©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Sep 15, 2025; 17(9): 108649
Published online Sep 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i9.108649
Published online Sep 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i9.108649
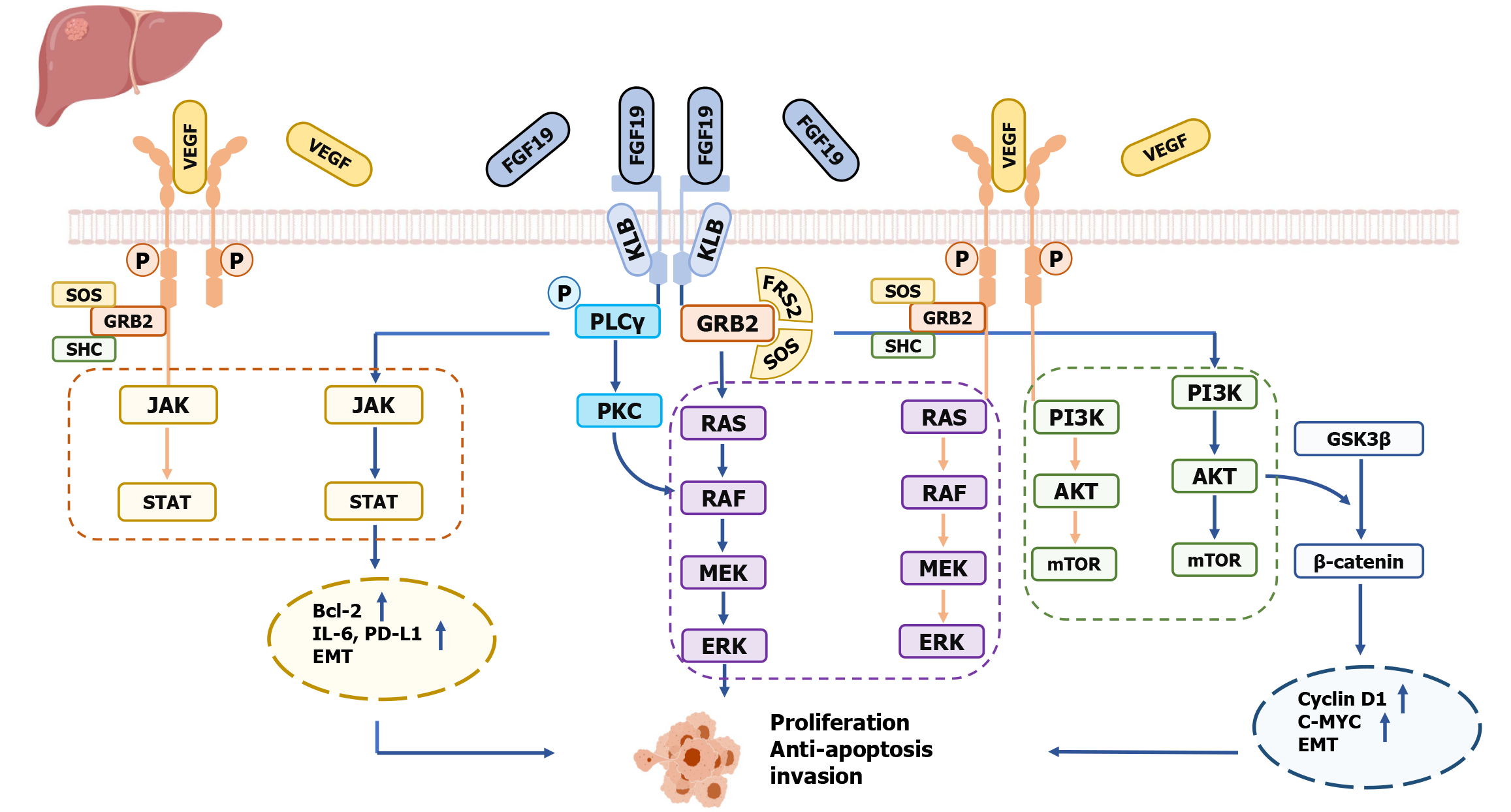
Figure 1 The aberrant fibroblast growth factor 19-fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 axis drives hepatocellular carcinoma.
Overexpression of fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) binds to fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4), leading to its phosphorylation and recruitment of FGFR substrate-2 (FRS2), GRB2, and SOS, which subsequently trigger a cascade of downstream effector proteins. The aberrant FGF19-FGFR4 axis primarily promotes tumor growth through the RAS-RAF-MAPK and PI3K-AKT signaling pathways. Additionally, it facilitates the phosphorylation of GSK3β, preventing the inactivation of downstream β-catenin. Activated FGFR4 can also activate the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Together, these mechanisms promote hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and resistance to apoptosis. Additionally, the FGF19-FGFR4 axis shares similar downstream molecules with the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor pathway. FGF19: Fibroblast growth factor 19; FGFR4: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; KLB: Β-Klotho; GRB2: Growth Factor receptor-bound protein 2; SOS: Son of sevenless homolog; FRS2: FGFR substrate-2; SHC: Src homology domain protein C1; JAK: Janus kinase; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; RAS: Rat sarcoma; RAF: Rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin; GSK3β: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β; C-MYC: Cellular myelocytomatosis; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma 2; IL-6: Interleukin-6; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1. This figure was created with BioGDP.com[32].
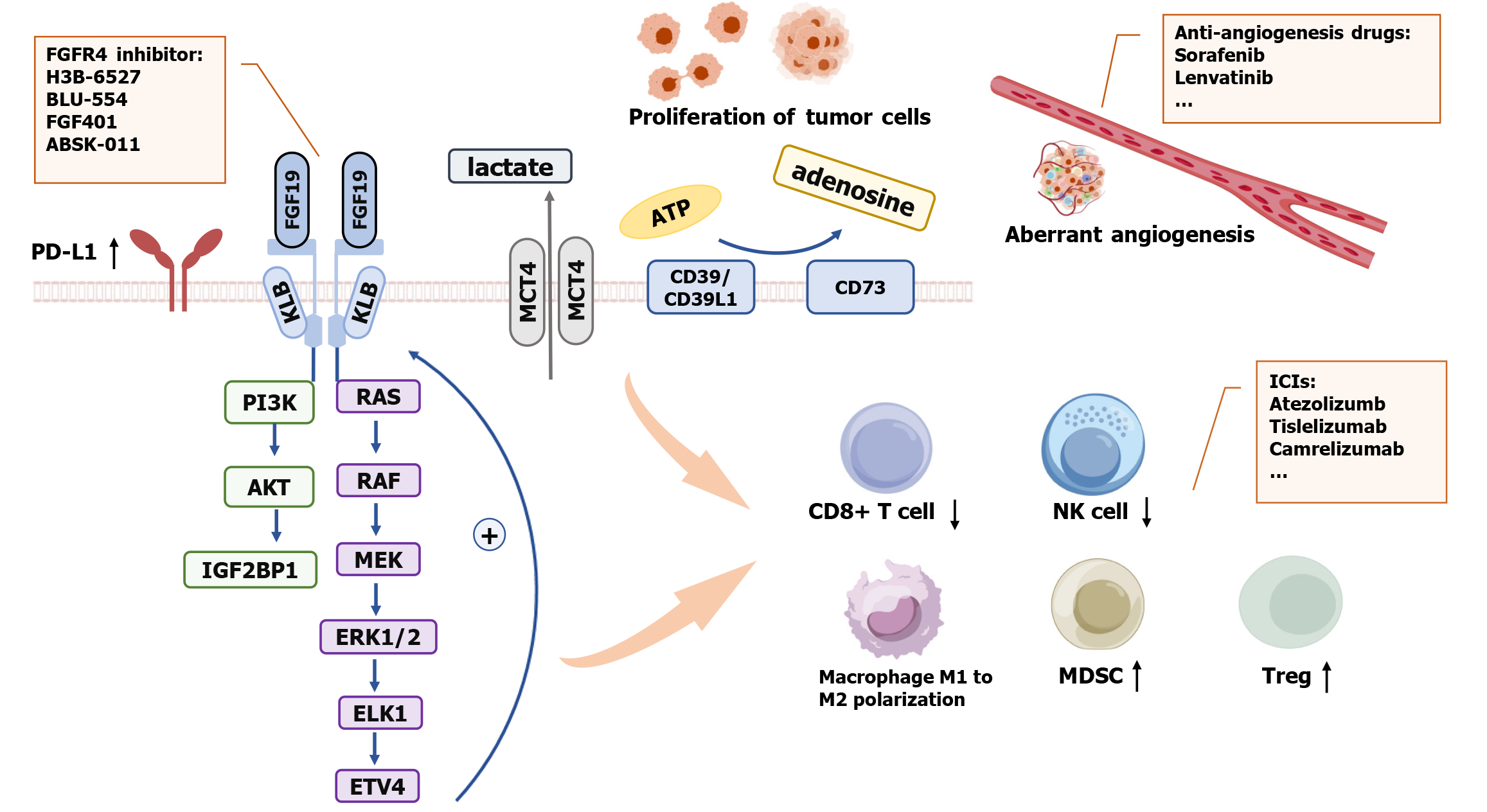
Figure 2 The aberrant fibroblast growth factor 19-fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 axis induces immune suppression.
The aberrant fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19)-fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) axis promotes IGF2BP1 expression by activating the PI3K-AKT pathway and can also increase ETV4 expression via the ERK 1/2-ELK 1 pathway. ETV4 can upregulate the expression of FGFR4, forming a positive feedback loop. Overexpression of FGF19 can promote tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis, leading to a hypoxic microenvironment. Hypoxia-inducible factors can induce upregulation of programmed death-ligand 1 through pathways such as lactic acid, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-CD39/CD73-adenosine. This ultimately induces immune suppression by reducing infiltration of CD8+ T cells and natural killer cells, polarization of macrophages from the M1 to M2, and increasing infiltration of MDSCs and regulatory T cells. The combination of FGFR4 inhibitors with anti-angiogenic drugs or immune checkpoint inhibitors can enhance the anti-tumor effect. FGF19: Fibroblast growth factor 19; FGFR4: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4; KLB: Β-klotho; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; IGF2BP1: Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1; RAS: Rat sarcoma; RAF: Rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; ELK: ETS-like gene; ETV4: E-twenty-six-specific sequence variant 4; MCT4: Monocarboxylate transporter 4; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; NK cell: Natural killer cell; ICI: Immune checkpoint inhibitor; MDSC: Myeloid-derived suppressor cell; Treg: Regulatory T cell. This figure was created with BioGDP.com[32].
- Citation: Zhan TA, Xia F, Huang HW, Zhan JC, Liu XK, Cheng Q. Fibroblast growth factor 19-fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 axis: From oncogenesis to targeted-immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(9): 108649
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i9/108649.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i9.108649