Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2015; 7(2): 300-314
Published online Mar 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i2.300
Published online Mar 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i2.300
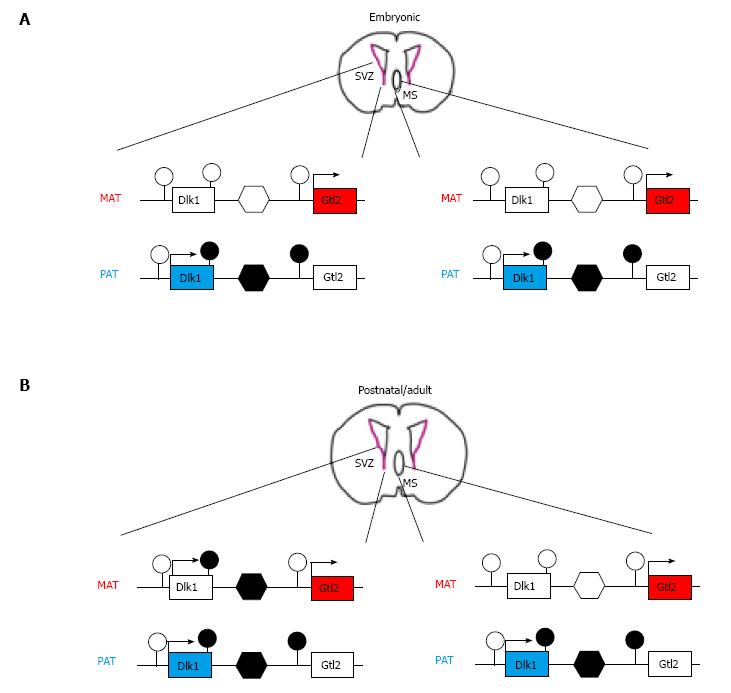
Figure 1 Genomic imprinting at the delta-like homolog 1 locus is reset in the subventricular zone.
A: Delta-like homolog 1 (Dlk1) is monoallelically expressed from the paternal allele during development. Silencing of the maternal allele takes place in non-neuronal and various neuronal tissues such as the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricle (SVZ) and the medial septum (MS). At the molecular level, maternal silencing results from the absence of DNA methylation at the intergenic, germ line-controlled differentially methylated regions (DMR) (unfilled hexagon), which resides between the Dlk1 and Gtl2 genes and their associated DMRs (unfilled lollipops). Conversely, methylation at the intergenic DMR (filled hexagon), the 3’ end Dlk1 DMR and the Gtl2 DMR (filled lollipops) associates with expression from the paternal allele. The same methylation patterns are present in the SVZ (left scheme) and MS (right scheme) at embryonic ages; B: Dlk1 shows biallelic expression from postnatal day 7 onward towards adulthood in the SVZ, but not in the MS. Hereby, the maternal methylation pattern closely resembles the one on the paternal allele (i.e., methylation at the 3’end Dlk1 DMR, the intergenic DMR, but not the Gtl2 DMR). At opposite, the methylation pattern in the MS is preserved and determines monoallelic Dlk1 expression.
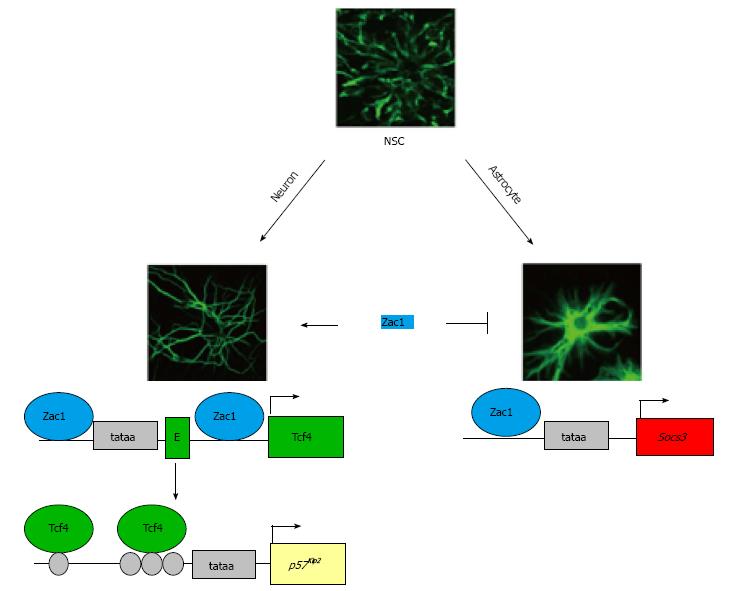
Figure 2 Imprinted Zac1 favors neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells.
The Zac1 gene is maternally imprinted and encodes a versatile transcriptional regulator. Zac1 expression is strongly induced during neuronal and astroglial differentiation of embryonic and adult neural stem cells (NSCs). During neuronal differentiation (left scheme), Zac1 binds to GC-rich DNA binding sites at the Tcf4 promoter and first intron to confer synergistic transactivation. As a result, enhanced Tcf4 expression promotes binding to and transactivation of the cyclin kinase inhibitor p57Kip2, which induces G1 arrest. Moreover, Zac1 binds to GC-rich DNA elements at the Socs3 promoter during astroglial differentiation (right scheme). Socs3 encodes a potent inhibitor of prodifferentiative Jak/Stat3 signaling and prevents precocious astroglial differentiation. The tataa-elements are boxed in light grey and the transcriptional start sites are symbolized by arrows. The first exon in the Tcf4 locus is depicted as a green box (labeled E) and coding exons of Tcf4 and Socs3 as green and red boxes, respectively. Tcf4 binds to various E-box motifs (light grey circles) localizing to the p57Kip2 regulatory region.
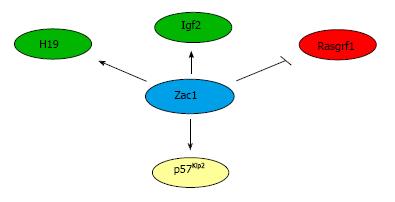
Figure 3 Zac1-dependent transcriptional regulation of imprinted genes.
Zac1 binds to the downstream enhancer of H19 and transactivates H19 and Igf2 expression in neuronal cells. In pancreatic progenitor cell, Zac1 bind to the promoter of the paternally imprinted Rasgrf1 gene and confers repression. Following neuronal differentiation of NSCs, Zac1 induces Tcf4, which binds at the promoter of the imprinted p57Kip2 gene and enhances G1 cell cycle arrest.
-
Citation: Daniel G, Schmidt-Edelkraut U, Spengler D, Hoffmann A. Imprinted
Zac1 in neural stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2015; 7(2): 300-314 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v7/i2/300.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v7.i2.300