©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2025; 17(10): 109898
Published online Oct 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i10.109898
Published online Oct 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i10.109898
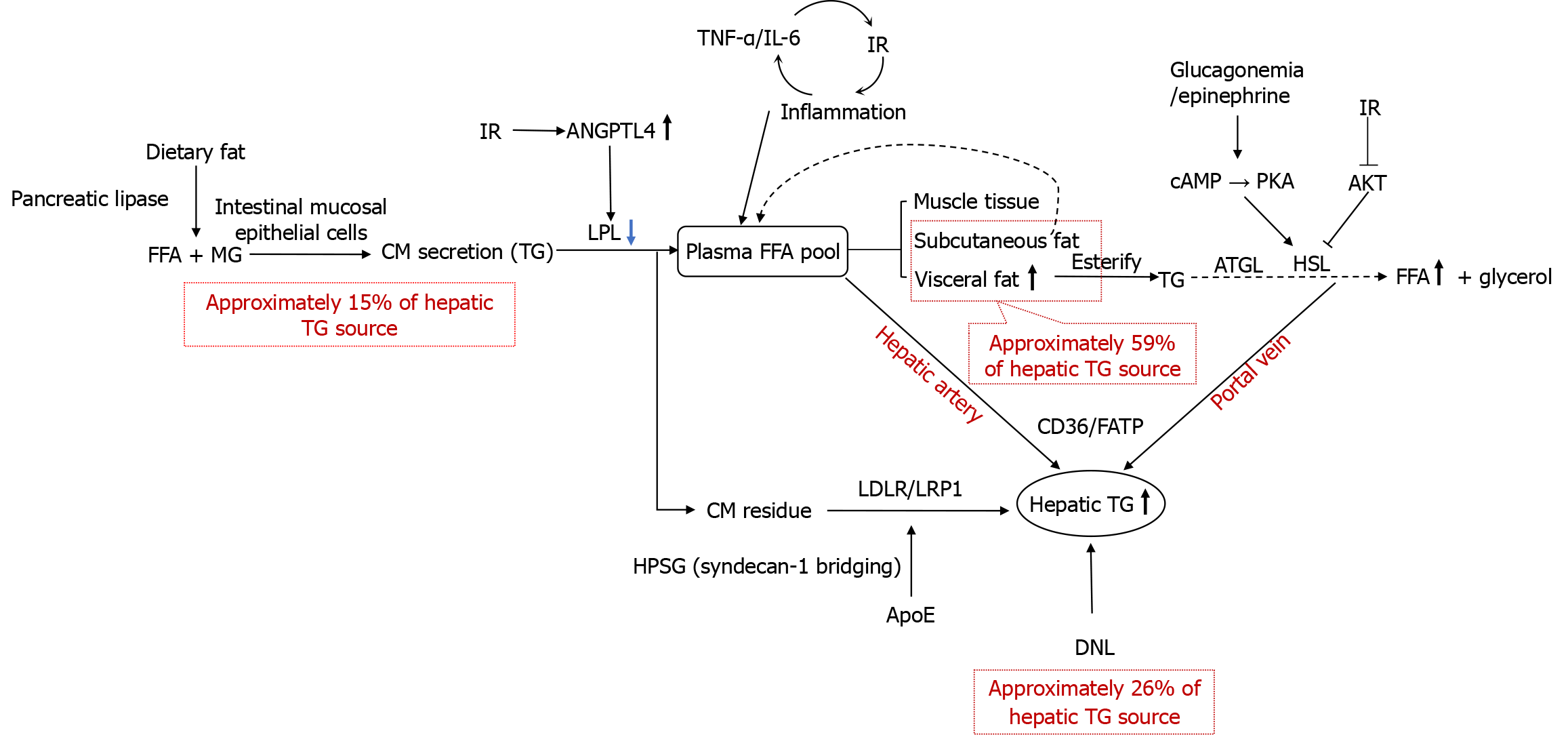
Figure 1 Dysregulation of extrahepatic lipid metabolism drives hepatic triglyceride deposition.
Extrahepatic lipid metabolic dysregulation drives liver triglyceride deposition via adipose tissue lipolysis (free fatty acid release) and chylomicron remnant uptake. Insulin resistance exacerbates lipoprotein lipase suppression and chylomicron remnant accumulation, while visceral adipose tissue hypermetabolism and inflammation synergistically promote the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic disease. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IR: Insulin resistance; ANGPTL4: Angiopoietin-like protein 4; FFA: Free fatty acid; MG: Monoglyceride; CM: Chylomicron; TG: Triglyceride; LPL: Lipoprotein lipase; cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA: Protein kinase A; AKT: Protein kinase B; ATGL: Adipose triglyceride lipase; HSL: Hormone-sensitive lipase; FATP: Fatty acid transport protein; LDLR: Low-density lipoprotein receptors; LRP1: Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1; ApoE: Apolipoproteins E; DNL: De novo lipogenesis.
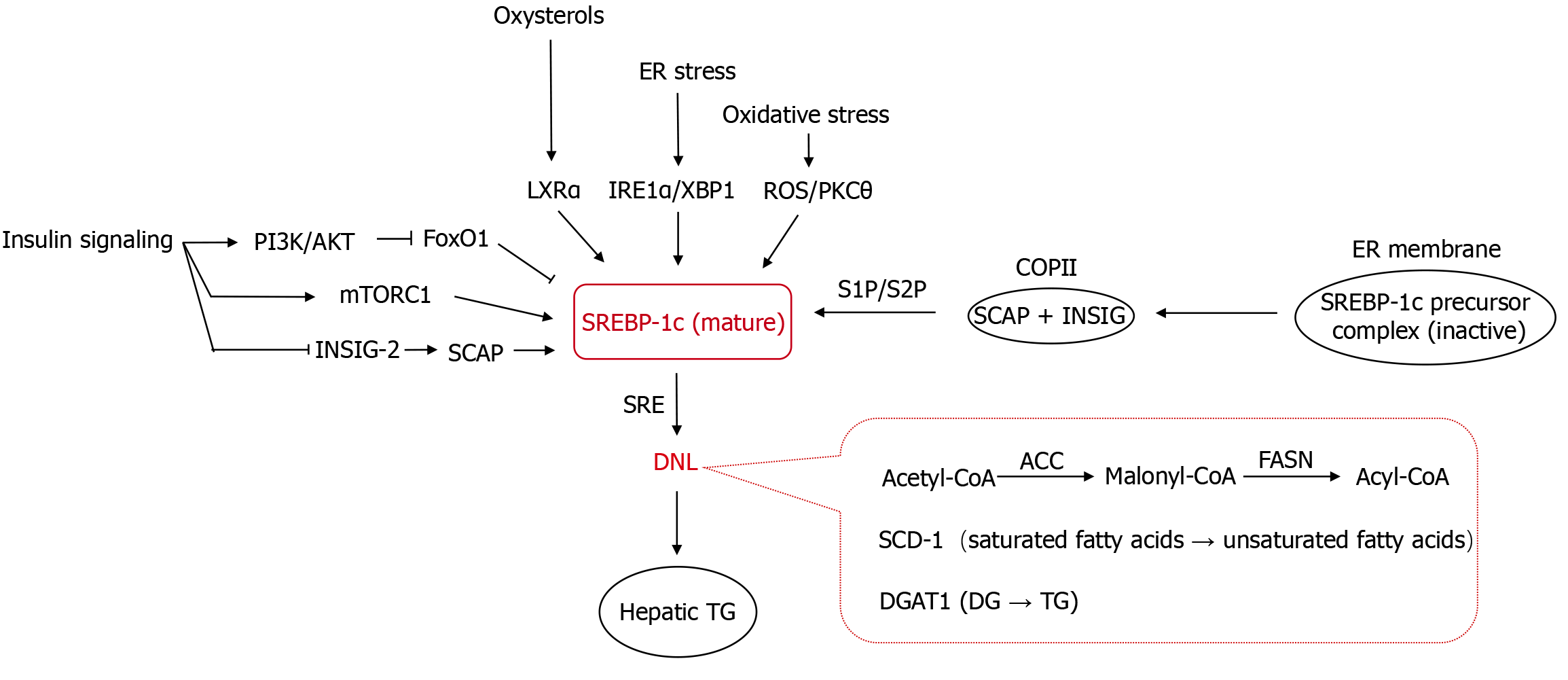
Figure 2 Hepatic sterol regulatory element-binding protein-lc integrates multiple signaling pathways and promotes de novo lipogenesis.
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-lc integrates insulin/inflammatory signals to upregulate lipogenic enzymes (acetyl-CoA carboxylase/fatty acid synthase), driving hepatic de novo lipogenesis and triglyceride accumulation. Targeted sterol regulatory element-binding protein-lc inhibition ameliorates steatosis, but triggers metabolic imbalance and cellular damage, requiring balanced therapeutic strategies. ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; LXRα: Liver X receptor alpha; IRE1α: Inositol-requiring enzyme 1 alpha; XBP1: X-box binding protein 1; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; PKC: Protein kinase C; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; FoxO1: Forkhead box protein O1; mTORC1: Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; INSIG: Insulin-induced gene; SCAP: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein cleavage-activating protein; SREBP-1c: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-lc; S1P: Signal peptide peptidase 1; S2P: Signal peptide peptidase 2; COP: Coat protein complex; SRE: Sterol regulatory element; DNL: De novo lipogenesis; ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; FASN: Fatty acid synthase; SCD-1: Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1; DGAT: Diacylglycerol acyltransferase; SPT: Serine palmitoyltransferase; TG: Triglyceride.
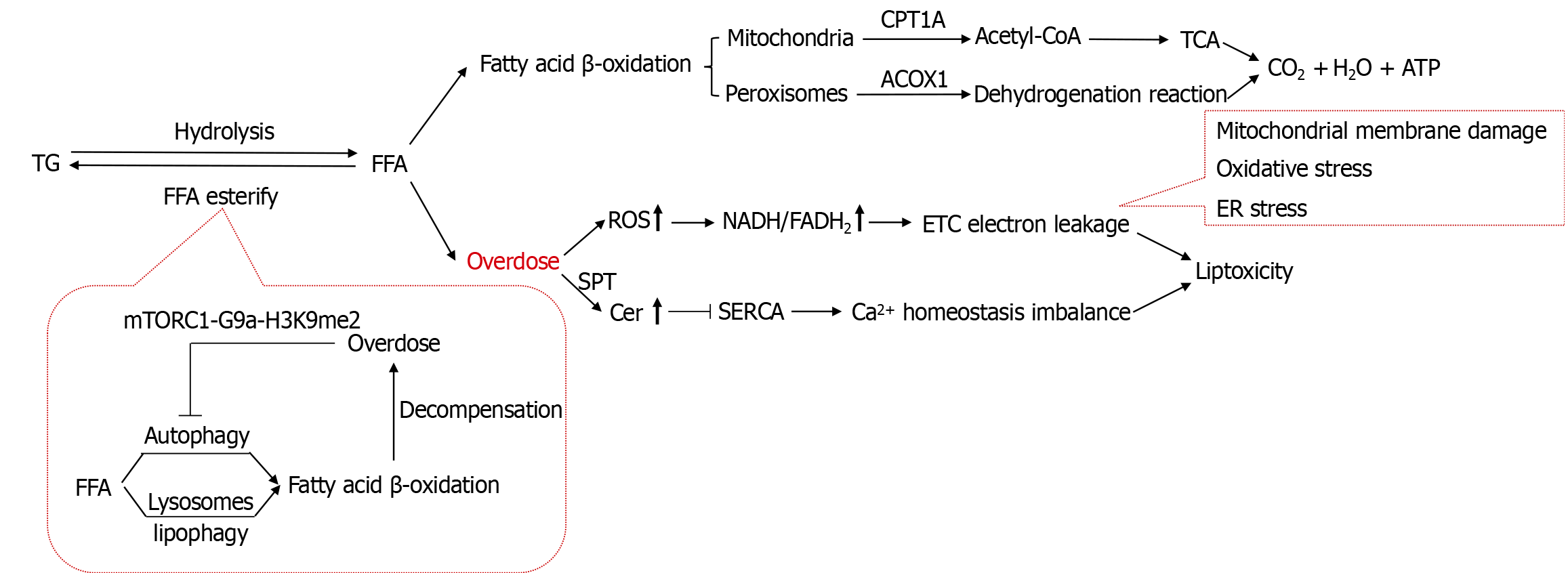
Figure 3 Dysregulated triglyceride catabolism in the liver enhances lipid toxicity.
Dysregulated hepatic triglyceride catabolism (adipose triglyceride lipase/carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A dysfunction) causes free fatty acid/ceramide accumulation, triggering oxidative stress and organelle damage. Impaired autophagy and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α dysregulation exacerbate lipotoxicity, synergistically driving metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic disease progression. TG: Triglyceride; FFA: Free fatty acid; CPT1A: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid cycle; ACOX1: Acyl-CoA oxidase 1; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; ETC: Electron transport chain; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; ATGL: Adipose triglyceride lipase; Cer: Ceramide; SERCA: Sarcoplasmic endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic disease; mTORC1: Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1.
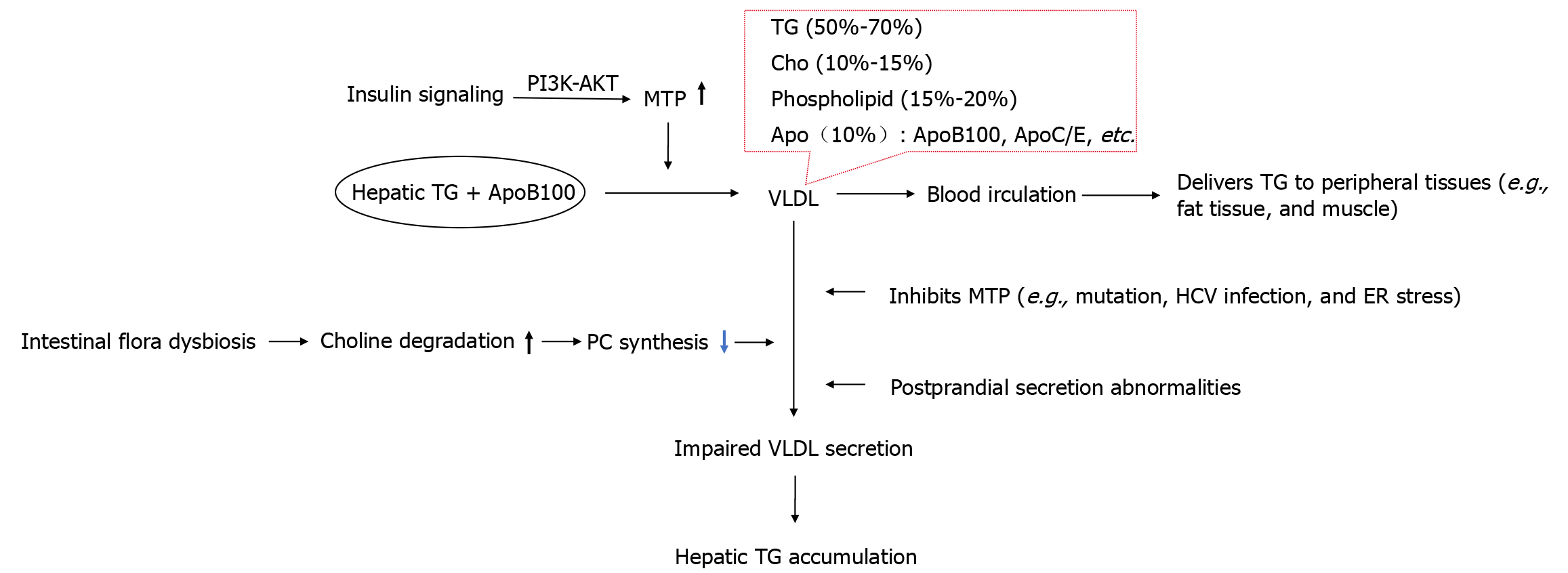
Figure 4 Hepatocyte lipid efflux impairment is an underestimated factor in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic disease.
Impaired hepatocyte lipid efflux (ApoB100/MTP dysfunction) suppresses very low-density lipoprotein secretion, causing triglyceride accumulation. Insulin resistance and gut dysbiosis synergistically disrupt lipid homeostasis, highlighting an underestimated pathogenic mechanism in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic disease. PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; TG: Triglyceride; Cho: Cholesterol; Apo: Apolipoproteins; VLDL: Very low-density lipoprotein; MTP: Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; PC: Phosphatidylcholine.
- Citation: Li SQ, Wu JH, Zhou Y, Wang CX, Xie L, Liu SY, Su YZ, He W, Chen H, Zhong WW, He YH. Hepatocyte nuclear factors dynamically regulate triglyceride metabolic reprogramming in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Mechanisms and implications. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(10): 109898
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i10/109898.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i10.109898