©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2025; 17(12): 110312
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i12.110312
Published online Dec 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i12.110312
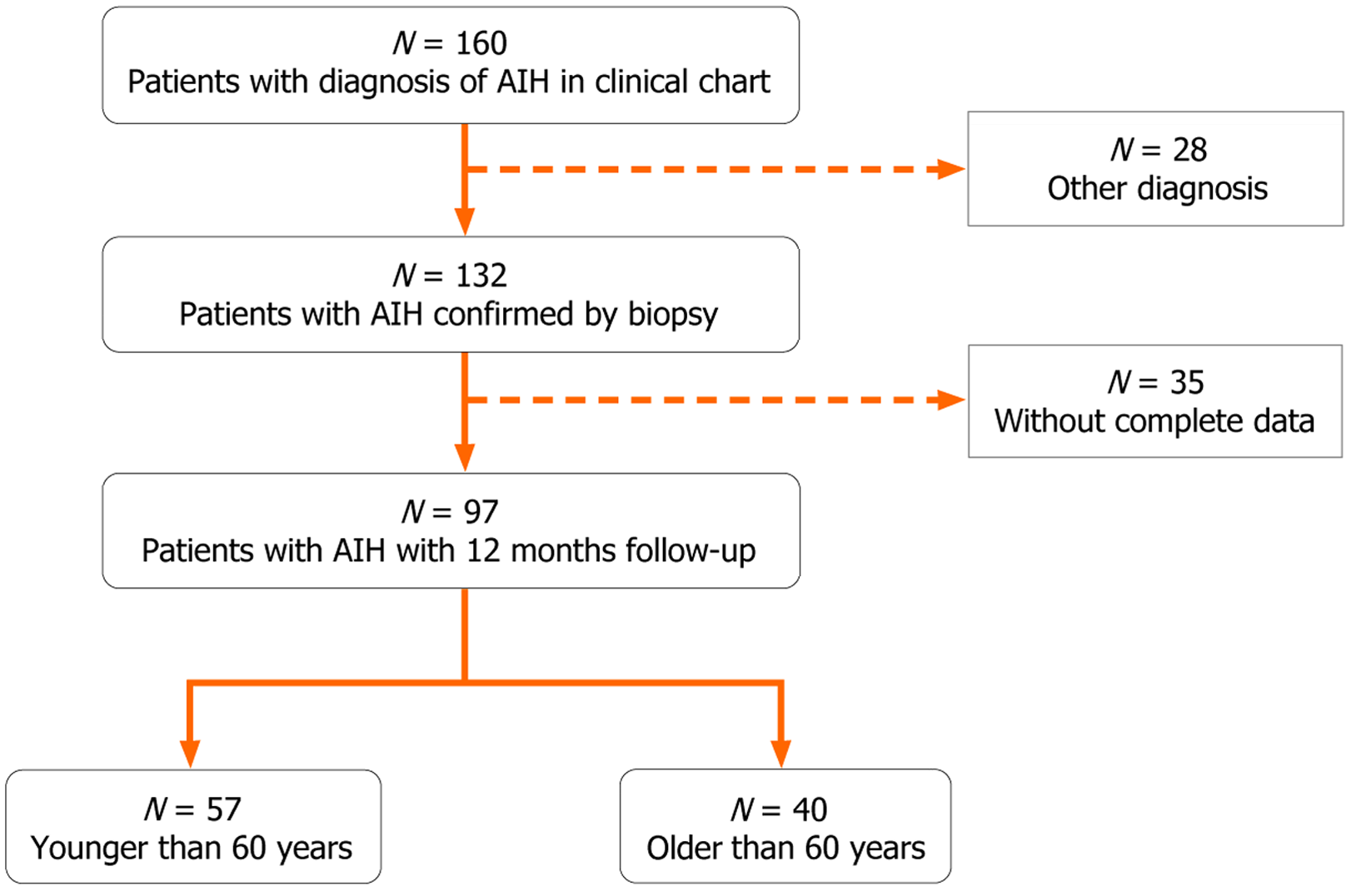
Figure 1 Patient selection flowchart.
Out of 160 patients with a clinical diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis, 132 had biopsy-confirmed disease. After excluding 35 patients due to incomplete data, 97 patients with at least 12 months of follow-up were included in the final analysis. These were stratified into two age groups: (1) 57 patients younger than 60 years; and (2) 40 patients aged 60 years or older. AIH: Autoimmune hepatitis.
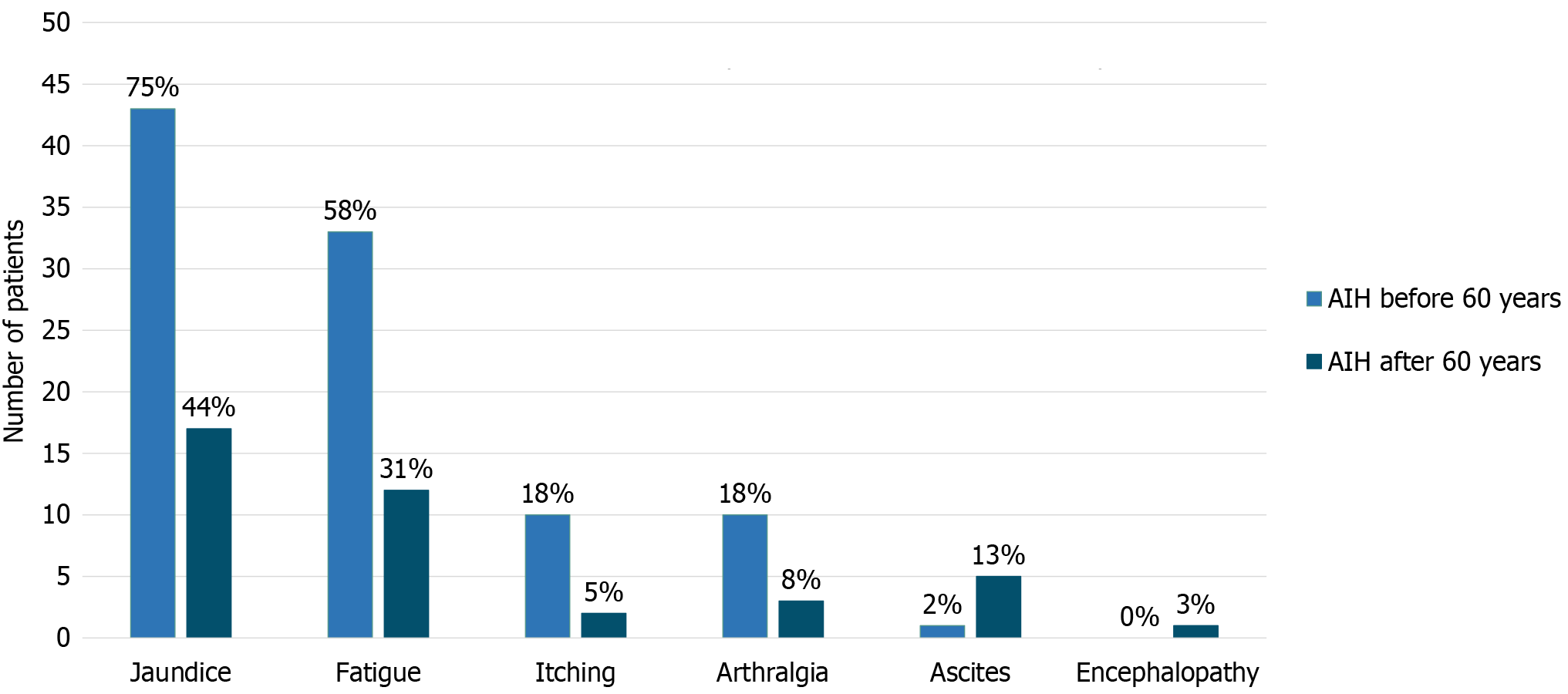
Figure 2 Symptoms at diagnosis in patients with autoimmune hepatitis diagnosed before and after 60 years of age.
Comparison of symptoms and signs at diagnosis between patients diagnosed with autoimmune hepatitis before age 60 (n = 57, light blue bars) and those diagnosed at or after age 60 (n = 40, dark blue bars). Percentages indicate the proportion of patients with each manifestation in each age group. Statistically significant differences were observed for jaundice (75% vs 44%, P = 0.002), fatigue (58% vs 31%, P = 0.09), and ascites (2% vs 13%, P = 0.028). AIH: Autoimmune hepatitis.
- Citation: Delgado J, Fuentes M, Simian D, Poniachik J, Urzúa Á. Impact of age on autoimmune hepatitis: A comparative study of patients diagnosed before and after sixty. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(12): 110312
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i12/110312.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i12.110312