Published online May 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i4.776
Revised: February 5, 2015
Accepted: March 5, 2015
Published online: May 26, 2015
Processing time: 199 Days and 16.6 Hours
AIM: To investigate whether fetal kidney stem cells (fKSC) ameliorate cisplatin induced acute renal failure (ARF) in rats and promote renal angiogenesis.
METHODS: The fKSC were isolated from rat fetuses of gestation day 16 and expanded in vitro up to 3rd passage. They were characterized for the expression of mesenchymal and renal progenitor markers by flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry, respectively. The in vitro differentiation of fKSC towards epithelial lineage was evaluated by the treatment with specific induction medium and their angiogenic potential by matrigel induced tube formation assay. To study the effect of fKSC in ARF, fKSC labeled with PKH26 were infused in rats with cisplatin induced ARF and, the blood and renal tissues of the rats were collected at different time points. Blood biochemical parameters were studied to evaluate renal function. Renal tissues were evaluated for renal architecture, renal cell proliferation and angiogenesis by immunohistochemistry, renal cell apoptosis by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase nick-end labeling assay and early expression of angiogenic molecules viz. vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) by western blot.
RESULTS: The fKSC expressed mesenchymal markers viz. CD29, CD44, CD73, CD90 and CD105 as well as renal progenitor markers viz. Wt1, Pax2 and Six2. They exhibited a potential to form CD31 and Von Willebrand factor expressing capillary-like structures and could be differentiated into cytokeratin (CK)18 and CK19 positive epithelial cells. Administration of fKSC in rats with ARF as compared to administration of saline alone, resulted in a significant improvement in renal function and histology on day 3 (2.33 ± 0.33 vs 3.50 ± 0.34, P < 0.05) and on day 7 (0.83 ± 0.16 vs 2.00 ± 0.25, P < 0.05). The infused PKH26 labeled fKSC were observed to engraft in damaged renal tubules and showed increased proliferation and reduced apoptosis (P < 0.05) of renal cells. The kidneys of fKSC as compared to saline treated rats had a higher capillary density on day 3 [13.30 ± 1.54 vs 7.10 ± 1.29, capillaries/high-power fields (HPF), P < 0.05], and on day 7 (21.10 ± 1.46 vs 15.00 ± 1.30, capillaries/HPF, P < 0.05). In addition, kidneys of fKSC treated rats had an up-regulation of angiogenic proteins hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, VEGF and eNOS on day 3 (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSION: Our study shows that fKSC ameliorate cisplatin induced ARF in rats and promote renal angiogenesis, which may be an important therapeutic mechanism of these stem cells in the disease.
Core tip: This study provides novel data on the therapeutic effect of culture expanded fetal kidney stem cells (fKSC) in acute renal failure (ARF). The fKSC represent primitive renal stem cells that express mesenchymal and renal progenitor markers. They exhibit in vitro angiogenesis and potential to differentiate into renal epithelial cells. On administration in ARF rats, they rapidly improve renal function and histology. The therapeutic effects of fKSC are accompanied with increased capillary density in kidney tissues suggesting that induction of renal angiogenesis may be an important therapeutic mechanism of these stem cells.
- Citation: Gupta AK, Jadhav SH, Tripathy NK, Nityanand S. Fetal kidney stem cells ameliorate cisplatin induced acute renal failure and promote renal angiogenesis. World J Stem Cells 2015; 7(4): 776-788
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v7/i4/776.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v7.i4.776
Acute renal failure (ARF) is characterized by rapid loss of renal function due to damage of renal tubular epithelial cells by ischemia, nephrotoxins or other means. Some cases of ARF spontaneously recover from renal injury while in others the recovery process is either delayed or does not occur at all, leading to chronic kidney disease (CKD), which is associated with high morbidity and mortality[1,2]. Thus, it is very important to restore normal structure and function of the kidney after ARF using a suitable regenerative therapy in order to prevent its progression into CKD[3]. Recent data suggest that injury of endothelial cells of small peritubular arterioles and capillaries plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of ARF by mediating hypoxia and impairment of renal perfusion that eventually results in injury of renal tubular epithelial cells and thereby loss of renal function[4-6]. Furthermore, reduction in renal capillary density following ARF may perpetuate the tubular epithelial injury leading to CKD[7,8]. These observations suggest that neovascularization of the kidney and regeneration of damaged renal tubular epithelial cells may be potentially effective in recovery from ARF.
During the past decade, stem cell based regenerative therapy has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy for ARF and stem cells derived from various sources are being extensively explored for the treatment of ARF[9,10]. However, a suitable stem cell type for therapeutic application in clinical ARF has not yet been identified. Fetal kidney stem cells (fKSC) represent a novel stem cell type for treatment of ARF because they are multipotent stem cells with an inherent ability to differentiate into cells of renal lineage. In addition, few studies have shown that embryonic or fetal kidney also contains a subpopulation of endothelial and epithelial progenitors[11-13] and hence fKSC may have an important role in neovascularization and the regeneration of the damaged kidney. However, there is a paucity of data on therapeutic effect of fKSC in ARF and no information is available about angiogenic role of these stem cells in mediating their therapeutic effect in the disease.
Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the therapeutic effect of fKSC in cisplatin induced ARF in rats and to evaluate whether neovascularization in the damaged kidney has a role in the therapeutic efficacy of these stem cells in the disease.
Experiments were performed on Sprague Dawley (SD) rats (220-250 g) purchased from Central Drug Research Institute, Lucknow, India. All animal experimental procedures in this study were performed as per guidelines of the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee and the Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA), India. The protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India.
The fKSC were isolated from SD rat fetuses at gestation day 16. The kidneys were removed from fetuses of 10 pregnant female rats (8-12 fetuses/animal), minced, and digested with 1 mg/mL collagenase type-IV (Worthington Biochemical, NJ, United States) in serum free α-MEM (Gibco, NY, United States) medium for 40 min at 37 °C with intermittent stirring in water bath. After two washes with α-MEM, the digested tissue was cultured at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 in 25 cm2 tissue culture flasks (BD, New Jersey, United States) in complete culture medium consisting of α-MEM medium, 2 mg/mL of Glutamax (Gibco, NY, United States), 16.5% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, NY, United States) and bacteriostatic level of penicillin-streptomycin (Gibco, NY, United States). After 48 h of seeding of fetal kidney cells, the culture media containing non-adherent cells were replaced. On day 3 adherent cells were harvested by trypsinization with TrypLE Express (Gibco, NY, United States) and further cultured in complete culture media. The cells of 3rd passage were used for this study.
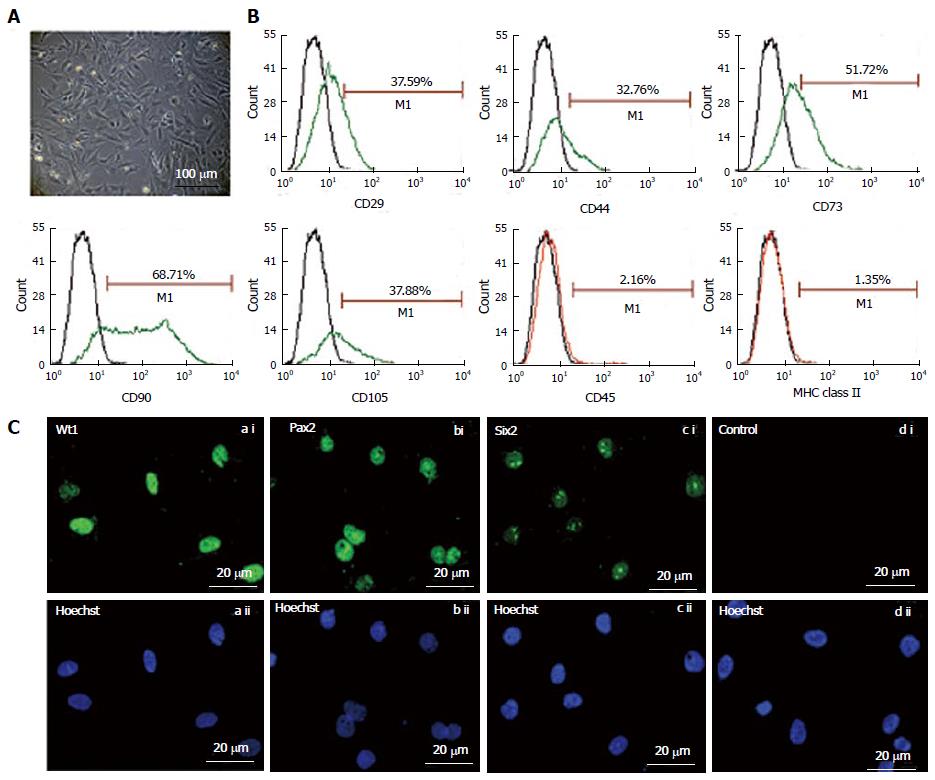
The fKSC were characterized by studying their expression of mesenchymal and renal progenitor markers. The expression of mesenchymal markers on fKSC was studied by flow cytometry. The fKSC at passage 3 were incubated for 30 min with following antibodies: Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) conjugated CD90 (Abcam, MA, United States), CD44 (BD Biosciences, CA, United States), phycoerythrin conjugated CD45 (Abcam, MA, United States), MHC class II (Abcam, MA, United States) and with unconjugated CD29 (Abcam, MA, United States), CD73 (BD Biosciences, CA, United States), CD105 (Santa cruz biotechnology, inc. CA, United States). The corresponding FITC-conjugated secondary antibodies (Abcam, MA, United States) were added in CD29, CD73 and CD105 tubes. Isotype-identical antibodies (IgG) served as controls.
Expression of renal progenitor markers viz. Wilms tumor1 (Wt1), paired box2 (Pax2), SIX homebox2 (Six2) was studied by immunocytochemistry. The cells were fixed with 4% para-formaldehyde for 1 h at room temperature and incubated overnight at 4 °C with following primary antibodies: Wt1, Pax2 (both from Abcam, MA, United States) and Six2 (Santa cruz biotechnology, Inc. CA, United States). After washing with PBS, cells were incubated with corresponding FITC-conjugated secondary antibodies and counter stained with Hoechst dye (Sigma-Aldrich, MO, United States). The fKSC incubated with non-immune serum or IgG in place of primary antibodies were used as negative controls. The images were obtained using Nuance Multispectral Imaging System (CRi Inc., MA, United States).
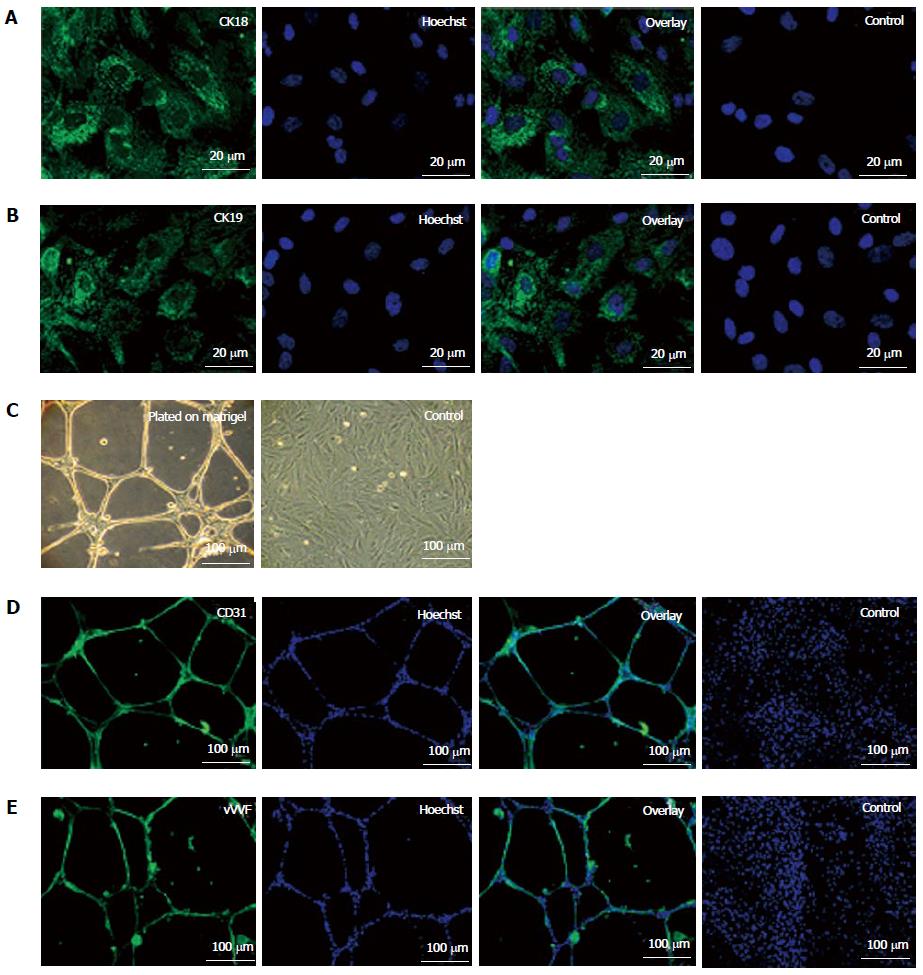
To induce epithelial differentiation, fKSC (2 × 104 cells/well) were cultured on cover slips in 6 well plate in complete culture medium containing 0.1 μmol/L Retinoic acid, 10 ng/mL activin-A and 50 ng/mL Bmp7 (all from R and D Systems, MN, United States). After 7 d, cover slips with induced fKSC were fixed in 4% para-formaldehyde for 1 h at room temperature. The fixed cells were incubated at 4 °C overnight with primary antibodies viz. cytokeratin (CK)18 and CK19 (Abcam, MA, United States). After washing with PBS, cells were incubated with corresponding FITC-conjugated secondary antibodies for 1 h at room temperature and counter stained with Hoechst dye (Sigma-Aldrich, MO, United States). The fKSC cultured without induction medium were used as negative controls.
The tube-formation assay was performed to assess the angiogenic potential of fKSC. Briefly, fKSC (2 × 104 cells/well) were seeded onto the growth factor reduced matrigel (BD Biosciences, CA, United States) coated cover slips in 6 well plate and incubated overnight in standard culture condition with complete medium. The cells were examined by phase contrast microscopy and immunocytochemistry. For immunocytochemistry, cells were fixed with 4% para-formaldehyde for 1 h at room temperature. The fixed cells were incubated at 4 °C overnight with primary antibodies viz. CD31 (AbD serotech, Oxford, United Kingdom) and Von Willebrand factor (vWF) antibody (Abcam, MA, United States). After washing with PBS, cells were incubated with corresponding FITC-conjugated secondary antibodies for 1 h at room temperature and stained with Hoechst dye. The fKSC cultured without growth factor reduced matrigel were used as negative controls.
ARF was induced in male SD rats (n = 36) weighing 200-225g by cisplatin injection as described by Ozyurt et al[14]. Briefly, the animals were given a single intra-peritoneal injection of cisplatin (0.5 mg in 1 mL of saline, sigma, United States) at a dose of 7 mg/kg of body weight. A significant increase in blood biochemical parameters and renal damage were observed in rats on day 5 of cisplatin injection. Hence at this time point, rats were randomized into two groups viz. fKSC treated group (n = 18) and saline treated group (n = 18) for evaluation of the efficacy of stem cell therapy. In addition, a group of healthy rats (n = 6) was also included in the study as healthy controls to compare renal function and histology of fKSC and saline treated groups.
The fKSC were labeled with PKH26, a red fluorescent cell linker (Sigma-Aldrich, MO, United States) according to manufacturer’s protocol. Labeling efficiency of PKH26 with fKSC and cell viability of labeled cells were > 95% and > 97% as revealed by fluorescent microscopy and trypan blue exclusion, respectively. On day 5 of cisplatin injection, a total of 2 × 106 PKH26 labeled fKSC in 150 μL of saline or 150 μL saline alone were injected intravenously through tail vein in each rat of fKSC treated or saline treated groups, respectively.
Animals were euthanized by barbiturate overdose (intravenous injection, 150 mg/kg pentobarbital sodium) before fKSC therapy (day 0) and after three days (day 3) and seven days (day 7) of fKSC therapy. Blood samples were collected to determine blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine levels by using commercial Span diagnostic kits with an autoanalyser (BioSytems BTS-330). The kidney tissues were excised to perform the assays described below.
Ten percent of formalin fixed kidney tissues were cut into 5 µm serial sections and stained with hematoxylin and eosin to evaluate sequential histopathological changes in saline and fKSC treated animals. Quantitative assessment of renal tubular necrosis was performed using the grading scores of Jablonski et al[15]. For immunohistochemical analysis, 5 μm thick paraffin sections of kidneys were deparaffinized with xylene and rehydrated in a series of alcohol and water. After rehydration, tissue sections were incubated with primary antibodies viz. aquaporin (AQP)1, vWF (both from Abcam, MA, United States) and CD31 (AbD serotech, Oxford, United Kingdom) and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA; BD Biosciences, CA, United States). After overnight incubation, sections were washed with PBS and incubated with corresponding FITC-conjugated secondary antibodies and then counter stained with Hoechst dye. Images were taken by Nuance Multispectral Imaging System (CRi Inc., MA, United States). To determine the capillary density, CD31 stained capillaries were counted in 10 randomly chosen high-power fields (HPF; 20 μm) using a fluorescent microscope and expressed as capillaries per HPF. To determine the number of proliferating cells in the kidney, PCNA positive nuclei were counted in 10 HPFs per section (20 μm) in the cortico-medullary area under a Nuance Multispectral Imaging System (CRi Inc., MA, United States) and the proliferative index was expressed as average number of PCNA+ cells /HPF.
Apoptotic scores in kidney tissue sections were measured by the terminal transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assay using an In Situ Cell Death Detection Kit (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) as per manufacturer’s instruction. Briefly, kidney sections were deparaffinized, rehydrated, and digested with proteinase K and labeled with TUNEL reaction mixture for 60 min at 37 °C. TUNEL positive nuclei were counted in 10 HPF per section in the cortico-medullary area at 20 μm magnification under a Nuance Multispectral Imaging System (CRi Inc., MA, United States) and the apoptotic index was expressed as average number of TUNEL+ cells /HPF.
Expression of angiogenic signaling molecules in the kidneys of rats was evaluated by western blotting on day 3 after fKSC therapy. The kidney tissues of animals were homogenized in RIPA buffer containing 1 mmol/L phenylmethanesulphonyl fluoride and 1% protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich, MO, United States). Kidney tissue homogenate was centrifuged at 10000 g for 10 min and the supernatant was stored in -80 °C. 40 mg proteins were loaded and separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. After electrophoresis, separated proteins were transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. The membranes were blocked with 5% BSA for 1 h at room temperature and then incubated at 4 °C overnight against primary antibodies viz. vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) (all from Abcam, MA, United States). β-Actin antibody (Abcam, MA, United States) was used as a loading control. Primary antibodies were detected by corresponding horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies using super signal west pico chemiluminescent substrate (Thermo scientific, IL, United States). The bands were quantified by densitometry using the Quantity One software (Bio-Rad, CA, United States).
The animal protocol was designed to minimize pain or discomfort to the animals. The animals were acclimatized to laboratory conditions (23 °C, 12 h/12 h light/dark, 50% humidity, ad libitum access to food and water) for two weeks prior to experimentation. All animals were euthanized by barbiturate overdose (intravenous injection, 150 mg/kg pentobarbital sodium) for tissue collection.
Values were expressed as mean ± standard error (SE). The statistically significant differences between groups were analyzed by one way-analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni multiple-comparison post hoc test. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism Software Version 5 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA) and a P value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
The fKSC exhibited spindle-shaped and polygonal morphology in culture (Figure 1A). Flow cytometry analysis showed that fKSC expressed CD29 (37.59%), CD44 (32.76%), CD73 (51.72%), CD90 (68.71%) and CD105 (37.88%), whereas the expression of CD45 and MHC class II was < 5% (Figure 1B). Immunocytochemistry revealed that fKSC also expressed renal progenitor markers viz. Wt1, Pax2 and Six2 (Figure 1C).
On treatment with specific induction medium, fKSC exhibited differentiation ability into epithelial cells as demonstrated by expression of CK18 and CK19 by immunocytochemistry (Figures 2A and B). When grown on matrigel, fKSC exhibited capillary-like tubular structures assessed by phase contrast microscopy (Figure 2C) and expressed endothelial markers viz., CD31 and vWF by immunocytochemistry (Figure 2D and E).
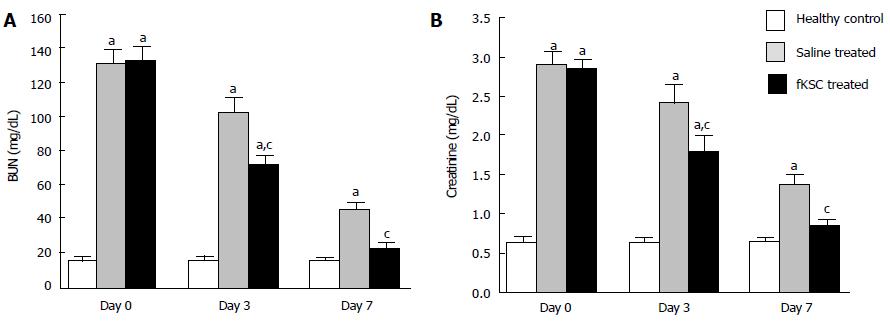
On the 5th day of cisplatin injection, the rats exhibited a significant increase in levels of both BUN and serum creatinine as compared to healthy controls (P < 0.05). The same day (day 0 of therapy), the rats were randomized to receive fKSC therapy or saline alone. On day 3 of therapy, fKSC treated group had significantly lower levels of these blood biochemical parameters as compared to saline treated group (P < 0.05), but both groups had significantly higher levels as compared to healthy controls (P < 0.05). On day 7 of therapy, the serum creatinine and BUN levels in the fKSC treated group were comparable to healthy controls but they were still significantly higher in the saline treated group in comparison to healthy controls (P < 0.05) (Figure 3A and B).
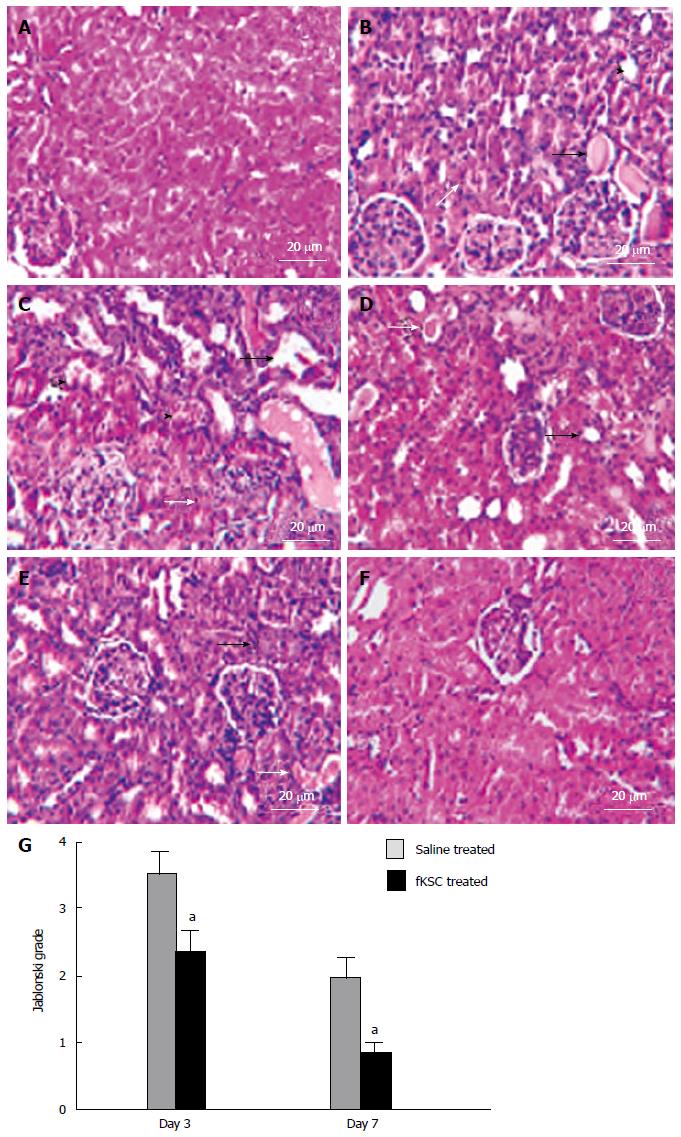
The kidneys of ARF rats on the 5th day of cisplatin injection showed severe tubular necrosis, hyaline cast formation, loss of brush border in the proximal renal tubules and tubular dilatation (Figure 4B). On day 3 of fKSC therapy, the kidneys showed a significant attenuation of tubular injury as compared to saline treated rats (Figure 4C and D) and Jablonski grading score revealed significantly lower necrosis in the kidneys of fKSC treated as compared to saline treated rats (2.33 ± 0.33 vs 3.50 ± 0.34, P < 0.05, Figure 4G). On day 7 of therapy, the kidneys of fKSC treated ARF rats showed disappearance of necrotic cells with almost normal architecture of tubules, whereas those of saline treated ARF rats still had necrotic tubular cells and hyaline casts (Figure 4E and F) and there was also a significant difference in Jablonski grading score between the fKSC treated and saline treated groups (0.83 ± 0.16 vs 2.00 ± 0.25, P < 0.05, Figure 4G).
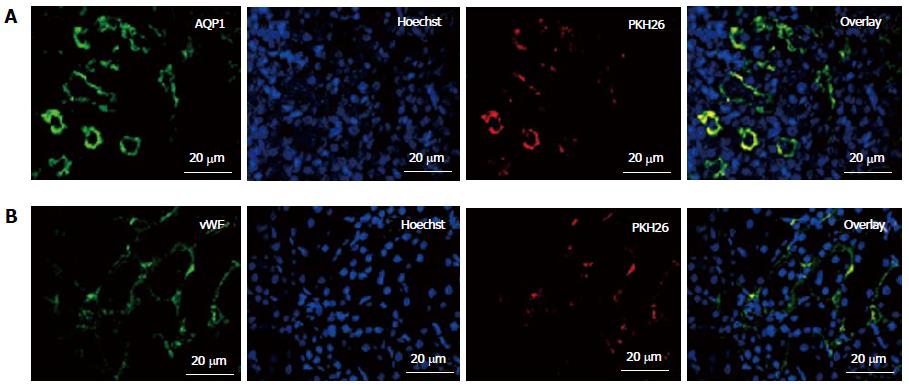
To study their engraftment, PKH26 labeled fKSC were evaluated in rat kidneys on day 7 of therapy. The fKSC were observed to engraft preferentially in renal tubules and capillaries stained with tubular epithelial marker AQP1 and endothelial marker vWF, respectively (Figure 5).
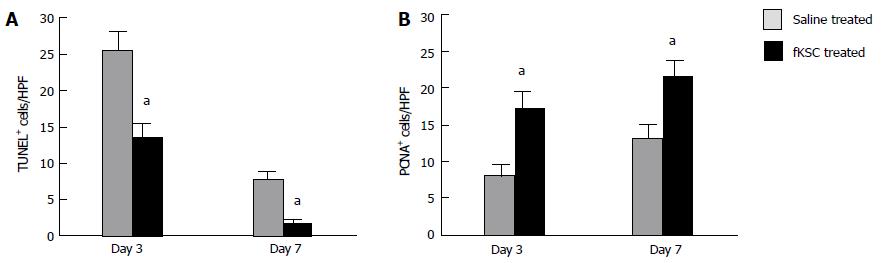
On day 3 of therapy, the TUNEL-positive cells in the kidneys of fKSC treated rats were significantly lower than those in the saline treated rats (P < 0.05). On day 7, their numbers further decreased significantly in fKSC treated rats as compared to those in the saline treated rats (P < 0.05; Figure 6A). On days 3 and 7 of therapy, the number of PCNA-positive cells in the kidneys of fKSC treated rats were significantly higher as compared to those in the saline treated rats (P < 0.05, Figure 6B).
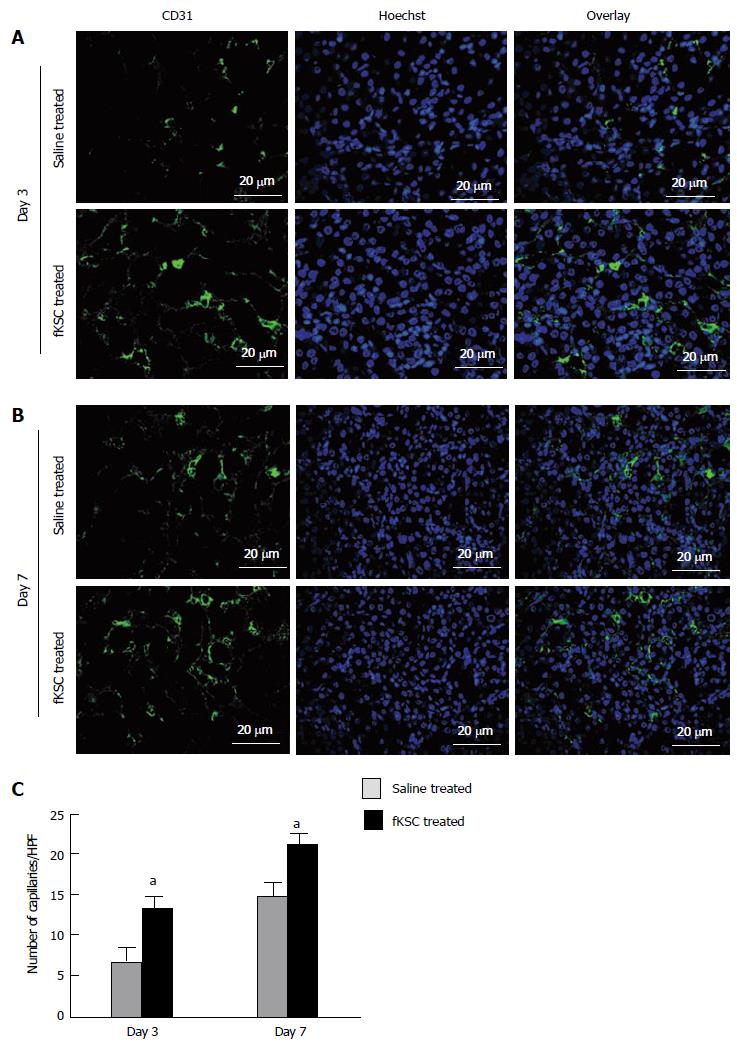
On day 3 of therapy, the morphometric analysis of CD31 labeled peritubular capillaries showed a significantly higher capillary density in the kidneys of fKSC treated than that in saline treated rats (13.30 ± 1.54 vs 7.10 ± 1.29, capillaries/HPF, P < 0.05). On day 7 of therapy, the capillary density in the kidneys of fKSC treated rats was further significantly increased than that in saline treated rats (21.10 ± 1.46 vs 15.00 ± 1.30, capillaries/HPF, P < 0.05; Figure 7).
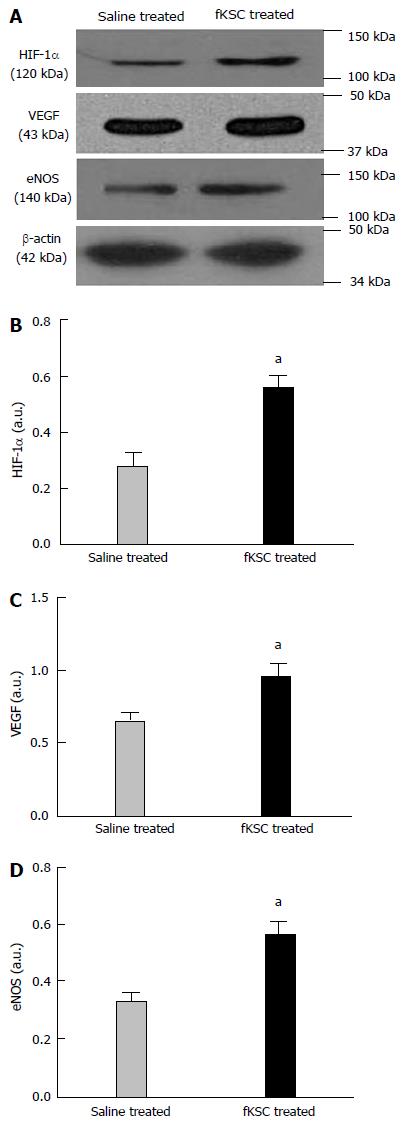
To determine the early angiogenic effect of fKSC, the protein expression of angiogenic signaling molecules were studied on day 3 of fKSC therapy. The expressions of HIF-1α, VEGF and eNOS in the kidneys of fKSC treated rats were significantly higher as compared to saline treated rats (P < 0.05; Figure 8).
The present study demonstrates that fKSC expressed mesenchymal as well as renal progenitor markers and exhibited the formation of CD31 and vWF expressing capillary-like structures and differentiation into CK18 and CK19 positive epithelial cells in vitro. The administration of fKSC in rats with cisplatin induced ARF resulted in rapid improvement in renal function and histology. The infused fKSC were observed to engraft in renal tubules and promote proliferation and reduce apoptosis of renal tubular cells. In addition, the kidneys of fKSC treated rats exhibited increased angiogenesis and up-regulation of angiogenic signaling molecules. To our knowledge this is the first study showing therapeutic efficacy of in vitro expanded fKSC in cisplatin induced ARF model and role of angiogenesis in renal regeneration by these stem cells.
We have recently observed that fKSC have maximal growth at a seeding density of 1000 cells/cm2, population doubling time of approximately 34 h and normal karyotype up to 3rd passage. In addition, these cells successfully differentiated into cells of all the three germ layers (communicated elsewhere). In the present study, we have observed that fKSC express mesenchymal (CD29, CD44, CD73, CD90 and CD105) as well as renal progenitor markers (Wt1, Pax2 and Six2). The Pax2 and Wt1 genes cross-regulate expression of each other during kidney development[16]. However, we have observed a high expression of these markers in fKSC. A plausible explanation of this could be that a significant proportion of fKSC are a population of stem cells of metanephric mesenchyme which have been shown to express both Pax2 and Wt1 transcription factors[13,17,18]. Similar to our observation high expression of Pax2 and Wt1 has recently been shown in human fetal kidney progenitors as well as human embryonal cells derived nephron progenitors[19]. The fKSC could be induced to differentiate in vitro into CK18 and CK19 positive epithelial cells. In addition, they exhibited an angiogenic potential as shown by the formation of CD31 and vWF positive capillary-like tubular structures when plated on matrigel. Two previous studies have shown that stem cells derived from whole fetal kidneys express mesenchymal and renal progenitor markers, but they have not studied their in vitro angiogenic potential and differentiation into epithelial cells[20,21]. However, corroborating with our data, one study has shown that human embryonic kidney derived CD24+ CD133+ stem cells exhibit in vitro differentiation into epithelial and endothelial lineages[22]. We did not evaluate the markers of other renal progenitors such as endothelial and epithelial ones on fKSC which may be a limitation of the present study.
To investigate their therapeutic effect in ARF, we infused intravenously PKH26 labeled fKSC in cisplatin induced rat model of ARF. On day 3 of therapy, we observed a significant improvement in the renal function and histology and on day 7 these parameters became comparable to healthy control rats indicating almost complete recovery. Similar to our data, culture expanded CD24+ CD133+ stem cells from human embryonic kidney have been shown to mediate a complete functional and structural recovery of glycerol induced ARF in SCID mice[22]. We observed that PKH26 labeled fKSC engraft in the damaged areas of the kidney and express vWF and AQP1 showing the integration of infused fKSC into damaged renal vasculature and tubules, respectively. It is difficult to distinguish whether vWF and AQP1 are expressed by endothelial and epithelial cells differentiated from infused fKSC or these markers represent fusion of administered fKSC with damaged kidney cells in the areas of engraftment. Similar to our observation, administration of human embryonic kidney derived CD24+ CD133+ stem cells in SCID mice with glycerol induced ARF and embryonic stem cell derived mesenchymal like progenitors in rats with cisplatin induced ARF have been shown to engraft into damaged renal tubules and vasculature of kidney[22,23].
The kidneys of fKSC treated ARF rats were observed to have a higher capillary density correlating with their structural and functional improvement as compared to saline treated ARF rats. In addition, on day 3 of fKSC therapy, there was an increased expression of HIF-1α and its downstream signaling molecules VEGF and eNOS in the kidneys of fKSC treated rats in comparison to saline treated rats, showing a role of early angiogenesis in the renal regeneration. It has been reported that HIF-1α also activates expression of Wt1, which in turn directly up-regulates VEGF and thus acts as an important regulator of angiogenesis[24-27]. The fKSC that were infused in ARF rats were already expressing Wt1, so we did not study its expression in the kidney tissues but as fKSC therapy up-regulated HIF-1α, it is likely that kidney tissues also have an up-regulation of Wt1. However, since the angiogenic role of Wt1 has mostly been reported in tumors, it is not known whether Wt1 also has a similar role in normal tissues like kidney. Corroborating with our data, it has been shown that acetazolamide administration in mice with ischemic kidney results in up-regulation of angiogenic molecules HIF-1α and eNOS in kidney tissue along with reduction in the apoptosis of renal tubular cells, increase in renal blood flow and improvement in renal function and histology[28]. Similarly, the VEGF has been shown to promote regeneration of cisplatin induced injury of renal tubular epithelial cells in vitro by inducing proliferation and reducing their apoptosis. In addition, administration of VEGF modified embryonic mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in cisplatin induced ARF in rodents has been shown to reduce renal apoptosis and promote microcirculation and cell proliferation in the damaged kidney[29]. There is no previous study showing angiogenic role of fKSC in ARF but in agreement with our study, it has been shown that a clonal cell line of MSC derived from kidney of adult Tie-2 green fluorescent protein transgenic mice exhibit in vivo angiogenesis and tubular regeneration by increasing epithelial proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis when administered in mouse model of renal ischemia[30]. These studies suggest that the improved capillary density, proliferation and reduced apoptosis in renal tissue observed by us following fKSC therapy may be mediated by the up-regulation of VEGF, HIF-1α and eNOS, and thus these molecules could play an important role in renal regeneration.
In conclusion, the present study shows that fKSC express mesenchymal and renal progenitor markers, exhibit an in vitro angiogenic potential and ability to differentiate into cells of renal epithelial lineage. The administration of fKSC in cisplatin induced ARF results in rapid recovery of renal function and histology, and promotes renal angiogenesis. Further studies on fKSC mediated renal angiogenesis and regeneration may lead to the development of novel pharmacological therapies for ARF.
We would like to extend our sincere thanks to Dr. Rituraj Konwar, Scientist, Endocrinology Division, CSIR-Central Drug Research Institute, Lucknow, India and Dr. SK Mandal, Consultant Statistician, Center for Bio-Medical Research Lucknow, India for extending laboratory facilities to perform the Flow cytometry and review of statistical analysis, respectively.
Tissue specific fetal stem cells represent the most suitable stem cell type for tissue regeneration/repair due to their inherent ability of tissue specific differentiation. Thus, stem cells derived from the fetal kidney may be a novel cell type for renal regenerative therapy. The epithelial and microvascular damage are the main events in acute renal failure (ARF) and this led us to evaluate whether fetal kidney stem cells (fKSC) mediate their therapeutic effect by augmenting renal angiogenesis in cisplatin induced ARF in rats.
The authors had demonstrated in the present study that fKSC differentiate into cells of epithelial lineage and exhibit angiogenic potential in vitro. Following infusion in ARF rats, they engraft in renal tubules and rapidly improve renal function and histology along with increased angiogenesis in the kidney tissues. It is thus logical to investigate whether induction of renal angiogenesis by fKSC is an important mechanism of renal regeneration and whether it is mediated by trans-differentiation of infused fKSC or their paracrine effect on resident kidney stem cells.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study showing therapeutic efficacy of in vitro expanded fKSC in ARF model and their in vitro and in vivo angiogenic potential suggesting that induction of renal angiogenesis may be an important therapeutic mechanism of these stem cells.
The fKSC represent primitive renal progenitors expressing mesenchymal as well as renal progenitor markers and treatment of ARF rats with these stem cells results in rapid recovery in renal function and histology leading to their normalization. Further studies using human fKSC or human embryonic stem cell derived renal progenitors with similar characteristics may lead to the development of clinical therapy for ARF.
The fKSC represent primitive renal progenitors and express mesenchymal as well as renal progenitor markers. They can be culture expanded to generate a requisite number of cells for therapeutic dose. They improve renal function and histology and lead to their normalization by inducing renal angiogenesis. It needs to be studied whether the angiogenesis observed in the kidney tissues in the fKSC treated rats is due to trans-differentiation of infused stem cells or by stimulation of resident endothelial cells or both.
It is a very interesting article about a possible protective role of fetal kidney stem cells in experimental model of acute renal failure.
| 1. | Schrier RW, Wang W, Poole B, Mitra A. Acute renal failure: definitions, diagnosis, pathogenesis, and therapy. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:5-14. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 227] [Article Influence: 10.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Coca SG, Singanamala S, Parikh CR. Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2012;81:442-448. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1731] [Cited by in RCA: 1671] [Article Influence: 119.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Cirio MC, de Groh ED, de Caestecker MP, Davidson AJ, Hukriede NA. Kidney regeneration: common themes from the embryo to the adult. Pediatr Nephrol. 2014;29:553-564. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Patschan D, Patschan S, Müller GA. Microvasculopathy in ischemic acute kidney injury: consequences and therapeutic implications. Panminerva Med. 2012;54:45-52. [PubMed] |
| 5. | Hörbelt M, Lee SY, Mang HE, Knipe NL, Sado Y, Kribben A, Sutton TA. Acute and chronic microvascular alterations in a mouse model of ischemic acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;293:F688-F695. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 137] [Cited by in RCA: 137] [Article Influence: 7.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Sutton TA, Fisher CJ, Molitoris BA. Microvascular endothelial injury and dysfunction during ischemic acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2002;62:1539-1549. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 410] [Cited by in RCA: 389] [Article Influence: 16.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Basile DP. Rarefaction of peritubular capillaries following ischemic acute renal failure: a potential factor predisposing to progressive nephropathy. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2004;13:1-7. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 170] [Cited by in RCA: 169] [Article Influence: 7.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Chade AR. Renal vascular structure and rarefaction. Compr Physiol. 2013;3:817-831. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 62] [Cited by in RCA: 107] [Article Influence: 8.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 9. | Morigi M, De Coppi P. Cell therapy for kidney injury: different options and mechanisms--mesenchymal and amniotic fluid stem cells. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2014;126:59. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 3.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Harari-Steinberg O, Pleniceanu O, Dekel B. Selecting the optimal cell for kidney regeneration: fetal, adult or reprogrammed stem cells. Organogenesis. 2011;7:123-134. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Dekel B, Reisner Y. Embryonic committed stem cells as a solution to kidney donor shortage. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2004;4:443-454. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Dekel B, Burakova T, Arditti FD, Reich-Zeliger S, Milstein O, Aviel-Ronen S, Rechavi G, Friedman N, Kaminski N, Passwell JH. Human and porcine early kidney precursors as a new source for transplantation. Nat Med. 2003;9:53-60. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 219] [Cited by in RCA: 188] [Article Influence: 8.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Oliver JA, Barasch J, Yang J, Herzlinger D, Al-Awqati Q. Metanephric mesenchyme contains embryonic renal stem cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002;283:F799-F809. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 86] [Cited by in RCA: 76] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Ozyurt H, Yildirim Z, Kotuk M, Yilmaz HR, Yağmurca M, Iraz M, Söğüt S, Gergerlioglu S. Cisplatin-induced acute renal failure is ameliorated by erdosteine in a dose-dependent manner. J Appl Toxicol. 2004;24:269-275. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Jablonski P, Howden BO, Rae DA, Birrell CS, Marshall VC, Tange J. An experimental model for assessment of renal recovery from warm ischemia. Transplantation. 1983;35:198-204. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 274] [Cited by in RCA: 295] [Article Influence: 6.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Eccles MR, He S, Legge M, Kumar R, Fox J, Zhou C, French M, Tsai RW. PAX genes in development and disease: the role of PAX2 in urogenital tract development. Int J Dev Biol. 2002;46:535-544. [PubMed] |
| 17. | Metsuyanim S, Harari-Steinberg O, Buzhor E, Omer D, Pode-Shakked N, Ben-Hur H, Halperin R, Schneider D, Dekel B. Expression of stem cell markers in the human fetal kidney. PLoS One. 2009;4:e6709. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 99] [Cited by in RCA: 94] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Yu CT, Tang K, Suh JM, Jiang R, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ. COUP-TFII is essential for metanephric mesenchyme formation and kidney precursor cell survival. Development. 2012;139:2330-2339. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Kang M, Han YM. Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into nephron progenitor cells in a serum and feeder free system. PLoS One. 2014;9:e94888. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 51] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Kim SS, Gwak SJ, Han J, Park HJ, Park MH, Song KW, Cho SW, Rhee YH, Chung HM, Kim BS. Kidney tissue reconstruction by fetal kidney cell transplantation: effect of gestation stage of fetal kidney cells. Stem Cells. 2007;25:1393-1401. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Kim SS, Park HJ, Han J, Gwak SJ, Park MH, Song KW, Rhee YH, Min Chung H, Kim BS. Improvement of kidney failure with fetal kidney precursor cell transplantation. Transplantation. 2007;83:1249-1258. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Lazzeri E, Crescioli C, Ronconi E, Mazzinghi B, Sagrinati C, Netti GS, Angelotti ML, Parente E, Ballerini L, Cosmi L. Regenerative potential of embryonic renal multipotent progenitors in acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:3128-3138. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 168] [Cited by in RCA: 157] [Article Influence: 8.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Luo J, Zhao X, Tan Z, Su Z, Meng F, Zhang M. Mesenchymal-like progenitors derived from human embryonic stem cells promote recovery from acute kidney injury via paracrine actions. Cytotherapy. 2013;15:649-662. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Wagner KD, Wagner N, Wellmann S, Schley G, Bondke A, Theres H, Scholz H. Oxygen-regulated expression of the Wilms’ tumor suppressor Wt1 involves hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). FASEB J. 2003;17:1364-1366. [PubMed] |
| 25. | McCarty G, Awad O, Loeb DM. WT1 protein directly regulates expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and is a mediator of tumor response to hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:43634-43643. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 51] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Katuri V, Gerber S, Qiu X, McCarty G, Goldstein SD, Hammers H, Montgomery E, Chen AR, Loeb DM. WT1 regulates angiogenesis in Ewing Sarcoma. Oncotarget. 2014;5:2436-2449. [PubMed] |
| 27. | Wagner KD, Cherfils-Vicini J, Hosen N, Hohenstein P, Gilson E, Hastie ND, Michiels JF, Wagner N. The Wilms’ tumour suppressor Wt1 is a major regulator of tumour angiogenesis and progression. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5852. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 62] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | An Y, Zhang JZ, Han J, Yang HP, Tie L, Yang XY, Xiaokaiti Y, Pan Y, Li XJ. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α dependent pathways mediate the renoprotective role of acetazolamide against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32:1151-1166. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Yuan L, Wu MJ, Sun HY, Xiong J, Zhang Y, Liu CY, Fu LL, Liu DM, Liu HQ, Mei CL. VEGF-modified human embryonic mesenchymal stem cell implantation enhances protection against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011;300:F207-F218. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 80] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Chen J, Park HC, Addabbo F, Ni J, Pelger E, Li H, Plotkin M, Goligorsky MS. Kidney-derived mesenchymal stem cells contribute to vasculogenesis, angiogenesis and endothelial repair. Kidney Int. 2008;74:879-889. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 120] [Cited by in RCA: 104] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |