©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Stem Cells. Oct 26, 2017; 9(10): 169-178
Published online Oct 26, 2017. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v9.i10.169
Published online Oct 26, 2017. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v9.i10.169
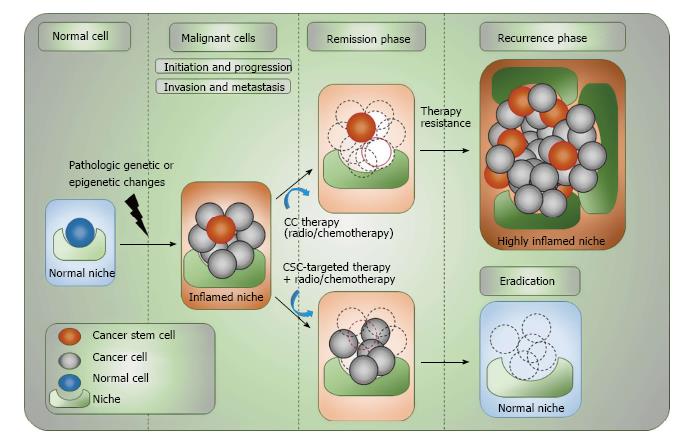
Figure 1 Complex organization of cancer initiation, progress, remission and relapse.
CSCs are capable of undergoing extensive cell proliferation after acquiring different pathologic genetic/epigenetic changes while retaining their stemness and giving rise to differentiated progenies. Acquiring further genetic/epigenetic changes during different stages of tumor progression will evolve CSCs, but this may also be advanced through having dynamic interplay with the stem cell-niche. Both CSCs and non-CSCs can be found at the invasive front of primary tumors, which is linked to the process of EMT. However, only CSCs are capable of surviving from immune-surveillance or conventional tumor therapies and are able to give rise to distance metastasis or cause cancer recurrence. The potential eradication of tumor cells and CSCs can be resulted only upon combination targeted therapeutic approaches. Tumor stem cell-targeting drugs should able to prolong the efficacy of cytotoxic tumor therapy and reduce the recurrence risk. CSC: Cancer stem cell; CC: Cancer cell; NC: Normal cell; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
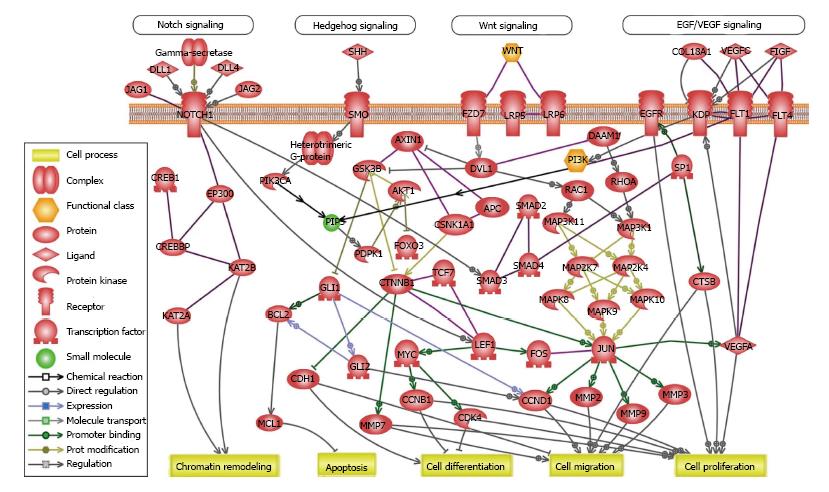
Figure 2 Crosstalk between cancer and cancer stem cell-related pathways.
Predicted crosstalk among Wnt signaling, Notch pathway, Hedgehog signaling and other cancer-related pathways like EGF/VEGF signaling in CSCs and cancer. Gene networks and canonical pathways were assessed using the Ariadne Genomics Pathway Studio® program and database (Elsevier). EGF: Epidermal growth factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; WNT: Wnt signaling pathways; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PIP3: Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5 trisphosphate; CSC: Cancer stem cell; SHH: Sonic Hedgehog.
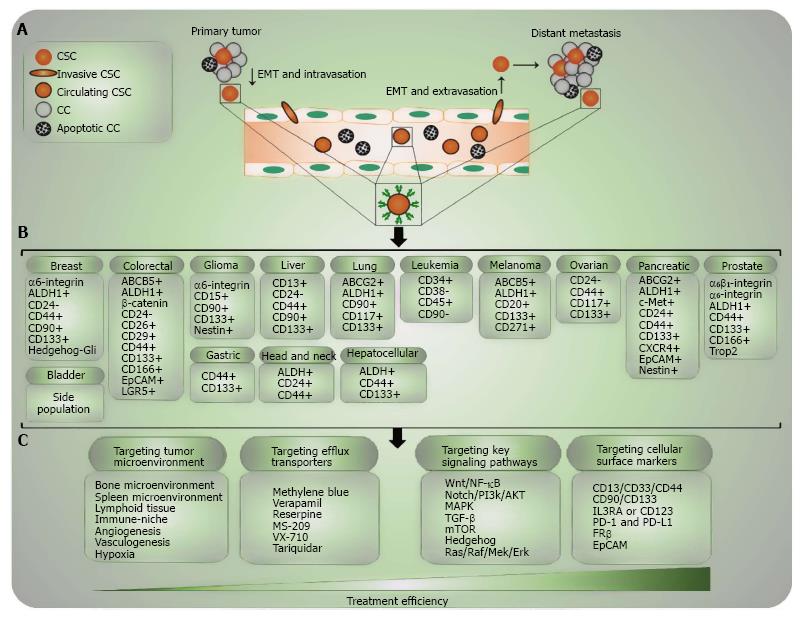
Figure 3 Tracing and targeting cancer stem cells.
A: The complex process of distant metastasis including invasion of the tumor microenvironment, EMT, shedding of CSCs into the blood stream (intravasation), MET and invasion of circulating CTCs to the other tissues (extravasation). Only circulating CSCs are able to survive in the circulating blood, escape from immune-surveillance and home to secondary organs; B: The list of known compilation CSC-related molecular markers for different solid tumors and hematopoietic malignancies. The level of specificity of these markers differs per each type of tumor. Markers are ordered alphabetically and not according to their sensitivity or specificity; C: Four important approaches of CSC-targeted therapy. CSC: Cancer stem cell; CC: Cancer cell; NC: Normal cell; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; MET: Mesenchymal-epithelial transition; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; TGF: Transforming growth factor; mTOR: Mechanistic target of rapamycin; RAS: Ras-activated signaling; PD-1: Programmed death 1; PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; EpCAM: Epithelial cell adhesion molecule.
- Citation: Radpour R. Tracing and targeting cancer stem cells: New venture for personalized molecular cancer therapy. World J Stem Cells 2017; 9(10): 169-178
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v9/i10/169.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v9.i10.169