©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2015; 7(2): 512-520
Published online Mar 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i2.512
Published online Mar 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i2.512
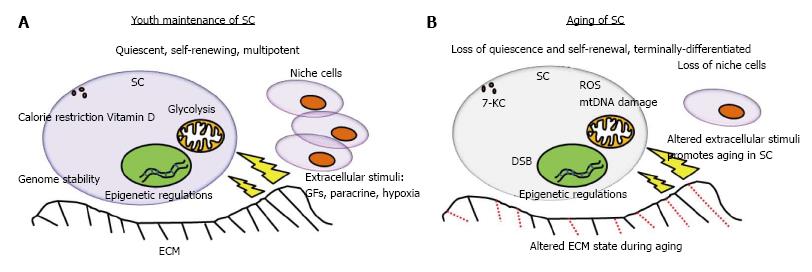
Figure 1 Stem cell maintenance and altered state during aging.
A: Secreted growth factors, paracrine, calorie restriction, hypoxic micro-environment, ECM, and niche cells maintain stem cell functions. Quiescent, self-renewing, and multipotent status of stem cell are further maintained through intracellular hypoxia-responsive element, epigenetic and genomic regulators, and mitochondria; B: However, the status of stem cell is altered with decreased niche cells, fragmented ECM, increased genomic and mitochondria DNA damage, and increased ROS during aging. ECM: Extracellular matrix; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SC: Stem cell.
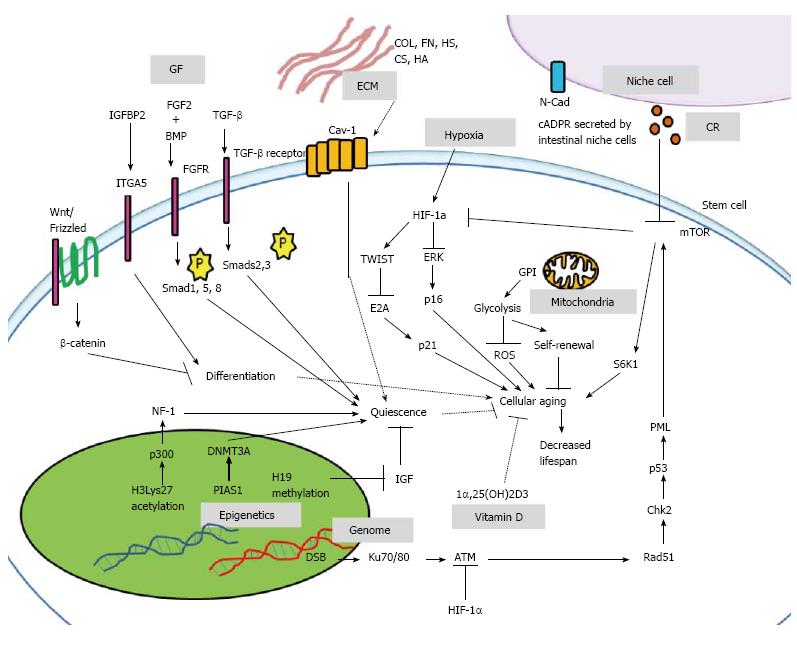
Figure 2 Signals and regulators of anti-aging in stem cell.
Up-regulation of phosphorylated Smad1, Smad5, Smad8 and Smad2, Smad3 proteins maintains stem cell quiescence. Epigenetic regulators p300, DNMT3A, and H19 also maintain stem cell quiescence. Hypoxia induces HIF-1α, a key regulator of p21 and p16 to prevent cellular aging. Under hypoxic condition, mitochondria undergo glycolysis to maintain self-renewal, and lower ROS production. With genome integrity maintained, the mTOR pathway is deactivated. In addition, stem cells interact with ECM, secreted factors from niche cells, and adhesive proteins to further maintain stem cell functions. GF: Growth factors; ECM: Extracellular matrix; CR: Calorie restriction; Wnt: Wingless/integrin; IGFBP2: Insulin-growth factor binding protein 2; ITGA5: Integrin alpha-5; FGF2: Fibroblast growth factor 2; FGFR: Fibroblast growth factor receptor; BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein; Smad: Mothers against decapentaplegic; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; Cav-1: Caveolin-1; Col: Collagen; FN: Fibronectin; HS: Heparin sulphate; CS: Chondroitin sulphate; HA: Hyaluronan; HIF-1: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1; E2A: Transcriptional factor E2; p21: Peroxidase 21; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; p16: Peroxidase 16; GPI: Glucosephosphate isomerase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; N-Cad: N-cadherin; cADPR: Cyclic ADP-ribose; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; S6K1: Ribosomal S6 kinase 1; DSB: Double-strand break; ATM: Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated protein kinase; Chk2: Checkpoint kinase 2; PML: Promyelocytic leukemia protein; NF-1: Neurofibromin-1; PIAS1: Protein inhibitors of activated Stats; DNMT3A: DNA(cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3A; IGF: Insulin-like growth factor; 1α, 25(OH)2D3: 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3.
- Citation: Wong TY, Solis MA, Chen YH, Huang LLH. Molecular mechanism of extrinsic factors affecting anti-aging of stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2015; 7(2): 512-520
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v7/i2/512.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v7.i2.512