©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Nov 15, 2025; 17(11): 110840
Published online Nov 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i11.110840
Published online Nov 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i11.110840
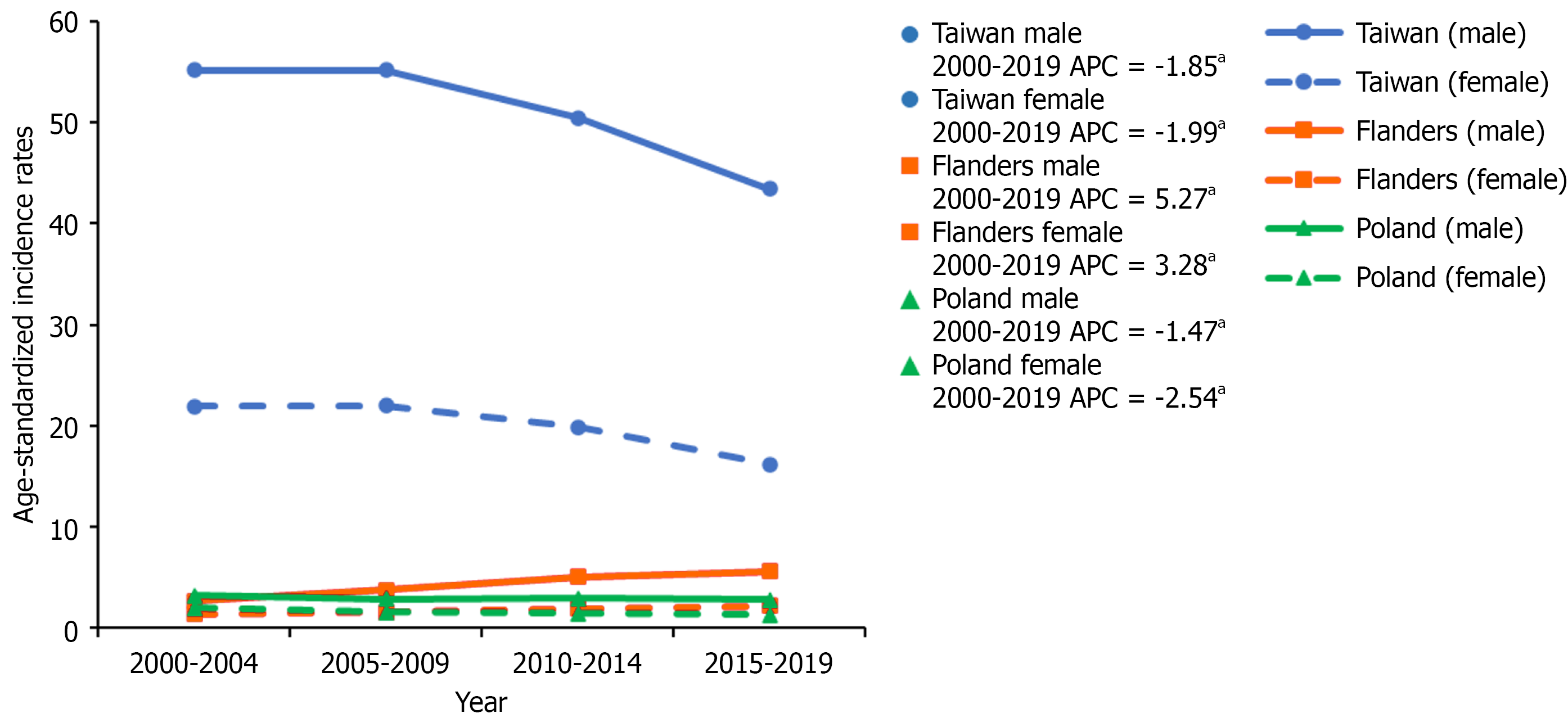
Figure 1 Age-standardized incidence rates (with age-truncated population ≥ 30 and ≤ 89 years) of hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan, Poland, and Flanders, 2000-2019, and estimated age-period-cohort change.
In Taiwan, the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) from 2000-2004 to 2015-2019 decreased significantly for both males and females, with age-period-cohort (APC) was -1.85 (95% confidence interval [CI]: -3.30 to -0.49) in males and -1.99 (95%CI: -3.92 to -0.16) in females. In Poland, the ASIR from 2000-2004 to 2015-2019 decreased significantly for both males and females with APC was -1.47 (95%CI: -1.92 to -1.10) in males and -2.54 (95%CI: -3.53 to -1.63) in females. In Flanders, the ASIR from 2000-2004 to 2015-2019 increased significantly for both males and females with APC was 5.27 (95%CI: 2.65-7.69) in males and 3.28 (95%CI: 2.95-3.53) in females. aP < 0.05.
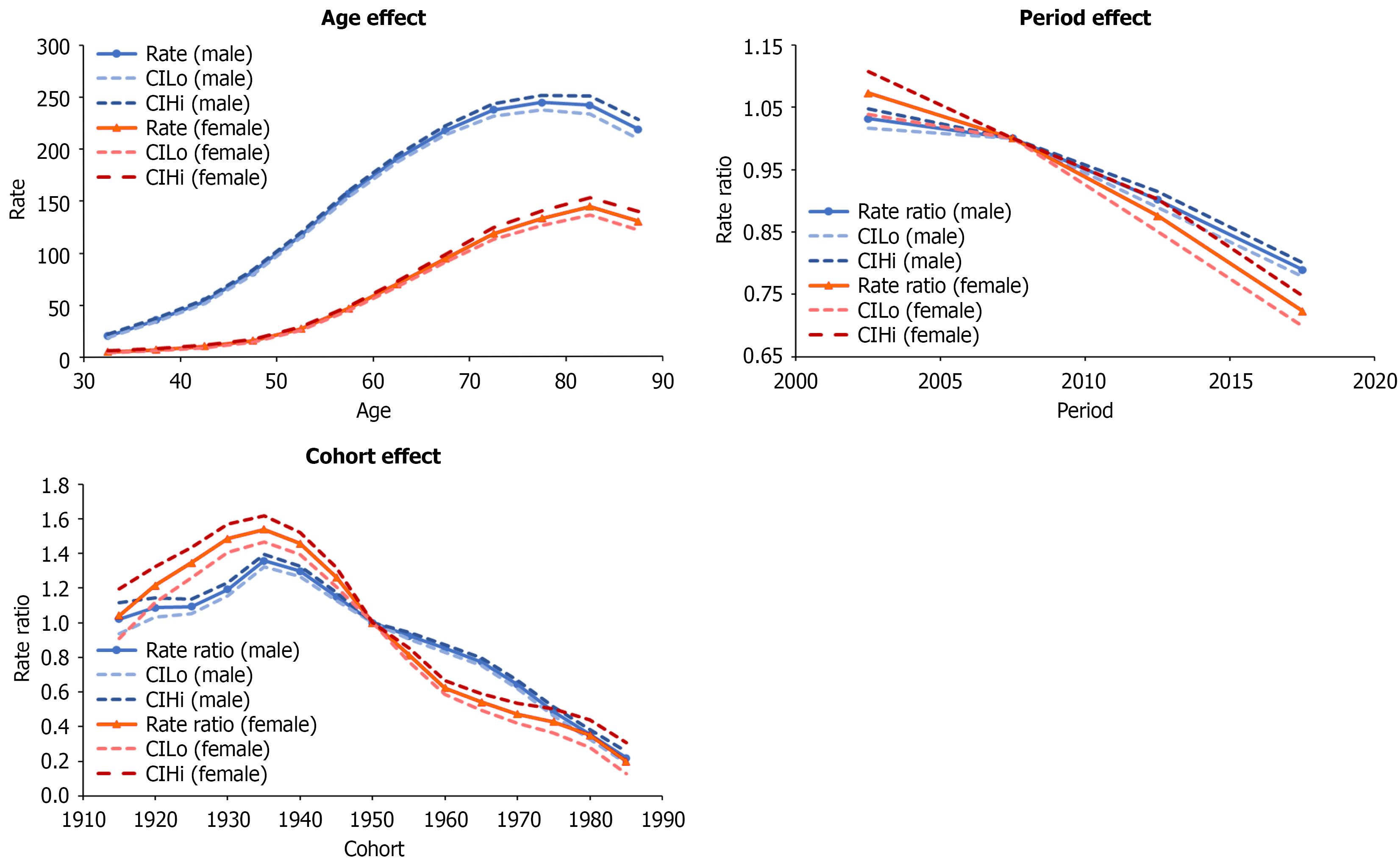
Figure 2 Age-period-cohort effects of hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan, 2000-2019.
The highest age effects were 243.99 in males aged 75-79 and 144.04 in females aged 80-84. The rate ratios of the period effects from 2000 to 2019 decreased for both males and females (1.03 to 0.79 and 1.07 to 0.72, respectively). The rate ratios of the cohort effects increased during 1915-1935 (1.02 to 1.36 in males and 1.04 to 1.54 in females), but continually decreased from 1935-1989 (1.36 to 0.22 in males and 1.54 to 0.20 in females). CIHi: Upper limit of 95% confidence interval; CILo: Lower limit of 95% confidence interval.
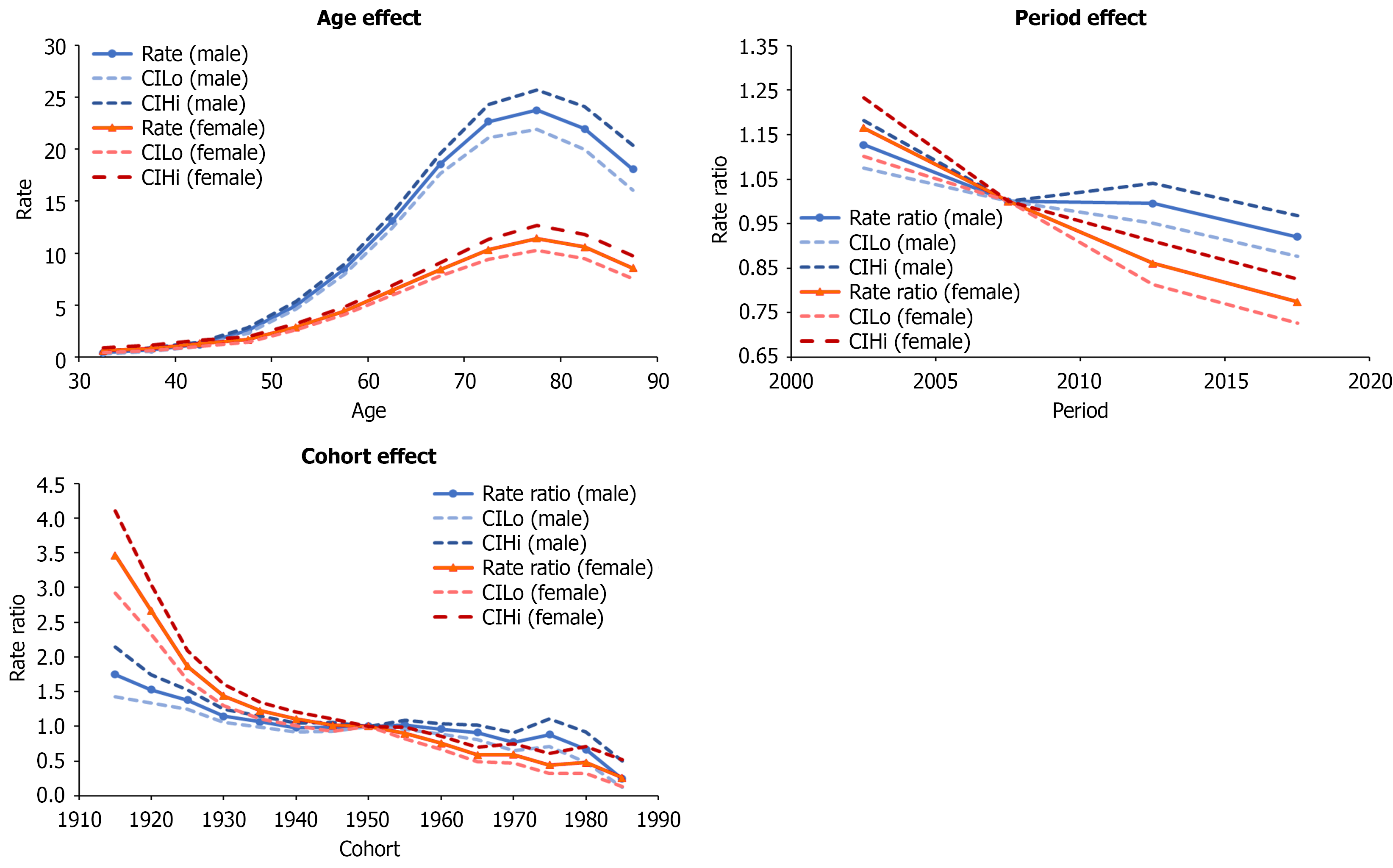
Figure 3 Age-period-cohort effects of hepatocellular carcinoma in Poland, 2000-2019.
The highest age effects were 23.73 and 11.42 in males and females aged 75-79. The rate ratios of the period effects from 2000 to 2019 decreased for both males and females (1.13 to 0.92 and 1.17 to 0.77, respectively). The rate ratios of the cohort effects continually decreased from 1915 to 1989 (1.75 to 0.25 in males and 3.46 to 0.26 in females). CIHi: Upper limit of 95% confidence interval; CILo: Lower limit of 95% confidence interval.
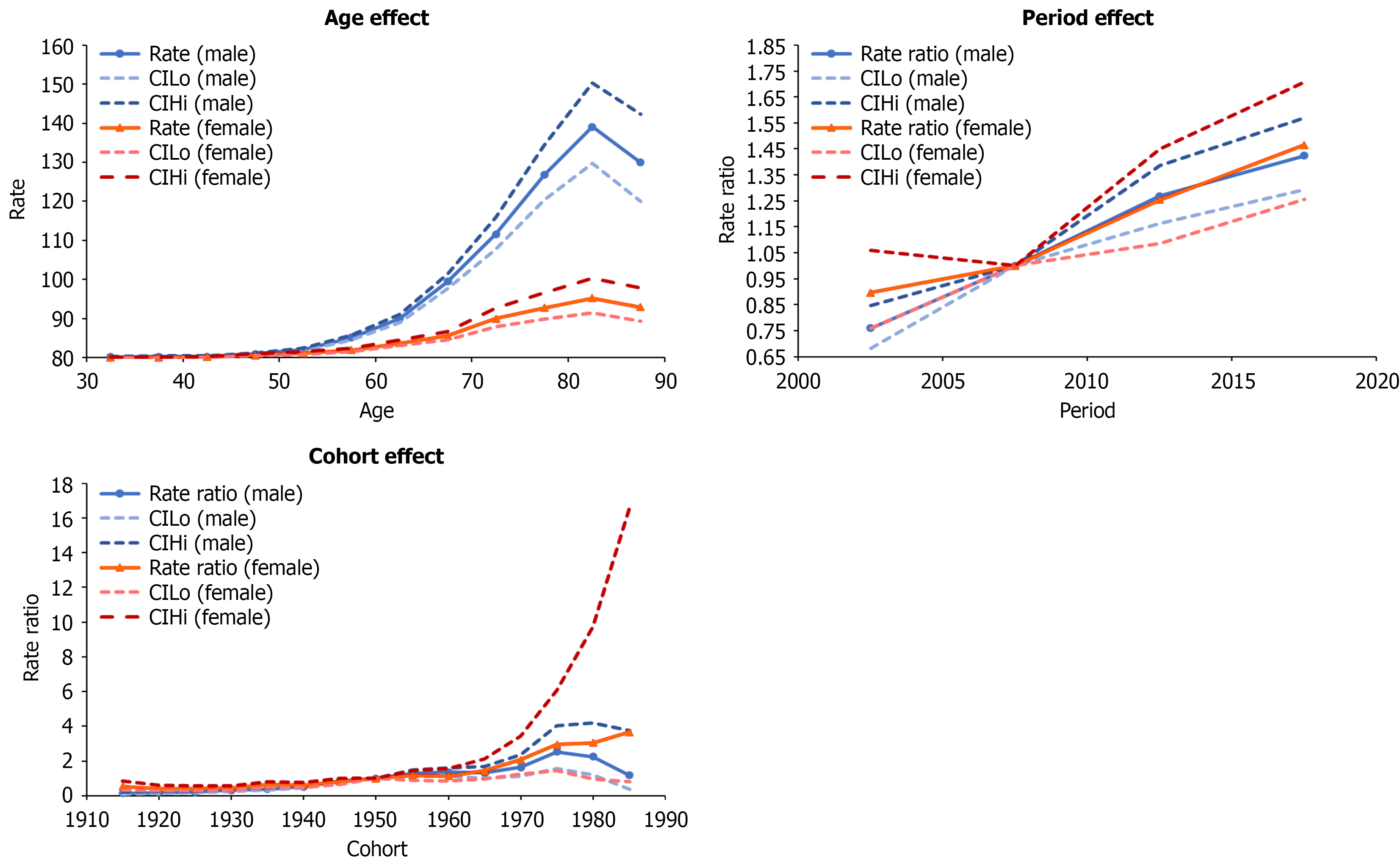
Figure 4 Age-period-and cohort effects of hepatocellular carcinoma in Flanders, 2000-2019.
The highest age effects were 118.08 and 30.46 in males and females aged 80-84. The rate ratios of the period effects from 2000 to 2019 increased for both males and females (0.76 to 1.42 and 0.90 to 1.47, respectively). The rate ratios of the cohort effects for males increased from 0.14 to 2.52 for 1915 to 1975, then decreased from 2.52 to 1.18 for 1975 to 1989. In females, rate ratios increased from 0.53 to 3.66 from 1915 to 1989. CIHi: Upper limit of 95% confidence interval; CILo: Lower limit of 95% confidence interval.
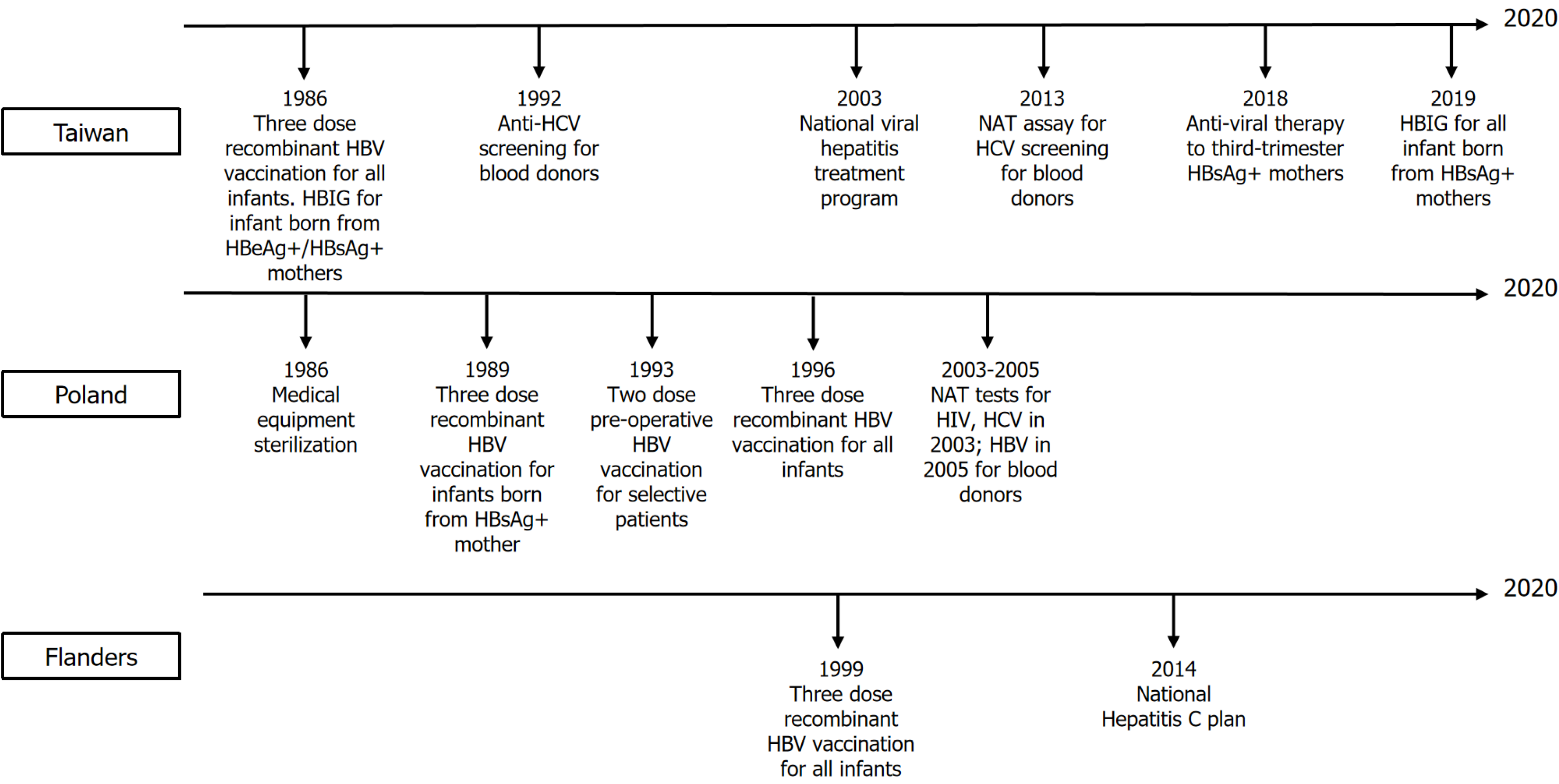
Figure 5 National or regional intervention timeline of preventing viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan, Poland, Flanders.
HBeAg: Hepatitis B e antigen; HBIG: Hepatitis B immune globulin; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus.
- Citation: Huang ZZ, Żmudka K, Ruggiano V, Hsu WL, Liu J, Chiang CJ, Chen YC, Wang V. Secular trend in universal hepatocellular carcinoma prevention: Taiwan, Poland, and Belgium experience. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(11): 110840
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i11/110840.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i11.110840