©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2025; 17(9): 108259
Published online Sep 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i9.108259
Published online Sep 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i9.108259
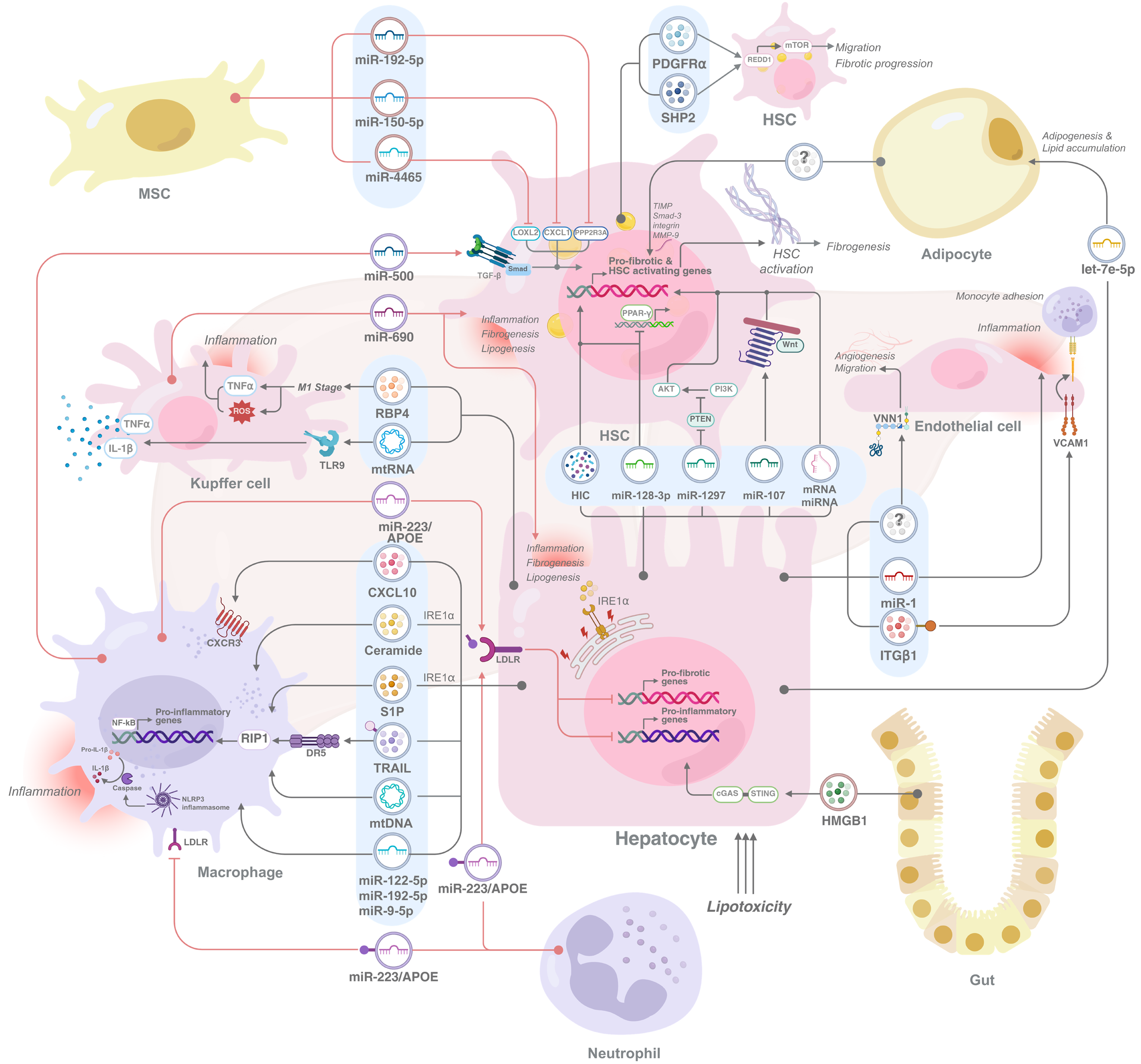
Figure 1 Extracellular vesicle-mediated cellular interactions in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease pathogenesis.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs), which act as key mediators of intercellular communication, facilitate the transfer of bioactive molecules, including proteins, lipids, and microRNAs, thereby significantly influencing recipient cell phenotypes and driving pathological processes. These EVs, which originate from diverse sources, such as hepatocytes, immune cells, and hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), contribute to the complex interplay of inflammation, fibrosis, lipid accumulation, and angiogenesis that characterizes metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Specifically, hepatocyte-derived EVs have been shown to activate macrophages, HSCs, endothelial cells, and adipocytes, thus promoting disease progression. Furthermore, immune cell-derived EVs play dual roles and are capable of both exacerbating and ameliorating MASLD. EVs from adipose tissue enhance fibrogenesis, whereas those from mesenchymal stem cells suppress HSC activation, highlighting their potential therapeutic implications. Finally, gut-derived EVs are implicated in further aggravating liver pathology in MASLD, underscoring the systemic impact of EV-mediated communication in this disease. mtDNA: Mitochondrial DNA; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin; RBP4: Retinol binding protein 4; APOE: Apolipoprotein E; TLRs: Toll‑like receptors; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; CXCL: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; CXCR: C-X-C motif chemokine receptor; R1P1: Receptor interacting protein kinase 1; miR: MicroRNA; HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; PDGFRα: Platelet derived growth factor receptor alpha; SHP2: Src homology region 2 domain‑containing phosphatase 2; VNN1: Vanin 1; ITGβ1: Integrin beta 1; HMGB1: High mobility group box 1; VCAM1: Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1.
- Citation: Boonkaew B, Charoenthanakitkul D, Suntornnont N, Ariyachet C, Tangkijvanich P. Extracellular vesicles in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: From intercellular signaling to clinical translation. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(9): 108259
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i9/108259.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i9.108259