©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Stem Cells. Sep 26, 2015; 7(8): 1078-1089
Published online Sep 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i8.1078
Published online Sep 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i8.1078
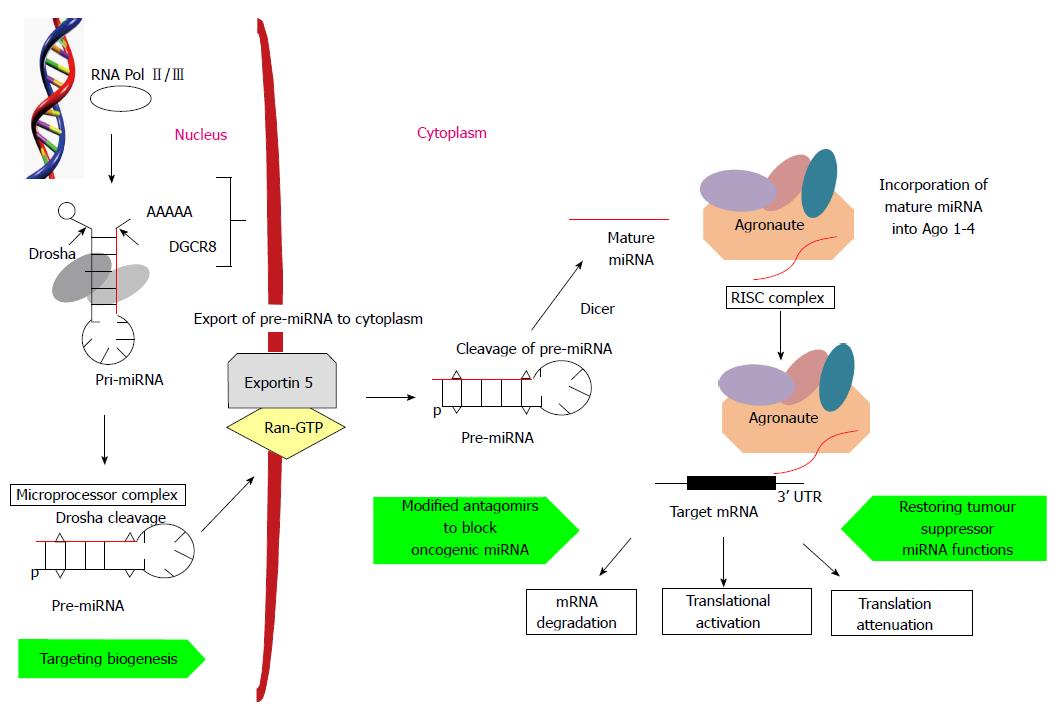
Figure 1 MicroRNA biogenesis, activity and potential therapeutic targets.
Mature miRNAs are generated from hairpin-like longer primary transcripts by two sequential processing steps mediated by a nuclear (Drosha) and a cytoplasmic (Dicer) RNAase III endonuclease. MiRNA then directs RISC to target mRNAs which share sequence complementation between seed region at 5’ end of mature miRNA and 3’UTR of target mRNA. Stability of miRNA:mRNA recognition and degree of complementation leads to translational activation but more commonly mRNA degradation and translational repression. Potential therapeutic target sites are shown which include steps during miRNA biogenesis and target mRNA recognition. 3’UTR: 3’ untranslated region; RISC: RNA-induced silencing complex; miRNA: MicroRNAs; Ago: Agronaute.
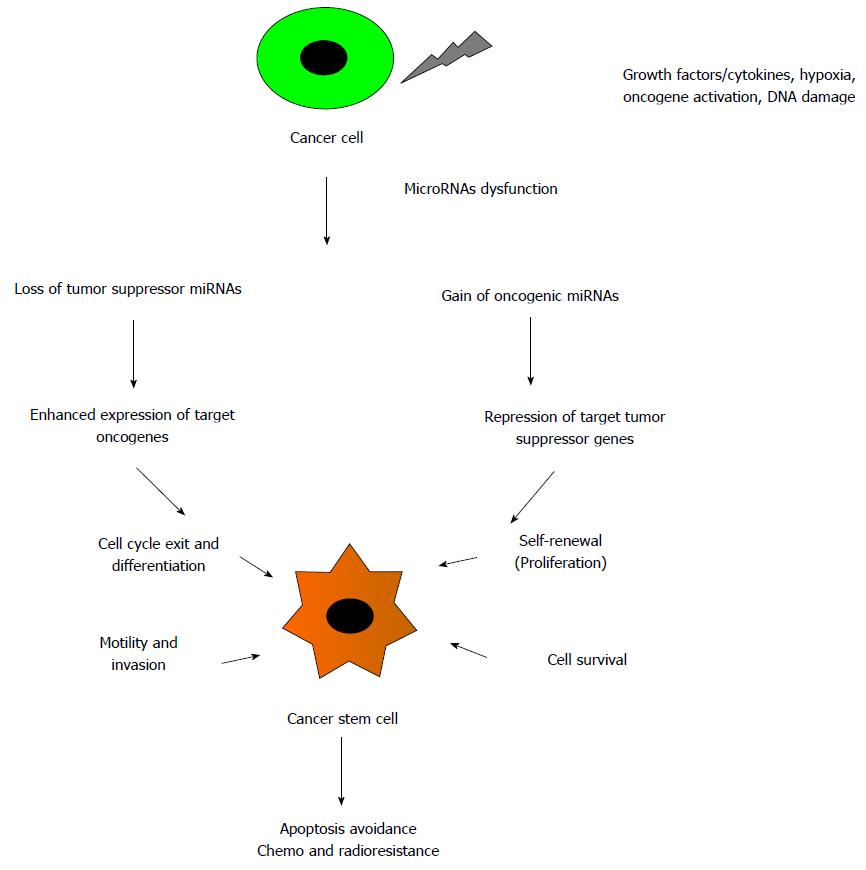
Figure 2 MicroRNAs affect and regulate the key properties of cancer stem cells.
Tumor microenvironment influences the maintenance and properties of CSCs. Secreted growth factors and cytokines from cancer cells, hypoxia, oncogene activation, DNA damage, errors in DNA repair and aberrant microRNA expression modify cancer cell functions by increasing the self-renewability, cell cycle exit and differentiation, epitheilal-to-mesenchymal transition, migration, invasion and survival rate in CSCs thus promote cancer progression and or tumor recurrence. CSCs: Cancer stem cells.
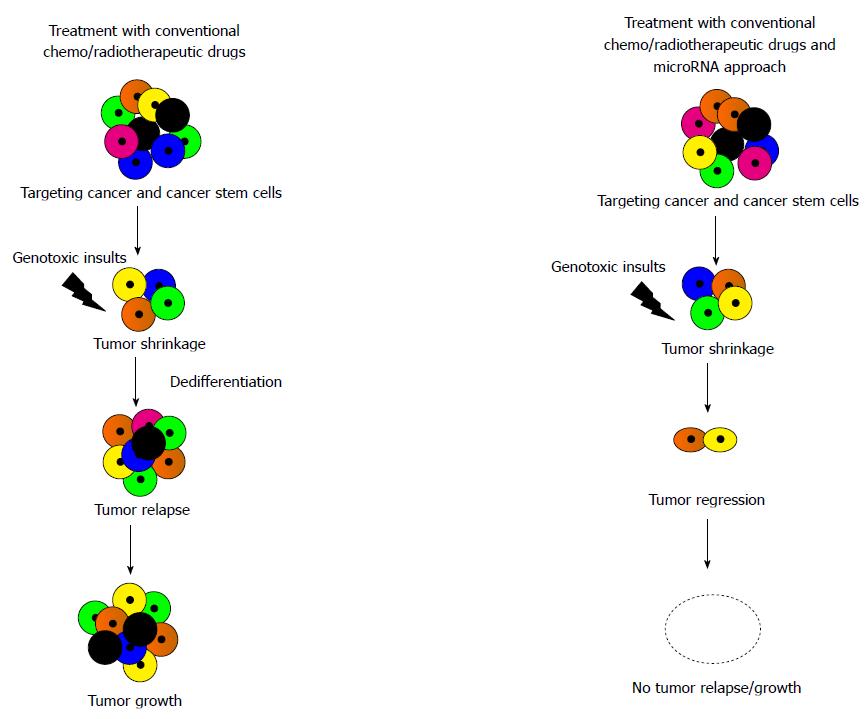
Figure 3 Effective novel tumor therapies.
Conventional chemo- and radio-therapeutic drugs target the bulk of tumor cell population and lead to tumor shrinkage. Cancer stem cells however develop resistance to these drugs and as a result of genotoxic insults, tumor cells relapse. MicroRNA approach along with the chemo and radiotherapeutic drugs as a novel treatment strategy target transit amplifying cells as well as differentiated cancer cells and induce differentiation in cancer stem cells thereby remove the bulk of tumor and also the source of cancer.
- Citation: Garg M. Emerging role of microRNAs in cancer stem cells: Implications in cancer therapy. World J Stem Cells 2015; 7(8): 1078-1089
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v7/i8/1078.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v7.i8.1078