©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2026; 18(2): 113348
Published online Feb 27, 2026. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v18.i2.113348
Published online Feb 27, 2026. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v18.i2.113348
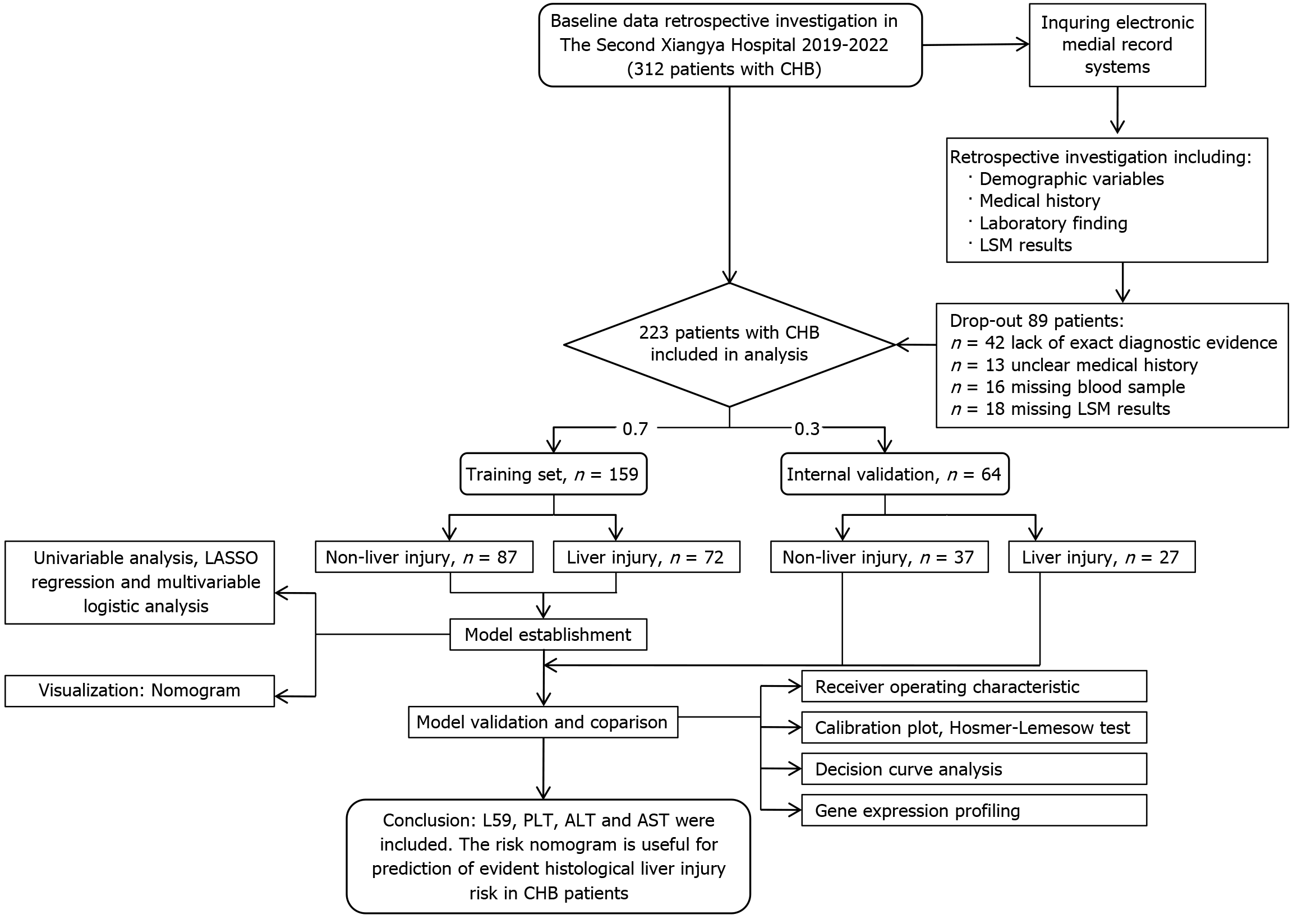
Figure 1 Study workflow.
CHB: Chronic hepatitis B; LSM: Liver stiffness measurement; LASSO: Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; PLT: Platelet; ALT: Alanine transaminase; AST: Aspartate transaminase.
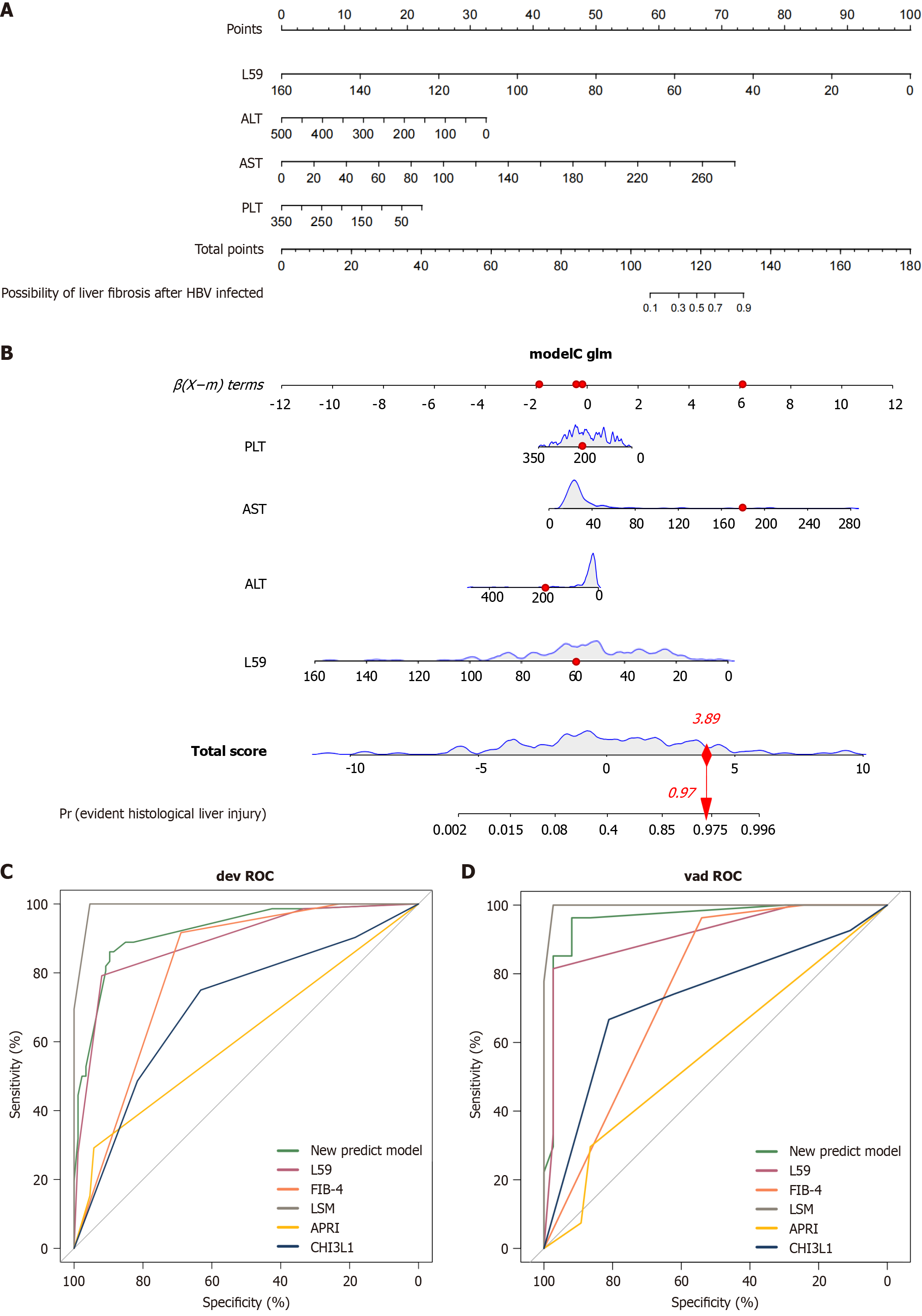
Figure 2 Nomogram to predict evident histological liver injury among patients with chronic hepatitis B.
A and B: Nomogram to predict the evident histological liver injury risk in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) infection. To use the nomogram, find the position of each variable on the corresponding axis, draw a line to the points axis for the number of points, add the points from all of the variables, and draw a line from the total point axis to determine the evident histological liver injury probabilities; C and D: Receiver operating characteristic curves of the multivariable logistic regression model for evident histological liver injury risk prediction in the training and validation group with CHB. PLT: Platelet; ALT: Alanine transaminase; AST: Aspartate transaminase; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; FIB-4: Fibrosis-4 index; LSM: Liver stiffness measurement; APRI: Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index.
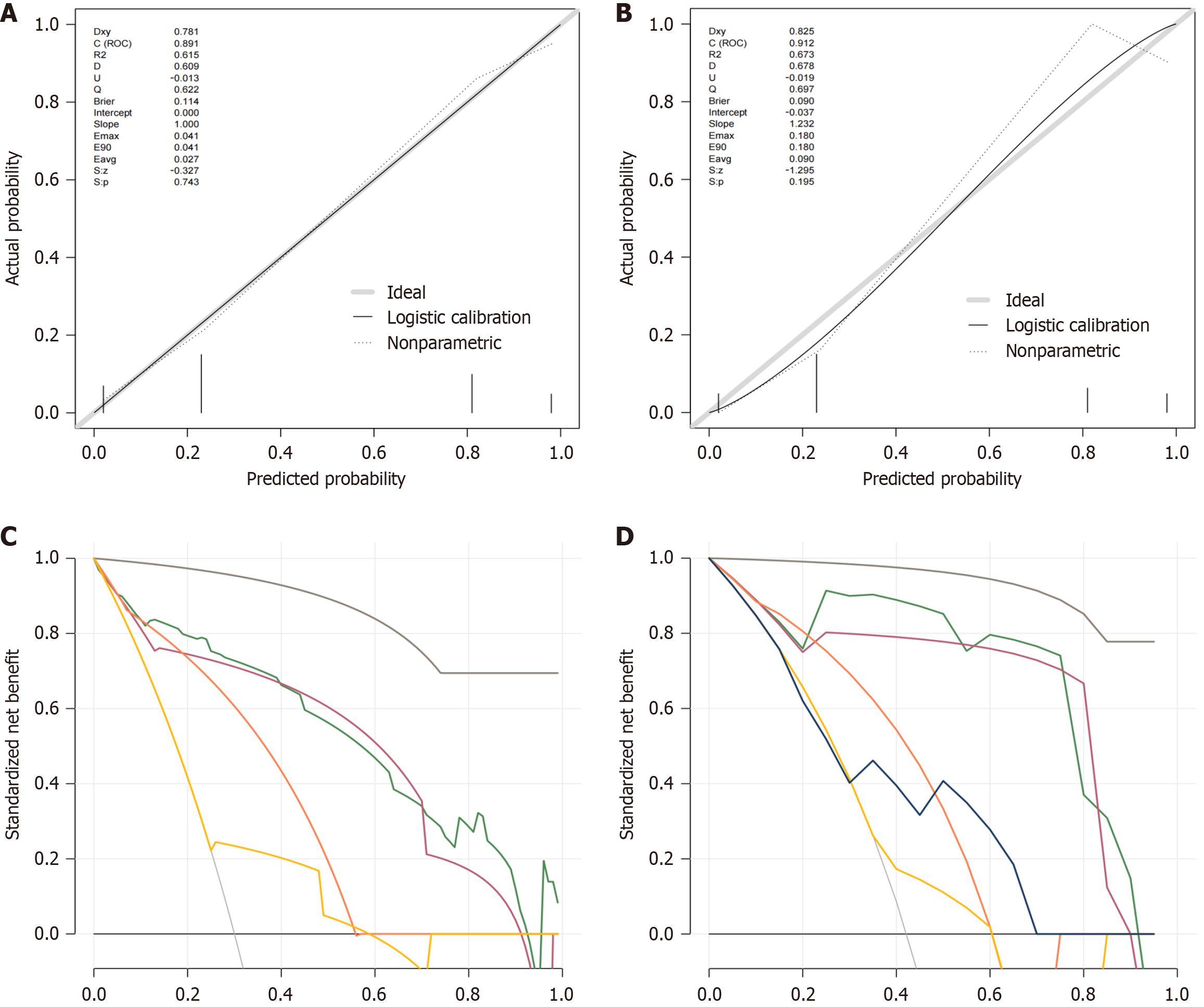
Figure 3 Performance of the novel nomogram.
A and B: Calibration plots of the multivariable logistic regression model for evident histological liver injury risk prediction in the training and validation group with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) infection; C and D: Decision curve analysis of the multivariable logistic regression model for evident histological liver injury risk prediction in the training and validation group with CHB infection.
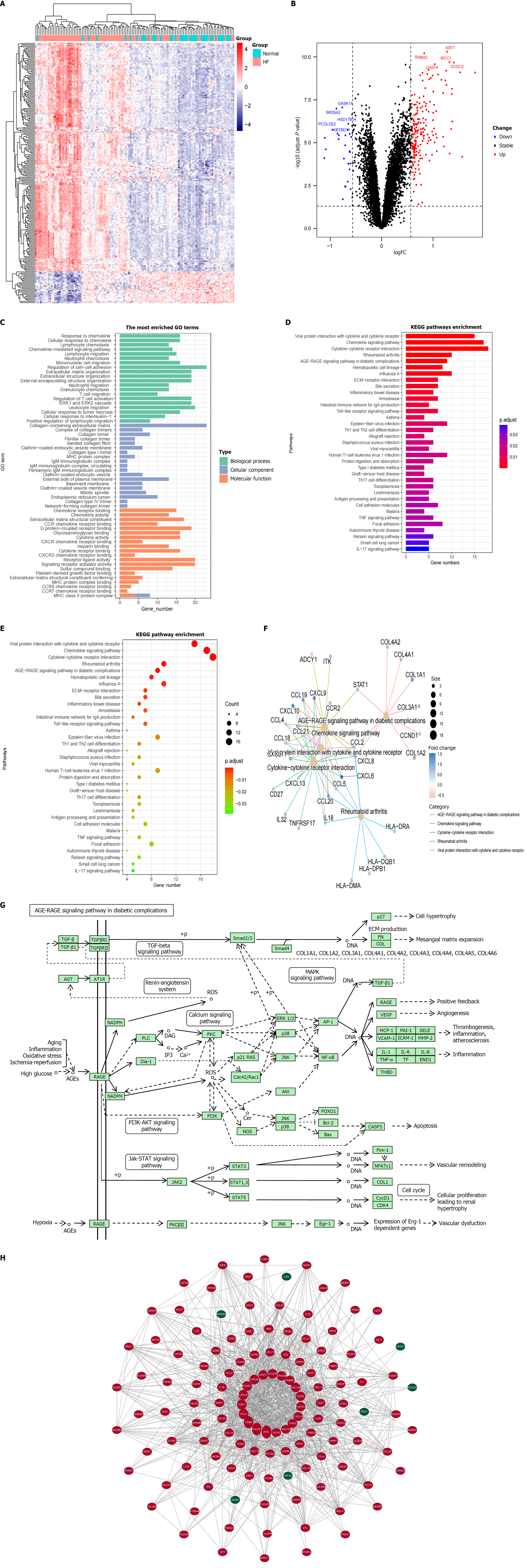
Figure 4 Identification of immune-related biomarkers for chronic hepatitis B using gene expression profiling.
A and B: Volcano plot showing the heatmap of top 30 differential genes upregulated and downregulated and differentially expressed genes in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients vs healthy controls; C: Gene Ontology (GO) functional annotation of signature genes; D-F: Functional annotation of the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) signaling pathway of signature genes. For all enriched GO and KEGG terms, P < 0.05; G: AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in CHB complications; H: Protein-protein interaction network regulation of genes in CHB.
- Citation: Dai ZS, Cao X, Jiang YF, He B. Predictive tool for evident histological liver injury in chronic hepatitis B patients: Development and validation. World J Hepatol 2026; 18(2): 113348
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v18/i2/113348.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v18.i2.113348