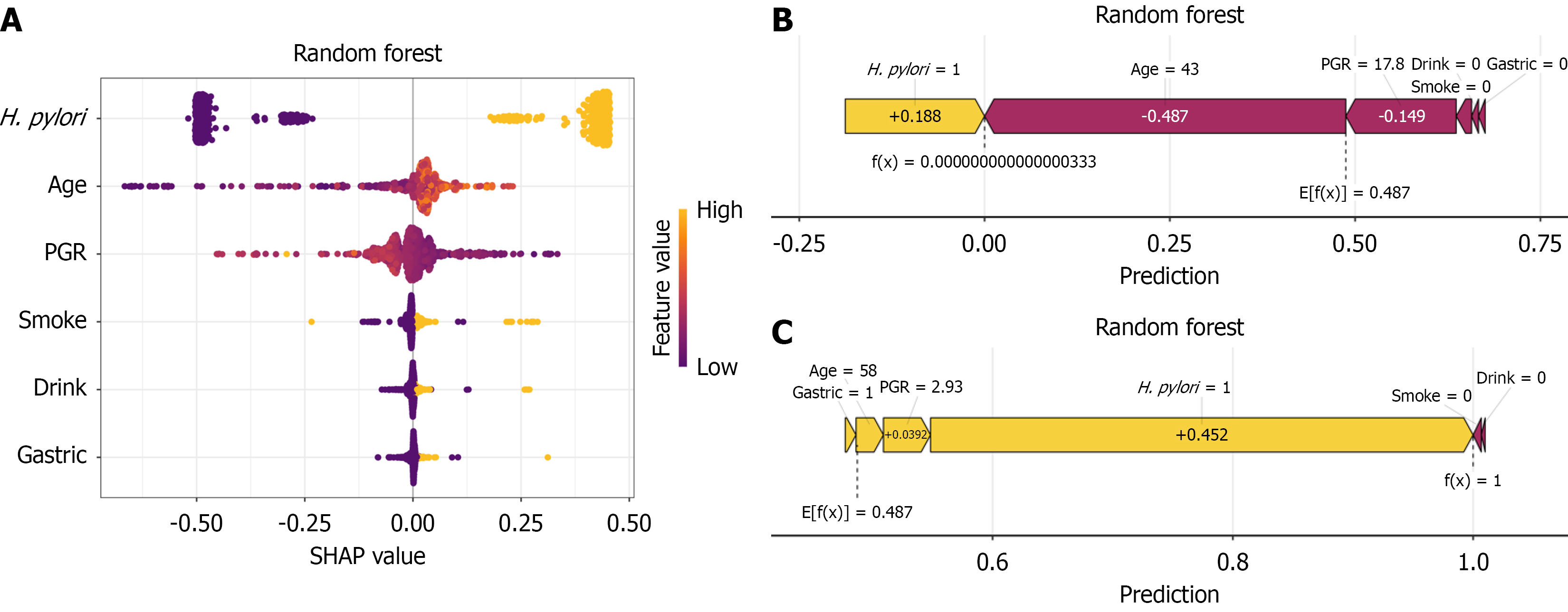
Figure 4 SHapley Additive exPlanation Model Interpretation.
A: Each point in the graph represents a feature, and the horizontal axis represents the SHapley Additive exPlanation value. The feature importance is ranked from top to bottom. Yellow points indicate higher feature values, and blue points indicate lower feature values; B and C: Interpretability analysis of two independent samples. Yellow represents a positive contribution to the model, and red represents a negative contribution. H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; PGR: Pepsinogen I/II ratio; SHAP: SHapley Additive explanation.
- Citation: Cao H, Han JL, Wu H, Si SP, Ding LJ, Ji L, Zhang HZ, Yin J, Zhou ZY, Zhang YN, Lv ZF, Tian WY, Zhan Q, Wang H, An FM. Risk prediction for chronic atrophic gastritis using a random forest model: A multicenter study. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2026; 18(2): 113959
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v18/i2/113959.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v18.i2.113959