©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Nov 15, 2025; 17(11): 110715
Published online Nov 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i11.110715
Published online Nov 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i11.110715
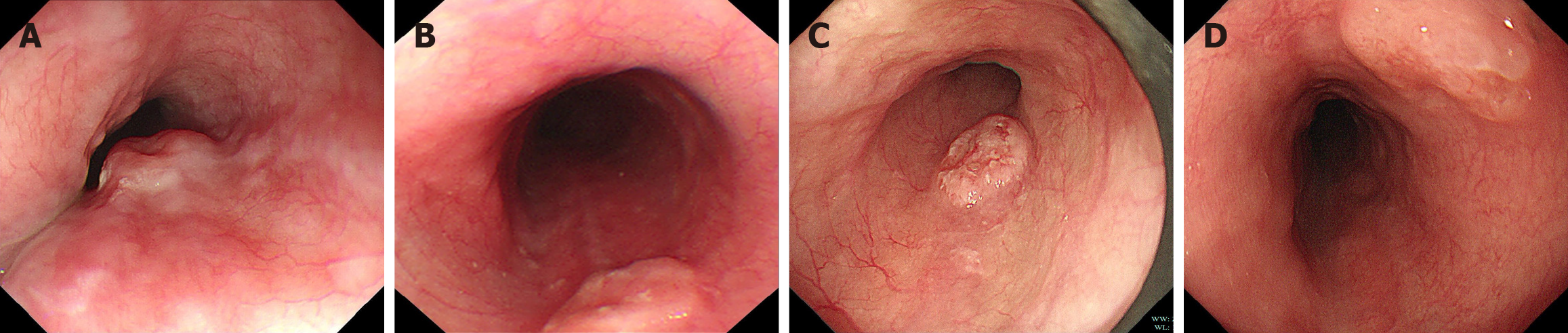
Figure 1 White light endoscopic images of cases 1 to 4.
A: Case 1, a 1.0 cm mucosal elevation with central depression was observed 30 cm from the incisors. The lesion was mobile on palpation; B: Case 2, a 1.2 cm lesion was noted 27 cm from the incisors; C: Case 3, a type 2A mucosal elevation, measuring approximately 1.2 cm × 0.7 cm, was observed 28 cm from the incisors. The lesion exhibited surface erythema, pallor, irregular granularity, erosion, spontaneous bleeding, and well-defined margins; D: Case 4, a mucosal elevation measuring approximately 1.1 cm with slight central depression was detected 30 cm from the incisors.
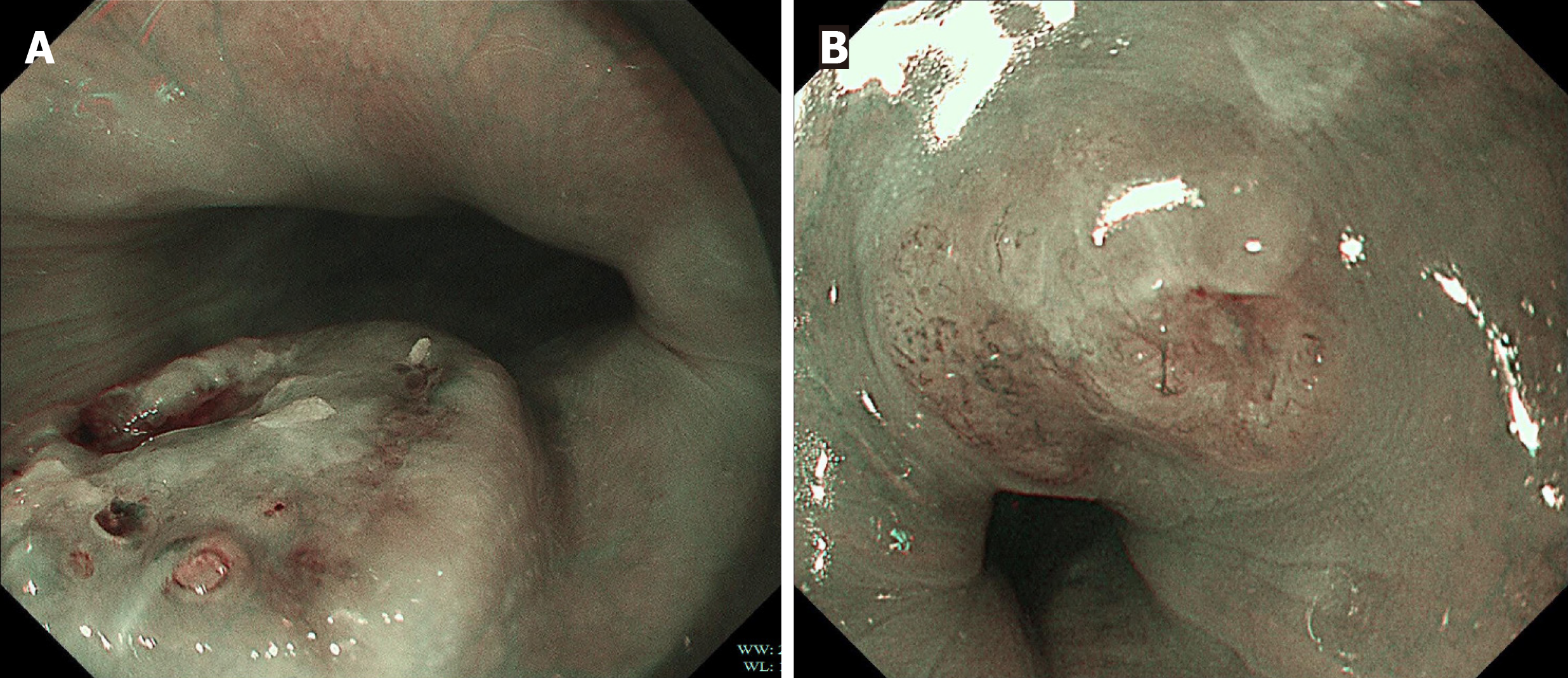
Figure 2 Magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging of case 3 and case 4.
A: Case 3, magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging revealed that the lesion at the area with redness was type B1-B2 vessels; B: Case 4, magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging revealed that the lesion at the area with redness was type B2 vessels.
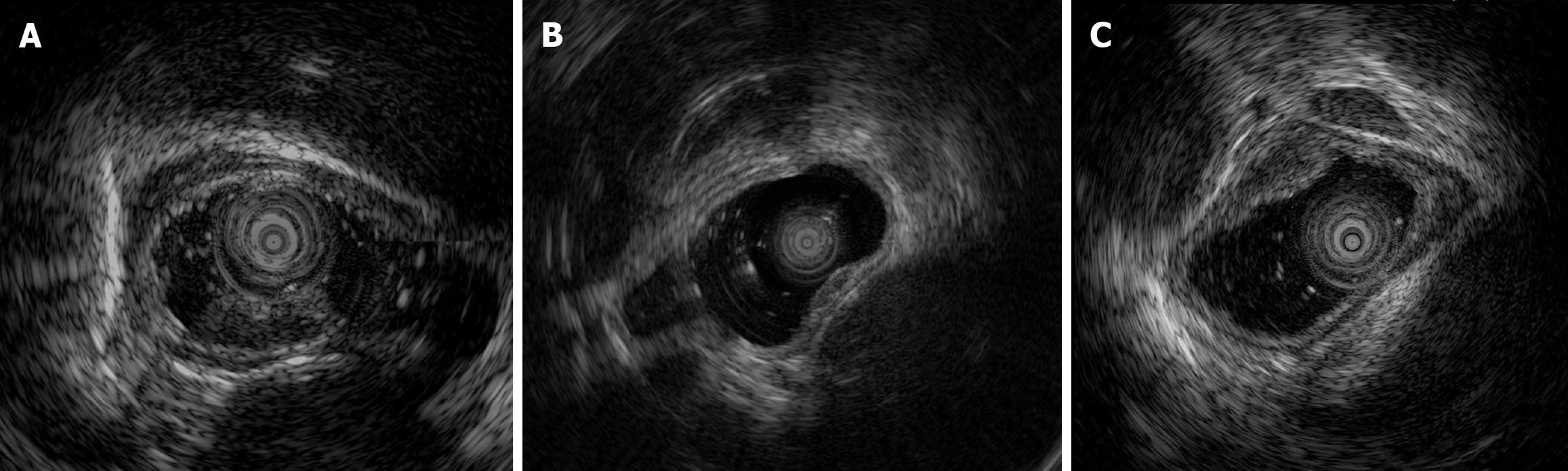
Figure 3 Endoscopic ultrasonography images of cases 1 to 3.
A: Case 1, after water immersion, a 12 MHz miniprobe scan revealed a well demarcated, homogenous, hypoechoic lesion measuring 0.94 cm × 0.36 cm within the muscularis mucosae; B: Case 2, after water immersion, a 12 MHz miniprobe scan revealed a lesion primarily characterized by thickening of the second layer with a measured thickness of 0.27 cm. The layer structure remained distinct, with intact muscularis propria and tunica albuginea; C: Case 3, after water immersion, a 12 MHz miniprobe scan revealed a hypoechoic lesion primarily involving the mucosal layer and partially extending into the superficial submucosa, with hypoechoic structures noted outside the esophageal wall.
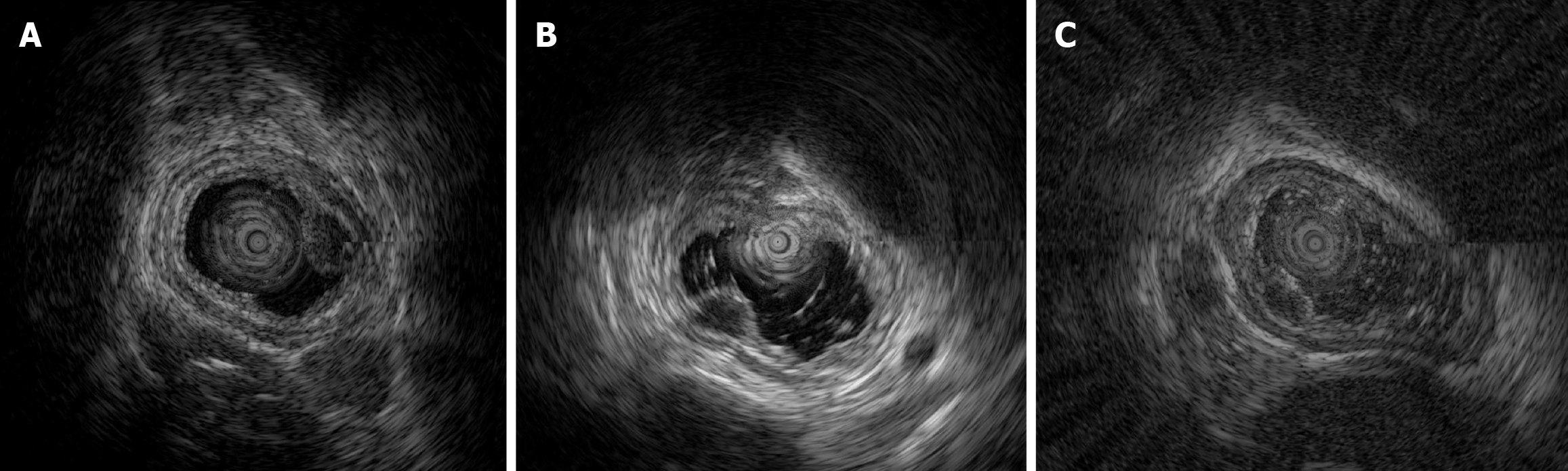
Figure 4 Endoscopic ultrasonography images of cases with esophageal leiomyoma.
A: Case 1, a submucosal elevation was observed 25 cm from the incisors with a smooth surface. After water immersion, a 12 MHz miniprobe scan revealed a well-defined, homogenous, hypoechoic lesion originating from the muscularis mucosae, measuring approximately 0.39 cm × 0.60 cm in cross-section. The surrounding esophageal wall layers appeared normal; B: Case 2, a submucosal elevation was observed 27 cm from the incisors with a smooth surface. After water immersion, a 12 MHz miniprobe scan revealed a well-defined, homogenous, hypoechoic lesion originating from the muscularis mucosae, measuring approximately 0.65 cm × 0.40 cm in cross-section. The surrounding esophageal wall layers appeared normal; C: Case 3, conventional gastroscopy revealed a spindle-shaped submucosal elevation approximately 1.0 cm in length, located 33 cm from the incisors, with localized surface depression. After water immersion, a 12 MHz miniprobe scan showed a well-defined, homogenous, hypoechoic lesion originating from the muscularis mucosae, measuring approximately 0.59 cm × 0.36 cm in cross-section. The surrounding esophageal wall layers appeared normal.
- Citation: Jin T, Zhou YW, Sun PS, Huang Y, Gao JG, Jin X. Unraveling the characteristics of early esophageal neuroendocrine carcinoma using multi-model endoscopy: A retrospective study of serial cases. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(11): 110715
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i11/110715.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i11.110715