©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Hepatol. Jan 27, 2026; 18(1): 112821
Published online Jan 27, 2026. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v18.i1.112821
Published online Jan 27, 2026. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v18.i1.112821
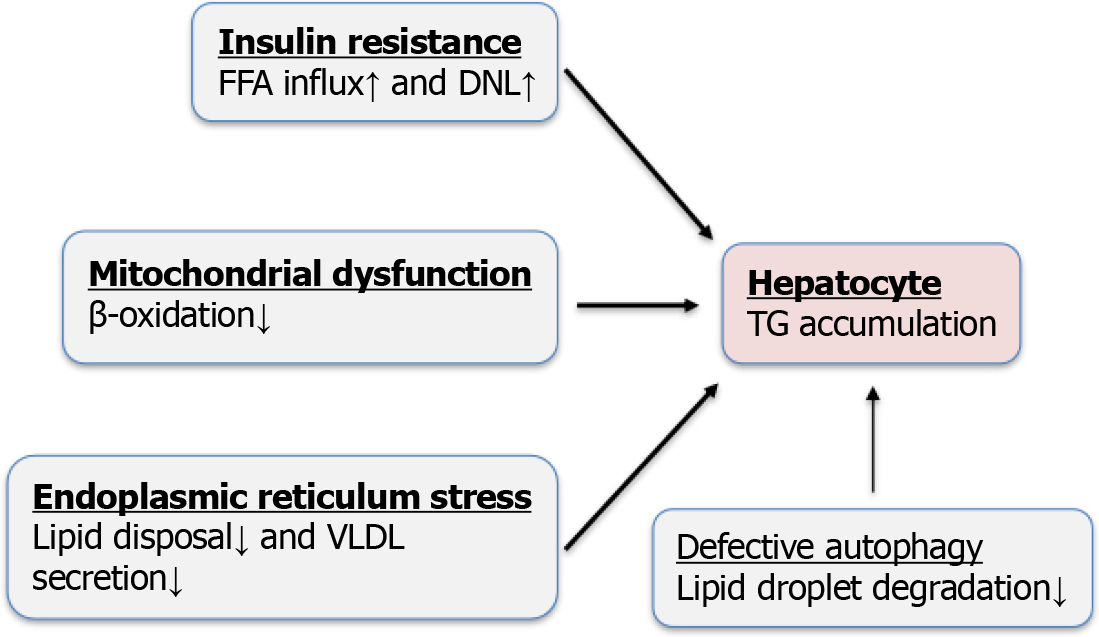
Figure 1 Mechanisms underlying hepatic steatosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
Hepatic steatosis develops when fatty acid input exceeds disposal. Major contributors include insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. In addition, defective selective autophagy (lipophagy) has been identified as an emerging mechanism that limits lipid droplet degradation and may exacerbate steatosis. DNL: De novo lipogenesis; FFA: Free fatty acid; TG: Triglyceride; VLDL: Very low-density lipoprotein.
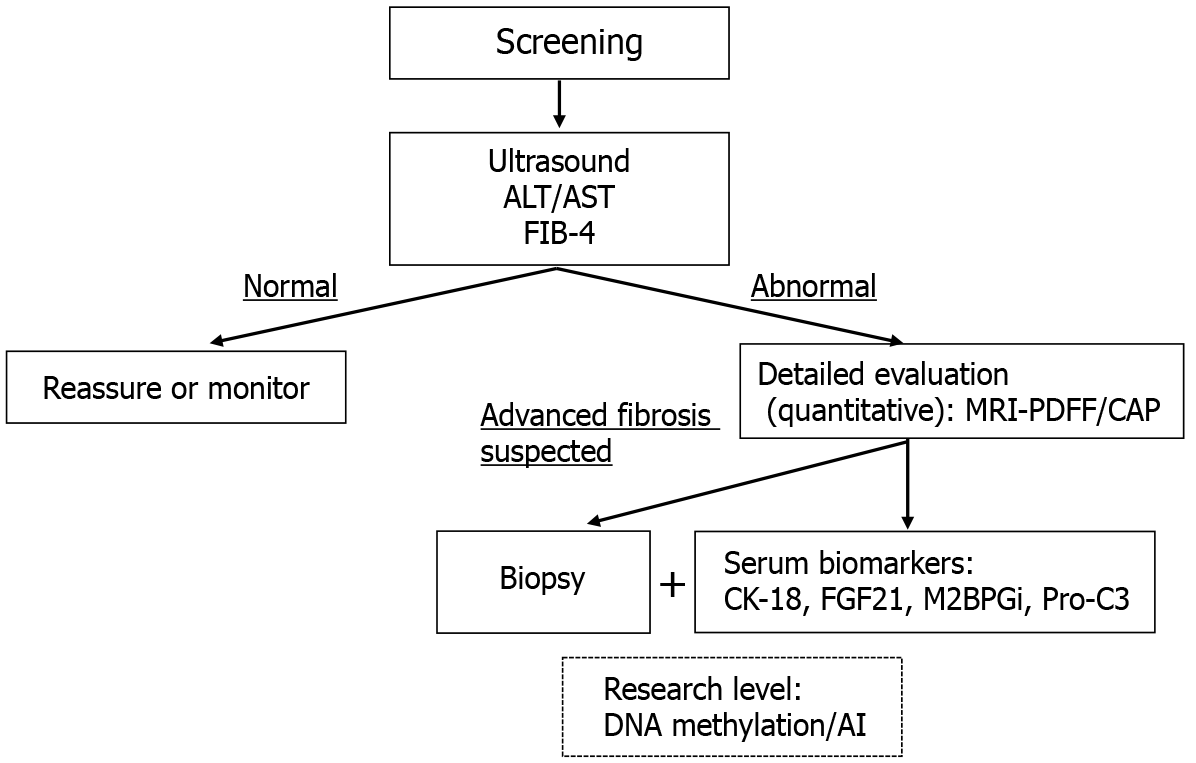
Figure 2 Diagnostic algorithm for hepatic steatosis evaluation.
This flowchart illustrates a stepwise approach to diagnosing hepatic steatosis based on clinical context. Screening typically begins with noninvasive methods such as ultrasound and liver enzyme assessment (alanine aminotransferase/aspartate aminotransferase) along with simple fibrosis scores (e.g., fibrosis-4). Patients with abnormal results proceed to more quantitative assessments using magnetic resonance imaging-proton density fat fraction or controlled attenuation parameter. In cases where advanced fibrosis is suspected, both serum biomarkers (e.g., cytokeratin-18, fibroblast growth factor 21, Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer, type III procollagen peptide) and liver biopsy may be considered. Biopsy remains the gold standard for histological confirmation. Emerging research-level diagnostic methods include DNA methylation profiling and artificial intelligence-based tools. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; FIB-4: Fibrosis-4; MRI-PDFF: Magnetic resonance imaging-proton density fat fraction; CAP: Controlled attenuation parameter; CK-18: Cytokeratin-18; FGF21: Fibroblast growth factor 21; M2BPGi: Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer; Pro-C3: Type III procollagen peptide; AI: Artificial intelligence.
- Citation: Moriyama K. Evaluation methods of hepatic steatosis: From conventional techniques to emerging biomarkers. World J Hepatol 2026; 18(1): 112821
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v18/i1/112821.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v18.i1.112821