©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Stem Cells. Aug 26, 2015; 7(7): 1010-1021
Published online Aug 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i7.1010
Published online Aug 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i7.1010
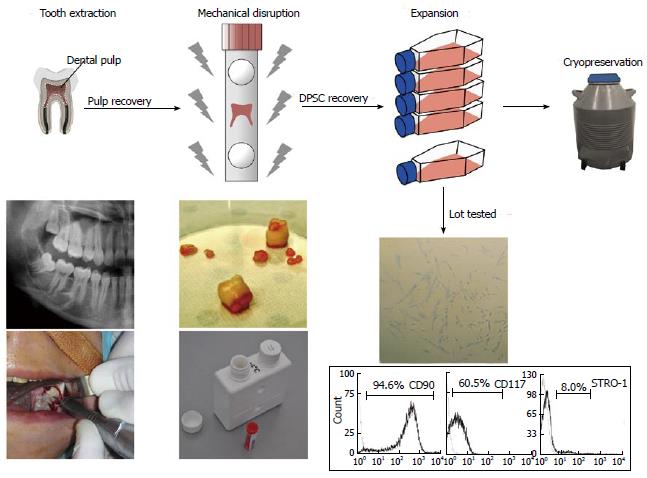
Figure 1 Dental Pulp tissue and dental pulp stem cell recovery.
Wisdom teeth are extracted in aseptic conditions and transferred to the cell bank in a sterile transport tube. The teeth are then cracked opened and the pulps are mechanically disrupted in a tissue grinder/homogenizer. The cell suspensions obtained are screened for expression of stemness markers by flow cytometry, before storage in liquid nitrogen. DPSC: Dental pulp stem cell.
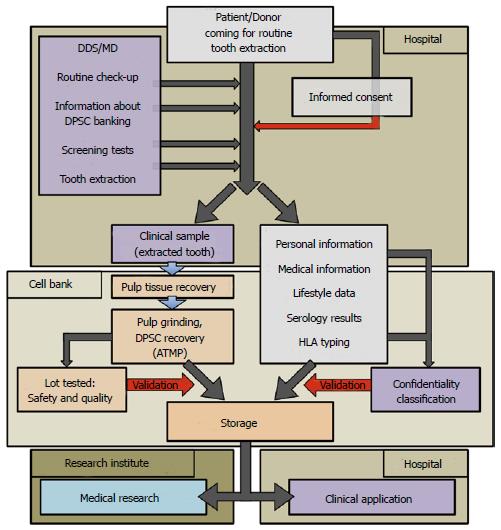
Figure 2 Process flowchart for current Good Manufacturing Practices manufacturing of dental pulp stem cell lots/therapeutic products.
The chart is divided into 4 areas: Hospital for tooth recovery, Cell Bank, Research Institute and Hospital for clinical applications: (1) Hospital: direct contact between patients and authorized medical staff, such as Medical Doctor (MD) or Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS). Clinical sample and donor’s personal data are recovered; (2) Cell Bank: current Good Manufacturing Practices manufacturing of Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMP) from the biological samples (dental pulps). All data concerning the donors are anonymous; (3) Research Institute: dental pulp stem cell (DPSC) lots are used for animal experiments to develop new therapeutics; and (4) Hospital: clinical grade DPSC lots are used for therapeutics. Red arrows represent critical parameters related to each step of processing (informed consent, quality, safety, confidentiality). HLA: Human leukocyte antigen.
- Citation: Collart-Dutilleul PY, Chaubron F, Vos JD, Cuisinier FJ. Allogenic banking of dental pulp stem cells for innovative therapeutics. World J Stem Cells 2015; 7(7): 1010-1021
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v7/i7/1010.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v7.i7.1010