©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Nov 16, 2025; 17(11): 111107
Published online Nov 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i11.111107
Published online Nov 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i11.111107
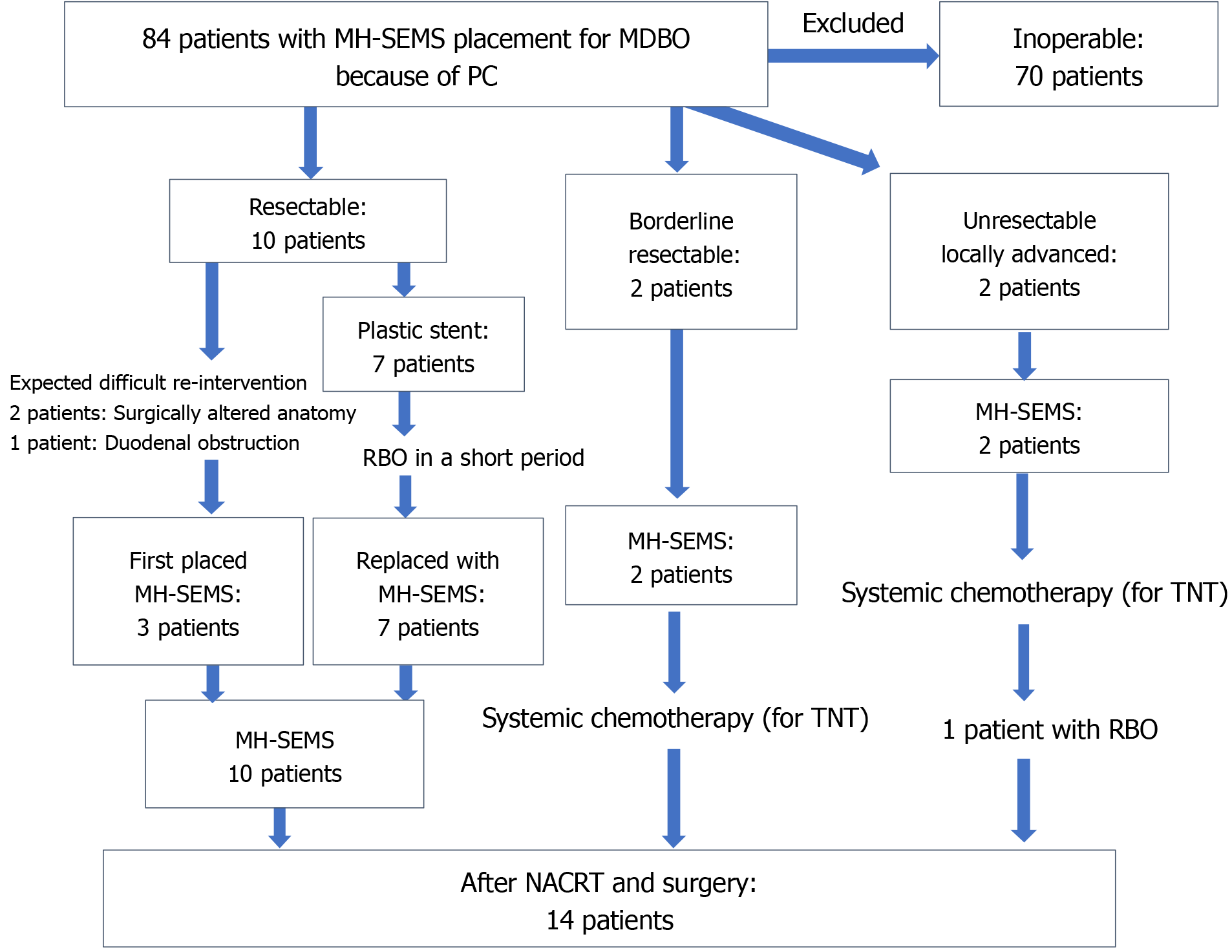
Figure 1 Patient flowchart.
MH-SEMS: Multi-hole self-expandable metallic stent; MDBO: Malignant distal biliary obstruction; NACRT: Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy; PC: Pancreatic cancer; RBO: Recurrent biliary obstruction; TNT: Total neoadjuvant therapy.
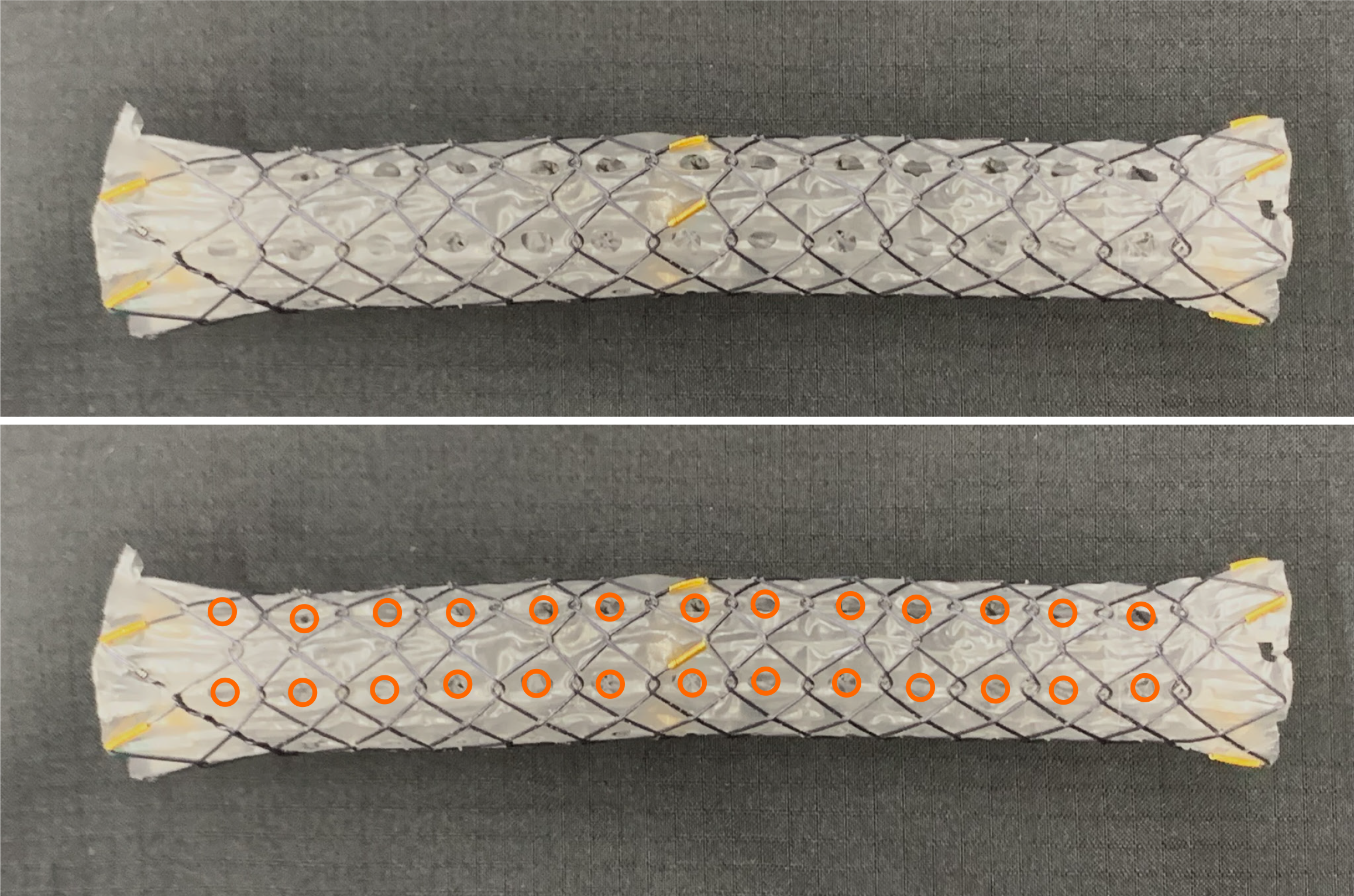
Figure 2 Multi-hole self-expandable metallic stent.
Six rows of side holes were drilled on the membrane, aligning with the longitudinal direction of the stent (orange circles). Each side hole had a diameter of 1.8 mm.
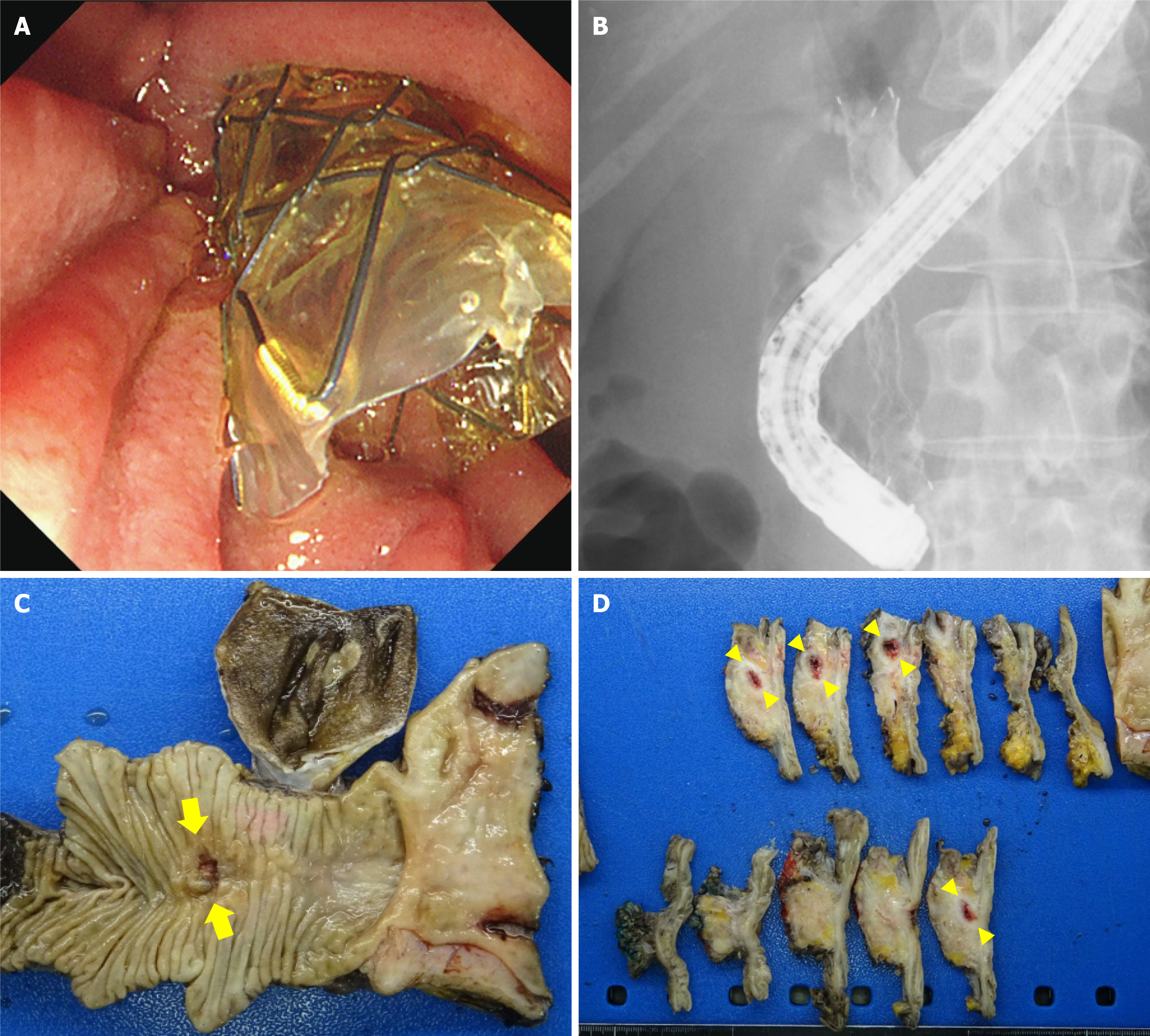
Figure 3 Endoscopic findings and resected specimens.
A: The endoscopic image. A multi-hole self-expandable metallic stent (MH-SEMS) was inserted in a patient with malignant distal biliary obstruction caused by borderline resectable pancreatic cancer with portal vein invasion; B: The fluoroscopic image of MH-SEMS; C: After surgery (pancreatoduodenectomy with portal vein resection), the stent was easily removed from the surgical specimen. The yellow arrow points to the Papilla of Vater after stent removal; D: The resected specimen was diagnosed appropriately without being affected by stent removal. The yellow arrowheads denote the common bile duct after stent removal.
- Citation: Asada S, Kitagawa K, Hanatani J, Motokawa Y, Osaki Y, Iwata T, Kaji K, Mitoro A, Nagai M, Yoshiji H, Sho M. Endoscopic biliary drainage with multi-hole self-expandable metallic stent during neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in pancreatic cancer. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2025; 17(11): 111107
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v17/i11/111107.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v17.i11.111107