©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. May 27, 2025; 17(5): 105769
Published online May 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i5.105769
Published online May 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i5.105769
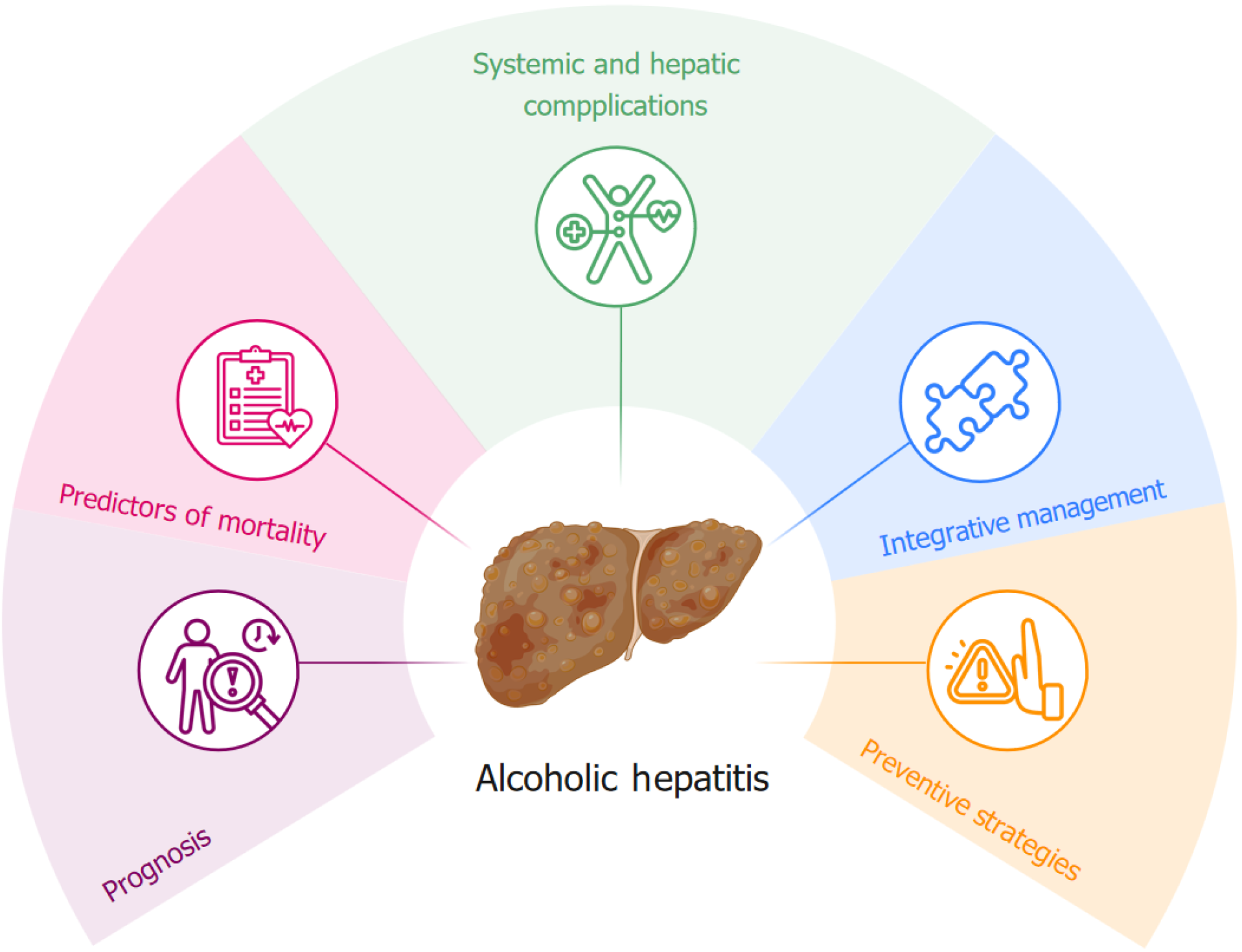
Figure 1 This diagram provides an overview of alcoholic hepatitis, highlighting the key factors that influence its prognosis, management and prevention.
Predictors of mortality include cirrhosis, renal dysfunction and malnutrition, which significantly influence outcomes. Prognostic tools, such as the Maddrey discriminant function, the model of end-stage liver disease, the Lille model and the Glasgow alcoholic hepatitis score, help stratify risk and guide treatment. Systemic and hepatic complications, such as hepatic encephalopathy, gastrointestinal bleeding and infections, contribute to disease progression and poor prognosis. Comprehensive treatment involves a multidisciplinary approach involving corticosteroid therapy, nutritional support, renal protection and early identification of nonresponders to optimize treatment. Preventive strategies, such as alcohol cessation programs, access to addiction treatment, public awareness campaigns, and policy interventions, are essential to reduce the incidence and burden of alcoholic hepatitis. This framework underscores the complexity of alcoholic hepatitis and the need for a multifaceted approach to improve patient outcomes.
- Citation: Ramírez-Mejía MM, Morales-Galicia AE, Méndez-Sánchez N. Prognostic challenges in alcoholic hepatitis: From scoring systems to clinical predictors. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(5): 105769
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i5/105769.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i5.105769