©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2025; 17(10): 110029
Published online Oct 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i10.110029
Published online Oct 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i10.110029
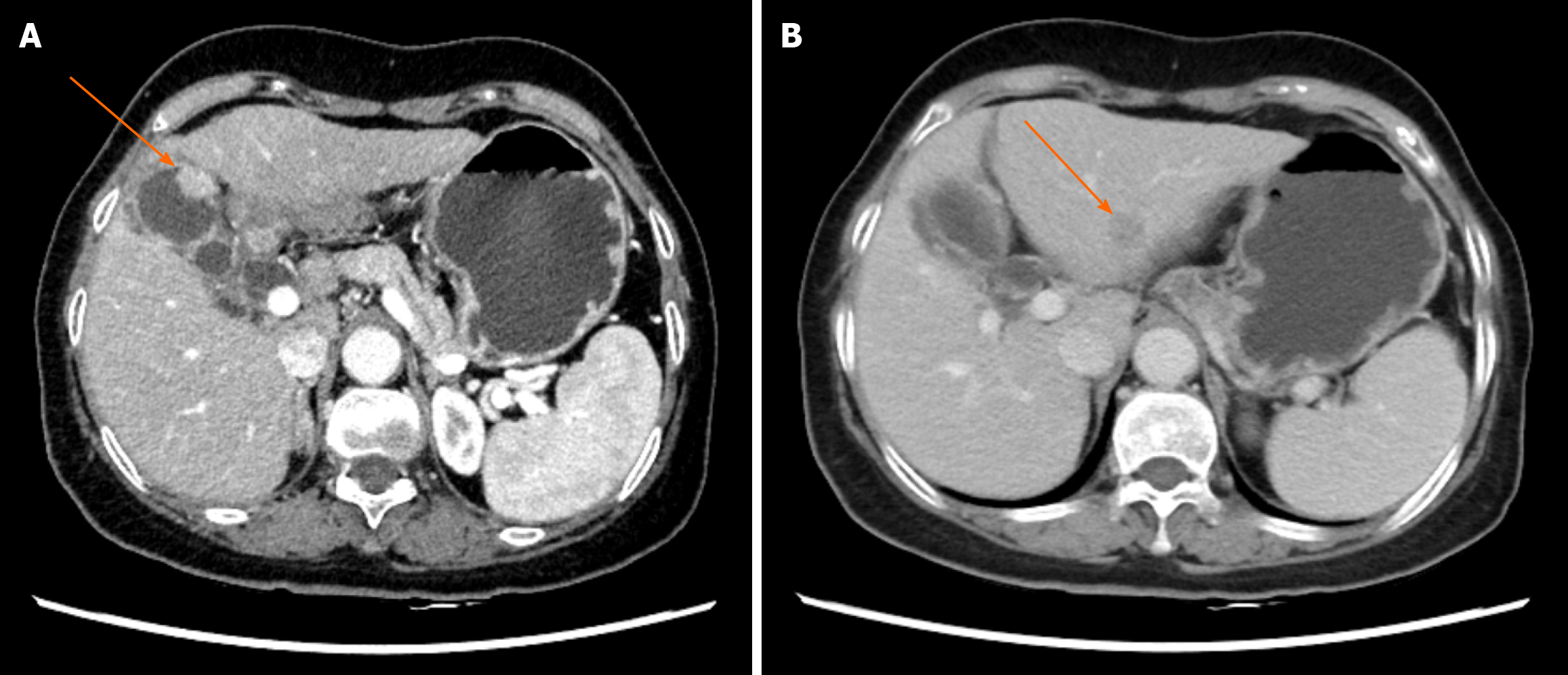
Figure 1 Abdominal computed tomography.
A: Abdominal computed tomography showing a 2.0 cm × 1.0 cm mass in the gallbladder. Arrow: Gallbladder mass (axial view); B: Abdominal computed tomography showing a 1.6 cm × 1.5 cm lesion in the left lateral lobe of the liver. Arrow: Liver lesion (axial view).
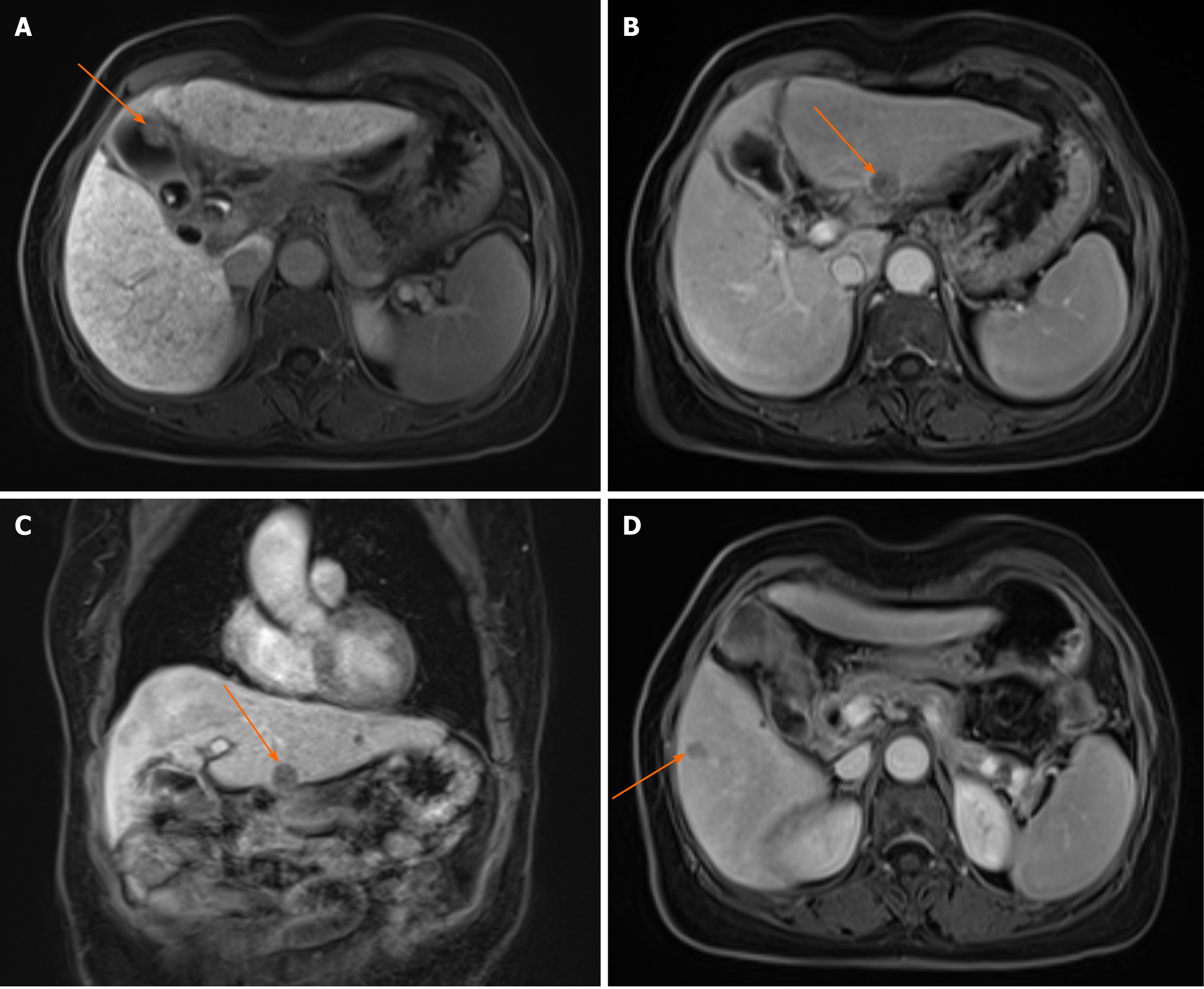
Figure 2 Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging scan.
A: Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan showing a 2.0 cm × 1.0 cm mass in the gallbladder. Arrow: Gallbladder mass (axial view); B: Abdominal MRI scan showing a 1.6 cm × 1.5 cm lesion in the left lateral lobe of the liver. Arrow: Liver lesion (axial view); C: Abdominal MRI showing a 1.6 cm × 1.5 cm lesion in the left lateral lobe of the liver. Arrow: Liver lesion (coronal view); D: Abdominal MRI scan showing a 1.0 cm × 0.8 cm lesion in segment VI of the liver. Arrow: Liver lesion (axial view).
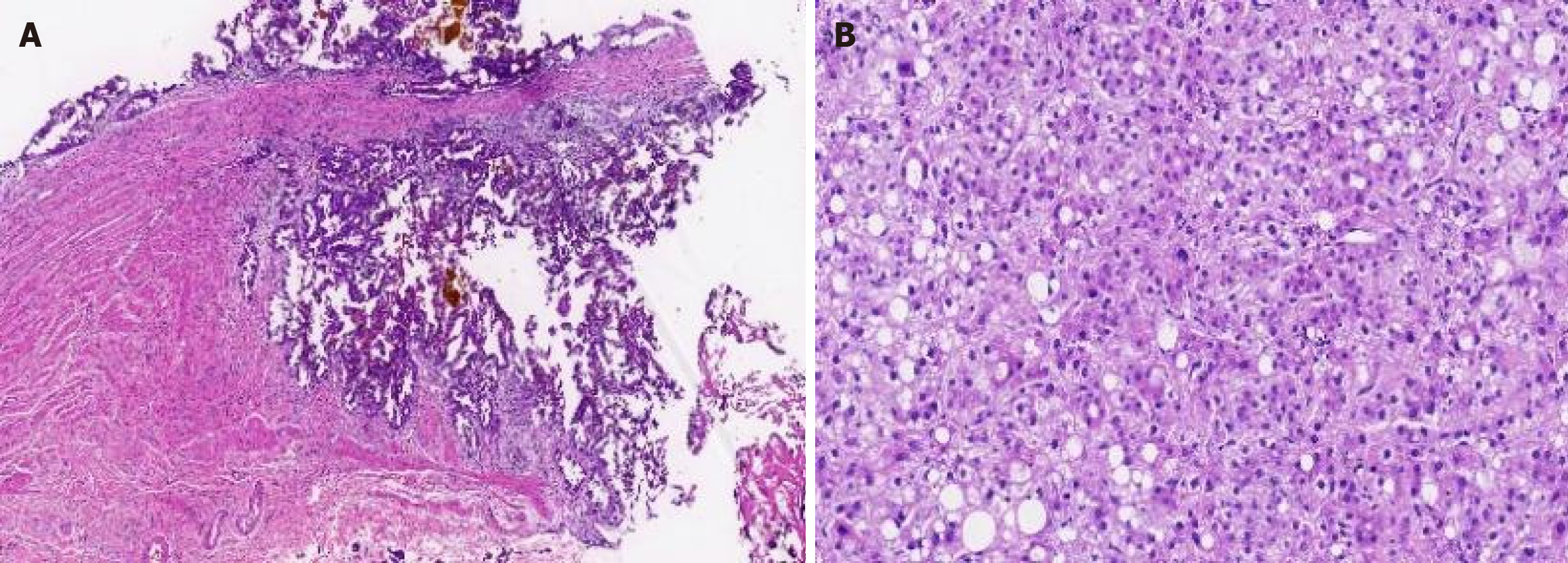
Figure 3 Microscopic view.
A: Microscopic view of gallbladder adenocarcinoma (with invasion into the muscular layer, 10 ×); B: Microscopic view of hepatocellular carcinoma (hematoxylin and eosin staining, 40 ×).
- Citation: Zhang K, Liu HL. Unusual presentation of synchronous double primary gallbladder and hepatic malignancies: A case report. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(10): 110029
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i10/110029.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i10.110029